[ad_1]
Word: This text was the MASS Analysis Evaluation cowl story for July 2023 and is a assessment of a recent paper by Van Vossel et al. In order for you extra content material like this, subscribe to MASS.
Key Factors
- Researchers categorized 95 novice trainees (38 ladies and 57 males) as having sluggish or quick twitch muscle fiber typology based mostly on intramuscular carnosine ranges. They examined the connection between fiber typology and reps to failure on the leg extension, leg curl, biceps curl, and triceps extension workout routines at a mixture of relative intensities starting from 40-80%.
- Topics categorized as quick twitch people carried out considerably fewer reps to failure on the leg extension, leg curl, and biceps curl than sluggish twitch-classified people. Nevertheless, the variety of reps carried out on the triceps extension was not considerably associated to fiber typology.
- The presently reviewed research means that people with a higher proportion of sort II fibers are likely to carry out fewer reps to failure on sure workout routines. Nevertheless, the correlations reported on this research weren’t very robust (all r ≤ 0.42); thus, it will be a stretch to say that reps to failure can predict fiber typology with excessive accuracy.
Whereas a point of scientific assist could be discovered at instances that one coaching model is superior to a different, we additionally perceive that rates of hypertrophy and strength gain are highly individual (2, 3, 4, 5). We can also say that, on common, people could carry out about 10 reps to failure with a load equivalent to 75% of 1RM on the squat or bench press. Nevertheless, substantial interindividual variation in reps carried out at a given relative depth (proportion of 1RM) exists. For instance, latest knowledge point out that educated women and men carried out a spread of 6 – 28 repetitions on a squat set to failure at 70% of 1RM (6).
That particular person variation sparks, what I imagine, is probably the most urgent coaching query we face immediately: why does this particular person variation exist? Relating to repetition efficiency, knowledge have proven (6) that a person’s physique mass explains 20% of the variance in reps carried out to failure at a given relative depth, with heavier people finishing fewer reps to failure. Nevertheless, that leaves 80% of the variance unexplained. One in style suggestion to clarify the remaining variance is that people with the next proportion of sort I fibers (sluggish twitch) have higher muscular endurance than these with sort II fibers. This suggestion is smart, as sort I fibers are extra immune to fatigue than sort II fibers. A earlier foray into this subject (7 – MASS Review) discovered that amongst 30 ladies and men, these with extra sort II fibers tended to carry out fewer squat reps to failure at 80% of 1RM, however the correlation wasn’t that robust (rho = –0.38), leaving the conclusions tenuous. Fortunately, a brand new research from Van Vossel et al. (1) investigated the connection between muscle typology and repetition efficiency at numerous relative intensities amongst 95 ladies and men.
Objective and Hypotheses
Objective
The reviewed research had three particular goals:
- To find out if maximal dynamic energy and isometric energy differed between people categorized into sluggish and quick typologies.
- To look at the connection between muscle typology and reps carried out to failure on leg extensions, leg curls, biceps curls, and triceps extensions.
- To look at if numerous components (relative depth and energy degree) influenced the variety of reps to failure.
Hypotheses
The researchers hypothesized that people with a quicker muscle typology (a higher proportion of sort II fibers) would have higher max energy and carry out fewer reps on numerous workout routines (leg extension, leg curl, biceps curl, and triceps extension).
Topics and Strategies
Topics
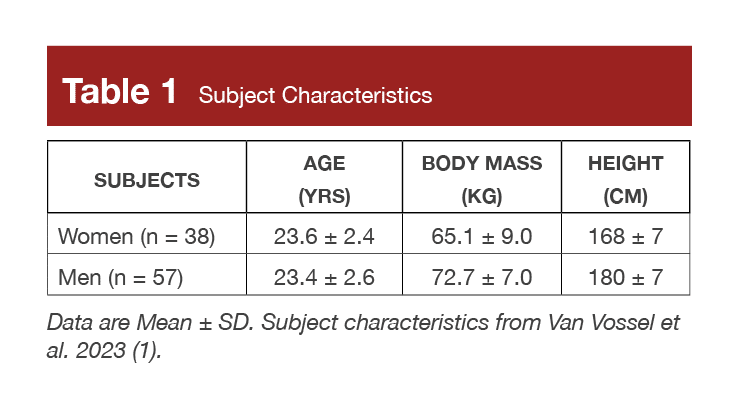
Ninety 5 ladies (n = 38) and males (n = 57) participated within the research. The researchers described the topics as “resistance coaching novices who had by no means participated in a structured resistance coaching program.” Further topic traits could be seen in Desk 1.
Pre-Testing for All Topics
Earlier than splitting topics into teams, the researchers wanted to find out muscle fiber typology. They did this by way of magnetic resonance spectroscopy, which identifies the chemical make-up of scanned tissue. On this case, the researchers examined the quantity of carnosine within the scanned muscle. As you may recall, carnosine is a dipeptide of which beta-alanine is the rate-limiting precursor (i.e., to extend muscle carnosine successfully, it is best to take beta-alanine somewhat than carnosine itself). Along with serving as a physiological buffer to delay fatigue, naturally occurring carnosine additionally signifies muscle fiber sort. Particularly, larger quantities of carnosine are related to extra quick twitch (sort II) fibers, whereas decrease quantities of carnosine are related to having extra sluggish twitch (sort I) fibers. With out moving into pointless specifics of the methodology, the researchers assessed fiber sort by means of this method for the vastus lateralis, gastrocnemius, and soleus after which estimated biceps, triceps, and hamstring typology from these muscular tissues. As soon as fiber sort was established, the researchers transformed carnosine content material to a z-score (extra on this within the Criticisms and Statistical Musings part), and topics have been categorized as quick twitch, intermediate twitch, or sluggish twitch. The researchers then assessed 1RM isometric leg extension torque for all topics.
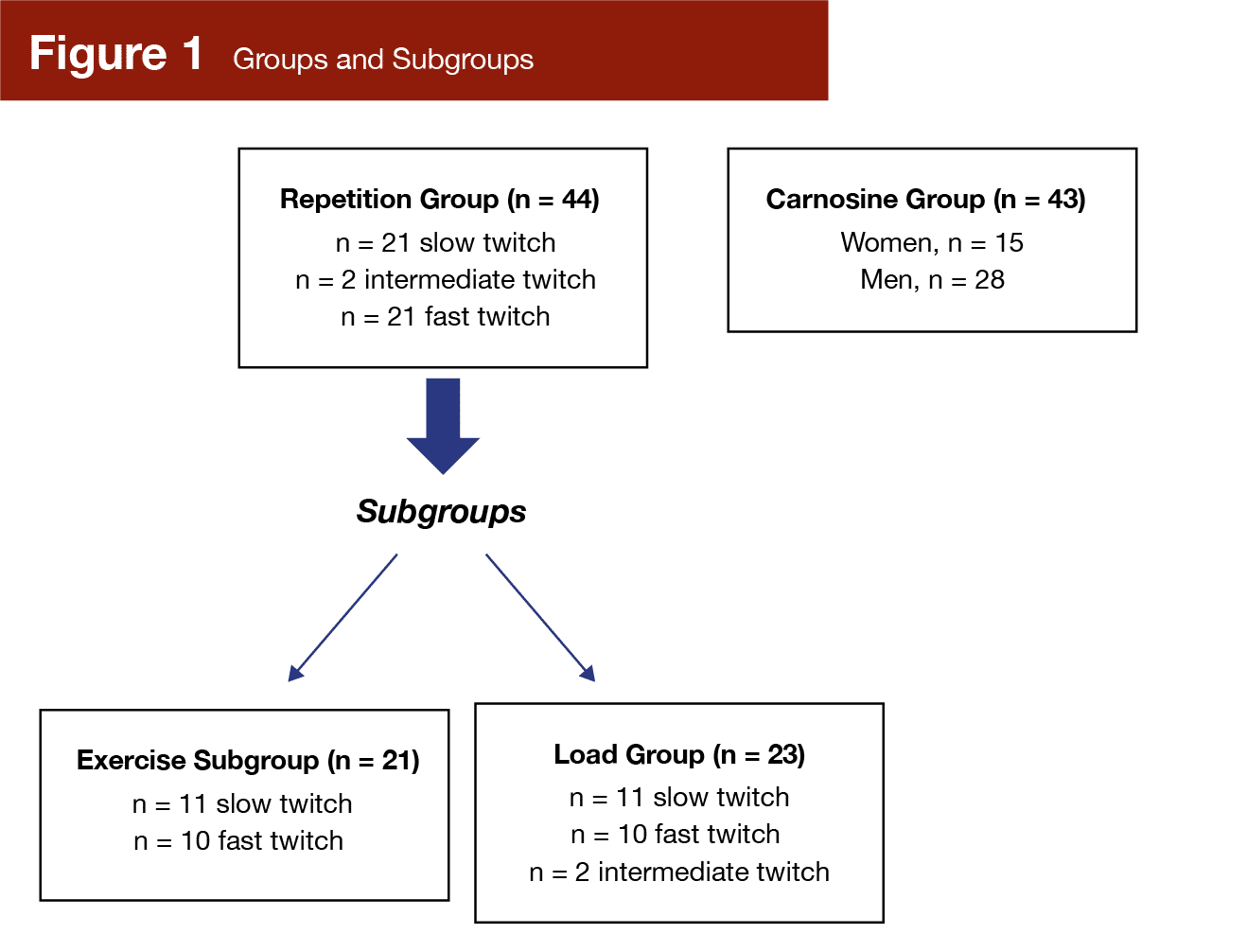
After these preliminary assessments for all 95 topics, the researchers cut up the topics into two teams to reply completely different analysis questions. One of many teams (the repetition group) contained a subgroup. Determine 1 offers a breakdown of group and subgroup construction; then, the next sections clarify the particular procedures.

Repetition Group
Along with testing leg extension isometric torque, all topics within the repetition group additionally examined their dynamic 1RM on leg extensions, biceps curls, triceps extensions, and leg curls. Subsequent, all people within the repetition group carried out three units to failure on leg extensions and biceps curls at 60% of 1RM. The train subgroup then carried out extra units to failure (the researchers didn’t specify what number of) at 60% of 1RM on the identical day, whereas the load subgroup carried out three extra units to failure at 80% of 1RM and extra units to failure at 40% of 1RM over two extra days.
Carnosine Group
One other 43 topics, the carnosine group, carried out solely three units to failure on leg extensions and curls following the preliminary assessments, however didn’t carry out any dynamic 1RM testing.
Strategies Abstract and Outcomes
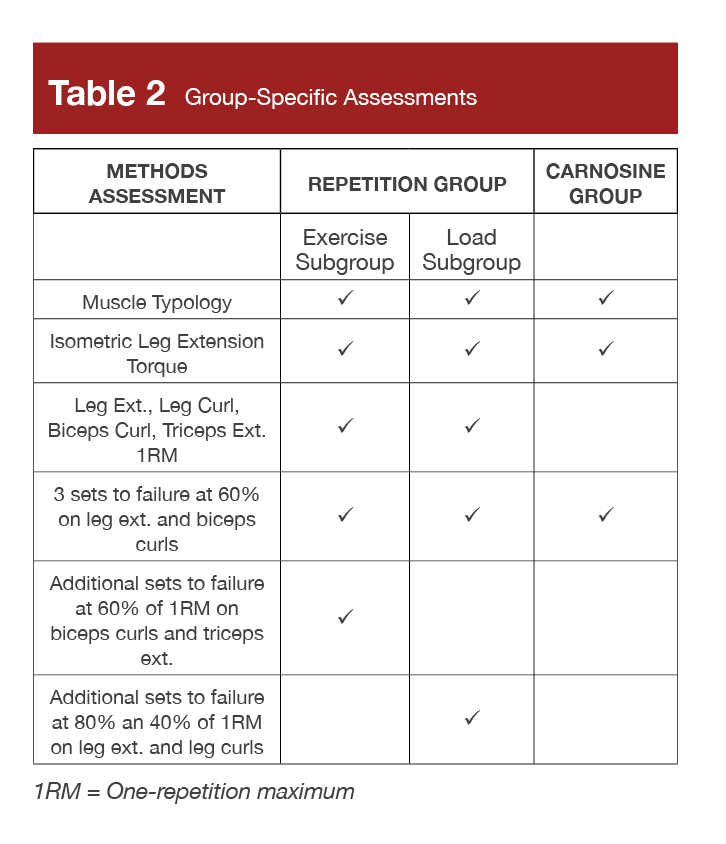
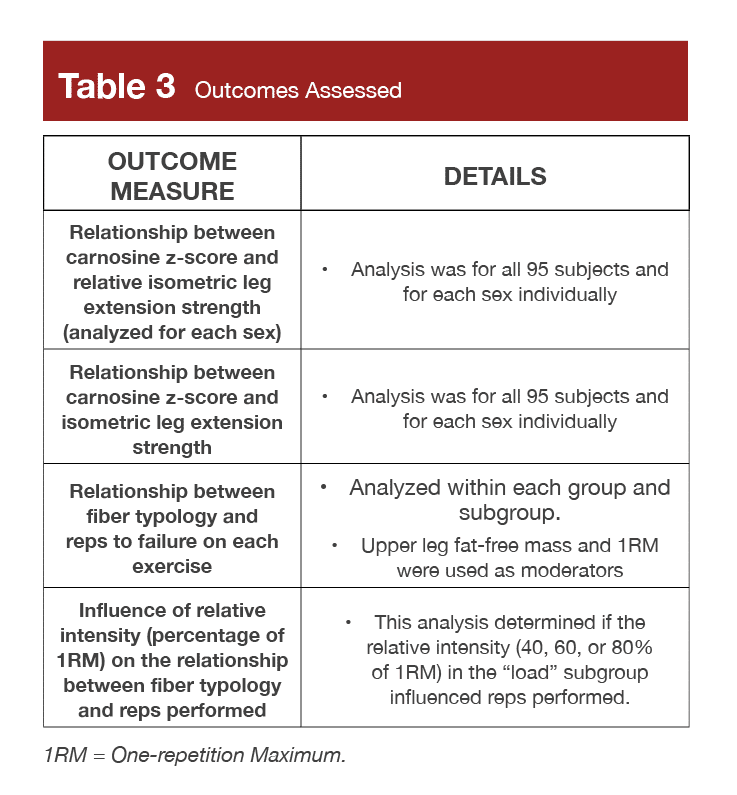
For readability, Desk 2 conveys every process completed by every group or subgroup, and Desk 3 lists the end result measures assessed in every group or subgroup. One other observe is that the researchers examined if higher leg fat-free mass (estimated from a scale), energy degree, or physique mass influenced the variety of reps carried out to failure.


Findings
The principle take house of the findings is that people categorized as having quick twitch muscle fiber typology tended to carry out fewer reps throughout units to failure on the leg extension, leg curl, and biceps curls than people categorized as having sluggish twitch fiber typology. Muscle fiber typology didn’t considerably affect reps carried out on the triceps extension. Additional particulars for all end result measures are within the following subsections.
Relationship Between Typology and Isometric Power
Throughout all topics, there was a major relationship between carnosine z-score and leg extension isometric torque (r = 0.30, p = 0.003) and relative torque (r = 0.22, p = 0.03), indicating that quick typology people might generate extra power (i.e., have been stronger). When damaged down by intercourse, solely males exhibited vital relationships between z-scores with each absolute (males: r = 0.37, p= 0.01; ladies: r = 0.19, p = 0.24) and relative (males: r = 0.26, p = 0.05; ladies: r = 0.16; p = 0.35) leg extension torque.
Relationship Between Typology and Reps Carried out
Leg Extension and Leg Curls
Quick twitch people carried out considerably fewer reps to failure than sluggish twitch people at 60% of 1RM on each the leg extension (p = 0.03) and leg curl (p = 0.01) (Determine 2). Additional, there was a major inverse relationship between carnosine z-score and reps carried out to failure on leg extensions and leg curls (r = –0.44; p = 0.003), indicating that quick twitch typology people tended to carry out fewer reps than sluggish twitch people. These findings weren’t considerably impacted by any covariate (higher leg fat-free mass, energy, or physique mass). There was additionally no vital interplay by set, which means that the speed of fatigue (lower in reps carried out from set to set) was not considerably completely different between quick and slow-twitch people. Nevertheless, coaching load (40, 60, or 80% of 1RM) did influence reps carried out within the load subgroup. Particularly, there have been vital inverse relationships between carnosine z-score and reps carried out at 60% (r = –0.41, p = 0.05) and 80% (r = –0.42, p = 0.04) of 1RM, however not at 40% (r = –0.23, p = 0.28). These findings point out that quick twitch people tended to carry out fewer reps than sluggish twitch people at 60 and 80% of 1RM however not at 40% of 1RM.
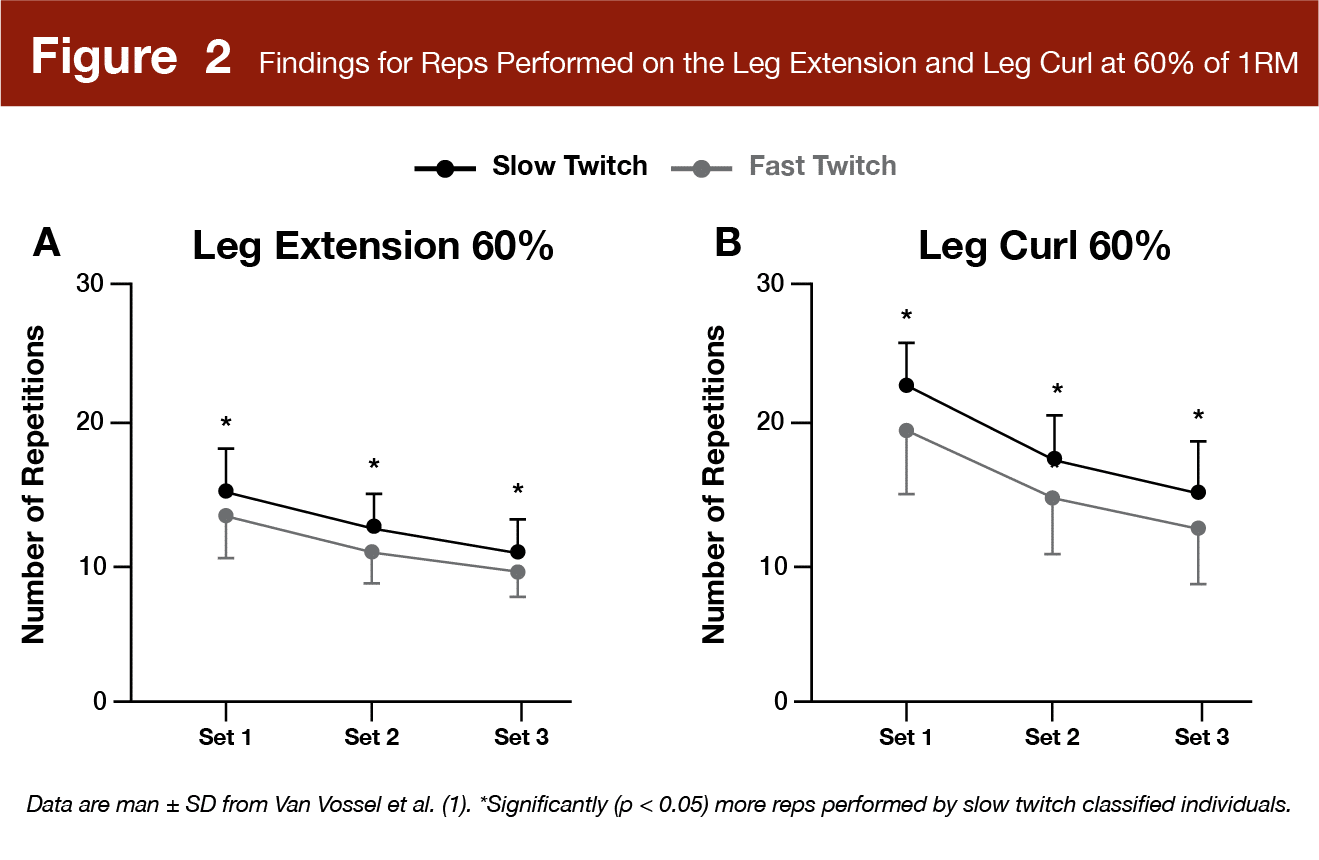

Biceps Curls and Triceps Extensions
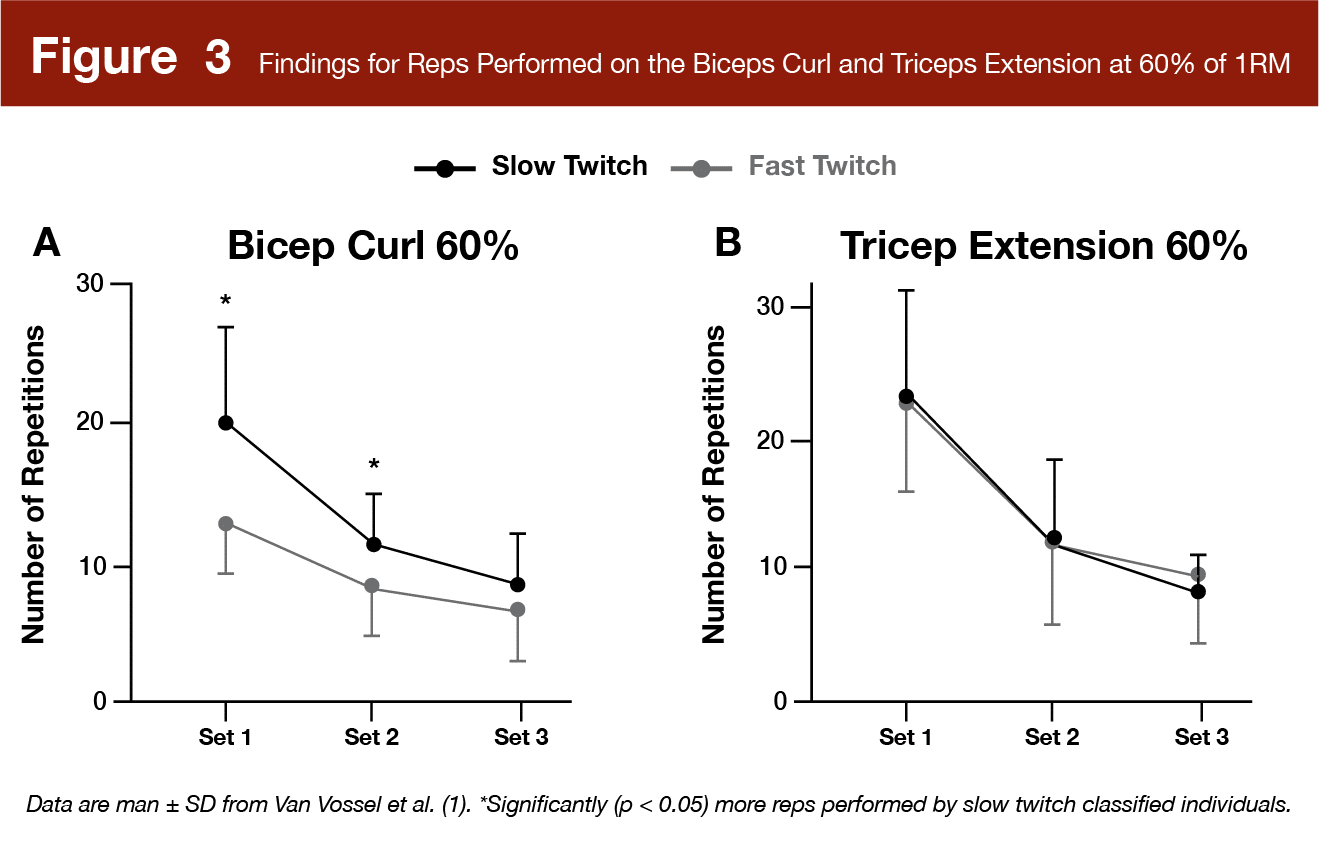
Quick twitch people carried out considerably fewer reps to failure at 60% of 1RM on the biceps curl (p = 0.02); nevertheless, there was no vital distinction between teams for reps carried out on the triceps extension (p = 0.96). Additional, reps carried out on both train weren’t considerably influenced by energy degree or physique mass (p > 0.05).

Variance in Reps Carried out
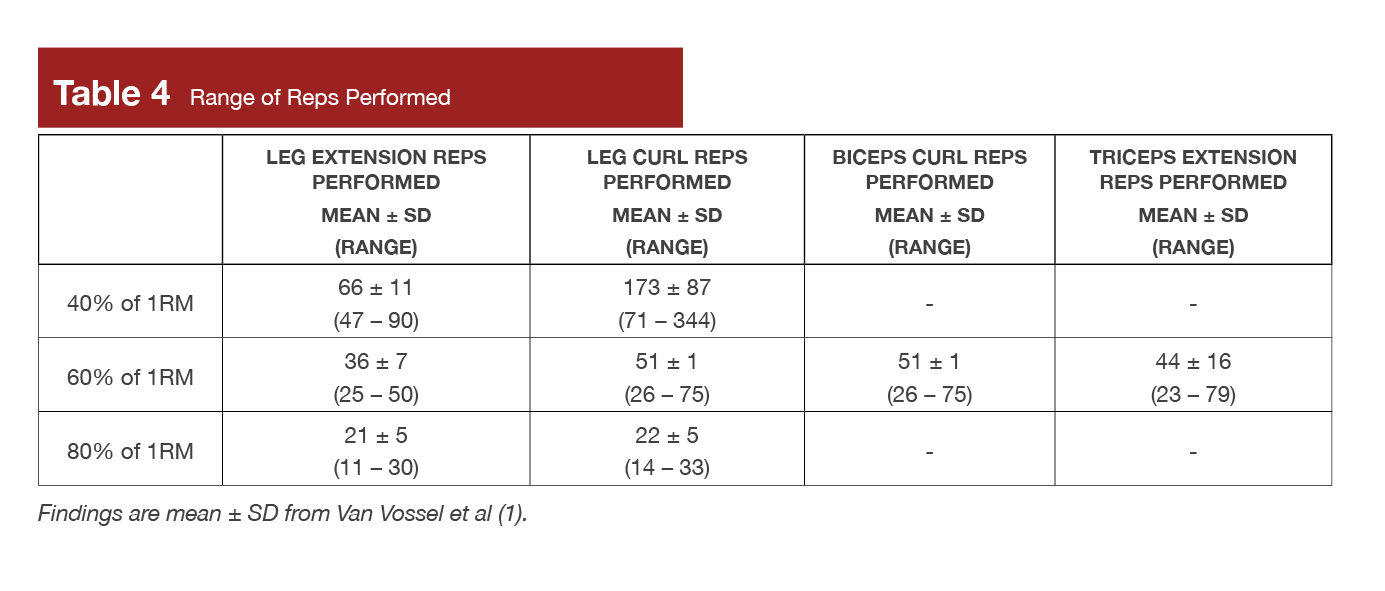
Lastly, I wish to spotlight the vary of reps carried out, which was huge. For instance, throughout three units of the biceps curl at 60% of 1RM, a spread of 18 – 62 reps was accomplished. The vary of reps carried out for all workout routines with all three units mixed is in Desk 4.

Criticisms and Statistical Musings
Whereas not a criticism per se, this part explains the strategies for these wanting a extra full understanding of how this research’s outcomes have been derived. A essential piece of the evaluation within the presently reviewed research was classifying topics as quick, sluggish, or intermediate twitch. To make this classification, a standardized “rating” wanted to be created to match people to a reference worth. On this research, the researchers had carnosine concentrations already established for a management inhabitants consisting of “energetic, wholesome non-athlete” people for the gastrocnemius and soleus (ladies = 112; males = 163) and the vastus lateralis (ladies = 56; males = 70). Due to this fact, to categorise people into excessive, intermediate, or sluggish twitch muscle fiber typologies, the researchers created a z-score for every particular person’s carnosine focus and in contrast that rating to the imply rating of the management dataset. A z-score is a standardized rating that signifies the magnitude of normal deviations the metric differs from the imply of the whole dataset. On this research, the z-score was calculated as z = (noticed worth) – (imply of the management knowledge set) / commonplace deviation of the management knowledge set. People have been categorized as sluggish twitch if they’d a z-score of ≤ -0.5, intermediate twitch with a z-score between -0.5 to +0.5, and quick twitch with a z-score of ≥5.
Interpretation
As acknowledged on this article’s introduction, I imagine probably the most essential questions in up to date coaching analysis are associated to figuring out the components that designate inter-individual variations in coaching responses. For instance, the speed of hypertrophy and energy is extremely variable (2, 3, 4, 5); some people develop extra with drop units and a few with conventional units (6), and the variety of reps carried out to failure at a given relative depth can also be extremely variable (6, 9, 10). But, we all know little or no about why the interindividual variance is so nice. Within the mid to late 2000s, knowledge revealed that these with extra satellite tv for pc cells and myonuclei per myofiber tended to expertise extra muscle progress (5). Extra not too long ago, researchers noticed that people who grew extra and gained extra energy in response to larger quantity coaching additionally tended to have higher ranges of ribosomal biogenesis (i.e., will increase in muscle ribosome content material) (11). Nevertheless, none of these findings are sensible for the coach and lifter. In follow, coaches and lifters have to make use of trial and error to find out what coaching model somebody responds greatest to. Due to this fact, analysis should try to look at sensible methods to clarify particular person variation.
Why Have a Sensible Fiber Typology Evaluation?
So, what’s sensible about assessing fiber typology by means of an imaging approach? Properly, nothing immediately. Nevertheless, if fiber typology can predict reps to failure, somebody might do a set to failure and decide whether or not they’re primarily quick or sluggish twitch. The following query is, why does figuring out if somebody is a quick or sluggish twitch particular person matter? Properly, there is a few proof that having this info might influence programming selections. For instance, except for realizing if a lifter has good muscular endurance, one research (12 – MASS Review) confirmed that people with the next proportion of sort II fibers took longer to recuperate from a maximal bout of biking than these with sort I fibers. The elongated restoration time might have an effect on coaching frequency and coaching quantity; thus, figuring out fiber sort classification might enable a lifter to handle their quantity per session accordingly to make sure acceptable restoration. Different examples embrace the chance that people categorized as quick twitch could also be extra liable to overreaching (13 – MASS Review) and that low-load blood-flow restriction coaching could preferentially trigger hypertrophy of sort I fibers. I’m undecided any of the above examples are definitive. Nevertheless, there’s sufficient analysis to recommend the chance {that a} easy rep take a look at to find out fiber typology may very well be sensible and helpful.
The Findings from Van Vossel et al. (1)
The presently reviewed research from Van Vossel et al (1) discovered that quick twitch people tended to carry out fewer reps to failure at 60% of 1RM on the leg extension, leg curl, and biceps curl however not on the triceps extension than sluggish twitch people. Moreover, quick twitch people additionally carried out considerably fewer reps to failure than sluggish twitch people at 80% of 1RM on the leg extension and leg curl; nevertheless, fiber typology didn’t considerably affect reps to failure at 40% of 1RM. There are two methods to interpret this knowledge. On the one hand, somebody might level to the considerably tenuous relationships between fiber typology with leg extension (r = –0.41) and leg curl (r = –0.42) at 60% of 1RM and say that the r2-value was solely about 0.20, which suggests fiber typology solely explains 20% of the variance in reps carried out. Somebody might additionally say that the p-values for the connection between typology and reps carried out at 60% (p = 0.05) and 80% (p = 0.04) of 1RM on the leg extension and leg curl barely crossed the importance threshold. Moreover, Corridor et al (7 – MASS Review) additionally reported correlations (Spearman correlations versus Pearson) (rho = –0.38; p = 0.039) that hardly crossed the importance threshold exhibiting a higher proportion of sort II fibers to be associated to fewer reps to failure at 80% of 1RM on the squat in educated ladies and men. Furthermore, one other research from Douris et al (14) discovered that when fiber typology was estimated from a 55-rep fatigue take a look at on a dynamometer, there was a major relationship between reps carried out and leg extension reps to failure at 70% of 1RM (r = –0.48; p = 0.02). Lastly, Terzis et al (15) discovered that energetic males with a sluggish twitch typology (fiber sort composition >50%) carried out just one extra rep to failure, on common, on the leg press in comparison with quick twitch people, which was not a statistically vital distinction. In different phrases, all of those findings barely cross the importance threshold, and one might conclude that these knowledge aren’t strong sufficient to conclude that rep assessments can be utilized to foretell fiber typology.
However, somebody might level to all of the aforementioned research (1, 7, 14, 15) and conclude that though the relationships aren’t significantly robust, they present a transparent development. The authors of the presently reviewed research, Corridor et al (7) and Douris et al (14) all noticed vital correlations exhibiting that sluggish twitch-classified people carried out extra reps to failure at relative intensities between 60 – 80% of 1RM. Moreover, one might argue that although the findings from Terzis et al weren’t vital, the yet one more rep, on common, in favor of sluggish twitch people follows the development of the opposite research. Additional, Terzis et al (15) did discover a vital relationship, and a reasonably robust one (r = 0.70; p = 0.01) between capillaries per mm2 of muscle cross-sectional space, in any other case often called ‘capillary density” and reps to failure at 70% of 1RM on the leg press. An optimist would say that discovering is vital as a result of sort I fibers sometimes have way more capillaries than sort II fibers (16), and capillaries have many mitochondria, cardio enzymes, and many myoglobin (offering extra oxygen to the muscular tissues), which all support sort I fibers’ fatigue resistance.
Though I’m cautiously optimistic, I take extra of the latter view on this subject as I feel these research present a transparent development. I don’t suppose the information are robust sufficient to make all out predictions; nevertheless, if somebody performs effectively above the imply (e.g., two commonplace deviations) for reps to failure, there may be actually sufficient knowledge to recommend that their fiber typology could have one thing to do with it. Nevertheless, the information aren’t sturdy sufficient to make particular claims akin to “each rep above the imply is related to 1% extra sort I fiber composition.” That sort of declare would require a way more exact take a look at with stronger correlations, and thus can be utterly inappropriate. My recommendation is to take this knowledge for what it’s price – there’s most likely one thing there, but it surely’s not but definitive sufficient to drive coaching selections.
It’s additionally price noting that Van Vossel et al (1) didn’t discover that sluggish twitch people carried out extra reps than quick twitch people on the mendacity triceps extension. The authors argue that one rationalization for that is that the triceps are overwhelmingly composed of quick twitch fibers. Additional, since researchers estimated triceps fiber typology from different muscular tissues, it’s seemingly that triceps composition was completely different from different muscular tissues and that every one topics had quick twitch dominant triceps. However, the gastrocnemius is a couple of 50/50 cut up between quick twitch and sluggish twitch, on common. Though the vastus lateralis tends to have extra quick twitch muscle fibers, researchers have reported a big variation 13 – 18% for fiber sort composition of the vastus lateralis. Due to this fact, reps to failure on some workout routines could also be affected by fiber typology greater than others.
Moderators of Rep Efficiency and Normal Variance in Reps Carried out
Within the presently reviewed research, fiber typology accounts for about 20% of the variance in rep efficiency on the leg extension and leg curl, which suggests 80% of the variance was unexplained. Curiously, the moderator’s intercourse, absolute energy, relative energy, and higher leg fat-free mass didn’t considerably have an effect on reps to failure. The issue that moderated the connection between typology and reps to failure was relative depth (load lifted). Particularly, typology was associated to reps carried out at 60% and 80% of 1RM however not at 40% of 1RM.
Analysis failing to determine predictors of reps carried out is fascinating, contemplating the massive interindividual variation. For instance, Desk 4 within the Findings sections illustrates that over three units to failure on the leg curl, the vary of reps carried out was 71 – 344 (40% of 1RM), 26 – 75 (60% of 1RM), and 14 – 33 reps (80% of 1RM). This phenomenon is current in lots of workout routines, as proven in a foundational research from Hoeger et al (9) in each educated and untrained ladies and men, in a research in each resistance-trained and endurance-trained people from Richens and Cleather (10), and from Cooke et al (6) in a research on educated ladies and men. Cooke et al (6) not solely discovered that educated ladies and men carried out a spread of 6 – 28 squat reps at 70% 1RM, however additionally they present in a a number of regression inspecting components (physique mass, body-fat %, femur size, age, and intercourse) influencing reps to failure that physique mass was virtually vital (p = 0.057). Whereas intriguing, extra analysis is required to substantiate the near-significant discovering that those that weigh extra are likely to carry out fewer reps to failure.
Further Ideas
One facet of the findings I nonetheless want to handle is the weak however statistically vital correlation (r = 0.22; p = 0.03) between isometric leg extension peak torque and fiber typology, indicating that quick twitch people are likely to have higher isometric leg extension energy. Nevertheless, fiber typology was not associated to dynamic energy in any train. This discovering is just like Machek et al (17 – MASS Review), who discovered that amongst 12 powerlifters, there was no vital relationship between sort II fibers and Wilks rating.
Total, many different components (e.g., leverages, muscle measurement, and many others.) affect repetition and energy functionality over simply fiber typology. Nevertheless, fiber typology impacts restoration. Due to this fact, these with a higher proportion of sort II fibers could want much less quantity and frequency to progress hypertrophy and energy than these with a higher proportion of sort I fibers. That hypothesis is tenuous, however I carry it as much as reveal the significance of figuring out components that may affect alter coaching variables akin to quantity, depth, and frequency. If analysis could make such sensible assessments, coaches and lifters can start to individualize coaching prescriptions with out present process vital trial and error.
Subsequent Steps
There are numerous instructions this analysis might go. One path is to recruit lifters, assess fiber typology, then observe them everywhere in the identical coaching program and look at if typology was associated to hypertrophy and energy features. Nevertheless, since assessing fiber sort distributions isn’t sensible, I’d prefer to see a research that assesses numerous sensible measures at baseline (reps carried out to failure, physique composition, and limb lengths, amongst different sensible metrics) and have these topics full a within-subjects design coaching research. On this proposed research, one limb might carry out extra regularly than the opposite. Theoretically, people who carry out fewer reps to failure throughout pre-testing would probably be quick twitch people and would wish extra restoration time and should profit from much less frequency. The identical research may be performed however with quantity between limbs manipulated as an alternative of frequency. There are numerous choices for what coaching variable to control. In the end, as I stated on the outset of this text, the idea of individualization is probably the most urgent query that analysis in our discipline wants to handle, so hopefully, we see extra on this space quickly.
Utility and Takeaways
- Van Vossel et al (1) discovered that people with a higher proportion of sort II fibers tended to carry out fewer reps to failure than sluggish twitch-classified people at 60% of 1RM on the leg extension, leg curl, and biceps curl. Fiber typology didn’t affect rep efficiency on the triceps extension.
- Much like Van Vossel et al, different analysis has additionally reported weak however statistically vital relationships between fiber typology and rep efficiency.
- Regardless of the numerous relationships between fiber typology and rep efficiency, the relationships aren’t robust sufficient for me to suggest that coaches and lifters can definitively predict fiber sort by performing a set to failure.
Get extra articles like this
This text was the duvet story for the July 2023 challenge of MASS Analysis Evaluation. In the event you’d prefer to learn the complete, 100-page July challenge (and dive into the MASS archives), you’ll be able to subscribe to MASS here.
Subscribers get a brand new version of MASS every month. Every challenge contains analysis assessment articles, video shows, and audio summaries. PDF points are often round 120 pages lengthy.
References
- Vossel KV, Hardeel J, Van de Casteele F, de Jager S, Lievens E, Boone J, Derave W. Muscle typology influences the number of repetitions to failure during resistance training. European Journal of Sport Science. 2023 Apr 25(just-accepted):1-21.
- Hubal MJ, Gordish-Dressman HE, Thompson PD, Worth TB, Hoffman EP, Angelopoulos TJ, Gordon PM, Moyna NM, Pescatello LS, Visich PS, Zoeller RF. Variability in muscle size and strength gain after unilateral resistance training. Medication & science in sports activities & train. 2005 Jun 1;37(6):964-72.
- Klemp A, Dolan C, Quiles JM, Blanco R, Zoeller RF, Graves BS, Zourdos MC. Volume-equated high-and low-repetition daily undulating programming strategies produce similar hypertrophy and strength adaptations. Utilized Physiology, Vitamin, and Metabolism. 2016;41(7):699-705.
- Erskine RM, Jones DA, Williams AG, Stewart CE, Degens H. Inter-individual variability in the adaptation of human muscle specific tension to progressive resistance training. European journal of utilized physiology. 2010 Dec;110(6):1117-25.
- Petrella JK, Kim JS, Mayhew DL, Cross JM, Bamman MM. Potent myofiber hypertrophy during resistance training in humans is associated with satellite cell-mediated myonuclear addition: a cluster analysis. Journal of utilized physiology. 2008 Jun 1.
- Cooke DM, Haischer MH, Carzoli JP, Bazyler CD, Johnson TK, Varieur R, Zoeller RF, Whitehurst M, Zourdos MC. Body mass and femur length are inversely related to repetitions performed in the back squat in well-trained lifters. The Journal of Power & Conditioning Analysis. 2019 Mar 1;33(3):890-5.
- Corridor EC, Lysenko EA, Semenova EA, Borisov OV, Andryushchenko ON, Andryushchenko LB, Vepkhvadze TF, Lednev EM, Zmijewski P, Popov DV, Generozov EV. Prediction of muscle fiber composition using multiple repetition testing. Biology of Sport. 2021 Jun;38(2):277-83.
- Angleri V, Ugrinowitsch C, Libardi CA. Particular person Muscle Variations in several Resistance Coaching Programs in Properly-Skilled Males. Worldwide Journal of Sports activities Medication. 2022 Jan;43(01):55-60.
- Hoeger WW, Hopkins DR, Barette SL, Hale DF. Relationship between repetitions and selected percentages of one repetition maximum: a comparison between untrained and trained males and females. The Journal of Power & Conditioning Analysis. 1990 Could 1;4(2):47-54.
- Richens B, Cleather DJ. The relationship between the number of repetitions performed at given intensities is different in endurance and strength trained athletes. Biology of sport. 2014 Jun 1;31(2):157-61.
- Hammarström D, Øfsteng S, Koll L, Hanestadhaugen M, Hollan I, Apro W, Whist JE, Blomstrand E, Rønnestad BR, Ellefsen S. Advantages of upper resistance‐coaching quantity are associated to ribosome biogenesis. The Journal of physiology. 2020 Feb;598(3):543-65.
- Lievens E, Klass M, Bex T, Derave W. Muscle fiber typology substantially influences time to recover from high-intensity exercise. Journal of utilized physiology. 2020 Mar 1;128(3):648-59.
- Bellinger P, Desbrow B, Derave W, Lievens E, Irwin C, Sabapathy S, Kennedy B, Craven J, Pennell E, Rice H, Minahan C. Muscle fiber typology is associated with the incidence of overreaching in response to overload training. Journal of Utilized Physiology. 2020 Oct 1;129(4):823-36.
- Douris PC, White BP, Cullen RR, Keltz WE, Meli J, Mondiello DM, Wenger D. The relationship between maximal repetition performance and muscle fiber type as estimated by noninvasive technique in the quadriceps of untrained women. The Journal of Power & Conditioning Analysis. 2006 Aug 1;20(3):699-703.
- Terzis G, Spengos Ok, Manta P, Sarris N, Georgiadis G. Fiber type composition and capillary density in relation to submaximal number of repetitions in resistance exercise. The Journal of Power & Conditioning Analysis. 2008 Could 1;22(3):845-50.
- Andersen JL. Muscle fibre type adaptation in the elderly human muscle. Scandinavian journal of drugs & science in sports activities. 2003 Feb;13(1):40-7.
- Machek SB, Hwang PS, Cardaci TD, Wilburn DT, Bagley JR, Blake DT, Galpin AJ, Willoughby DS. Myosin heavy chain composition, creatine analogues, and the relationship of muscle creatine content and fast-twitch proportion to Wilks coefficient in powerlifters. The Journal of Power & Conditioning Analysis. 2020 Nov 1;34(11):3022-30.
[ad_2]
Source link








