[ad_1]
Notice: This text was the MASS Analysis Evaluate cowl story for Could 2023 and is a overview of a recent paper by Smith et al. If you need extra content material like this, subscribe to MASS.
Key Factors
- Adjustments in satellite tv for pc cell quantity and ribosome content material after 10 weeks of resistance coaching, together with acute myofibrillar protein synthesis in response to a single train bout, have been assessed in 34 untrained younger ladies to find out the extent to which these outcomes have been predictive of muscle hypertrophy in increased and decrease responders.
- There was no important affiliation between the change in vastus lateralis cross-sectional space and myofibrillar protein synthesis (r = 0.095; p = 0.602) or modifications in muscle ribosome content material (r = 0.014; p = 0.937). Satellite tv for pc cell quantity elevated considerably in increased responders (p = 0.026), however not decrease responders (p = 0.118), and the % change in satellite tv for pc cells per fiber was correlated with the imply change in fiber cross-sectional space (r = 0.471; p = 0.007).
- Though the authors report that satellite tv for pc cell abundance was extra reflective of the resistance coaching response than muscle ribosome content material, they acknowledge that that is inconsistent with earlier knowledge, and that a number of methodological limitations preclude their capacity to low cost a job for ribosome biogenesis within the hypertrophic response.
Skeletal muscle hypertrophy entails a rise within the diameter of particular person muscle fibers, which leads to a rise in whole cross-sectional space. Hypertrophy happens when the speed of muscle protein synthesis exceeds that of muscle protein breakdown. Protein synthesis requires the next steps:
- In a course of often called transcription, sections of DNA are copied to kind three varieties of RNA: messengerRNA (mRNA), transferRNA (tRNA) and ribosomalRNA (rRNA). Consider mRNA because the template, or the set of directions, for protein synthesis. rRNA and ribosomal proteins kind the constructing website and tRNA transports supplies to the positioning.
- The following step is named translation, by which tRNA attaches to particular amino acids in line with the mRNA directions, and brings them to the ribosomes the place proteins are synthesized. You may need heard the time period “ribosome biogenesis,” which is the method of creating new ribosomes. The translational capability of the muscle fiber depends on the variety of obtainable ribosomes; a constructing website is required to construct new proteins. On this sense, muscle protein synthesis and ribosome content material are inextricably linked.
The mRNA, or “directions,” are copied from DNA within the nucleus. As a muscle fiber grows, its capacity to maintain up with the transcriptional and translational necessities turns into extra restricted (3). On this state of affairs, satellite tv for pc cells (muscle stem cells) can help by donating nuclei, including to the “equipment” obtainable for translation, and, thus, rising translational capability.
There’s compelling proof to display “increased” and “decrease” hypertrophic responders to resistance coaching. The underlying components could embody variations within the untrained state, together with genetics, satellite tv for pc cell quantity, and ribosome content material (2). In some instances, excessive responders seem to expertise a higher enhance in muscle protein synthesis and ribosome content material in response to resistance coaching, leading to a bigger enhance in muscle dimension in comparison with that of low responders (2). The differential response to coaching could embody the rise in myonuclei or transforming of the extracellular matrix as a result of satellite tv for pc cell proliferation (2).
These physiological variations between increased and decrease responders have been explored in males, and it’s unclear if there might be sex-based variations. Thus, Smith and colleagues assessed protein synthesis, modifications in satellite tv for pc cell quantity, and modifications in ribosome content material in younger, untrained ladies (1). This was a secondary evaluation of a subset of contributors in a research from the identical lab group that investigated the affect of peanut protein supplementation on energy and hypertrophic outcomes (4). The aim of the evaluation, which included 34 untrained younger ladies, was to find out the extent to which the next outcomes have been predictive of muscle hypertrophy, and in the event that they differed between increased and decrease responders:
- Acute myofibrillar protein synthesis following an train bout
- Continual modifications in satellite tv for pc cell quantity in response to resistance coaching
- Adjustments in ribosome content material in response to resistance coaching
The researchers assessed the 24-hour myofibrillar protein artificial response to a single train session, which consisted of three-repetition most (RM) leg press, barbell bench press, and hex-bar deadlift energy assessments, adopted by two units of 10 repetitions of every train at 50% of the contributors’ estimated 1RM. Then the contributors accomplished supervised resistance coaching periods twice per week (one increased load session and one decrease load session) for 10 weeks. The workouts included the leg press, barbell bench press, knee extension, hex bar deadlift, and lat pull down. The upper load periods consisted of 5 units of 6 repetitions, whereas the decrease load periods consisted of 4 units of 10 repetitions.
Greater and decrease responders have been labeled utilizing a composite change rating (from baseline to post-training) of the next variables: Twin-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) lean/mushy tissue mass, vastus lateralis cross-sectional space (measured with ultrasound), mid-thigh muscle cross-sectional space (measured with peripheral quantitative computed tomography), and 3RM hex-bar deadlift energy (Determine 1). Primarily based on the composite scores of the 34 contributors, the eight people within the higher quartile have been labeled “increased responders” and the eight people within the decrease quartile have been labeled “decrease responders.” The authors within the presently reviewed research assert that an inclusive, multidimensional strategy to delineating responder sub-groups ought to embody energy and hypertrophy measures. It’s value acknowledging that statistically quantifying true response heterogeneity is quite difficult, and there may be a lot disagreement about easy methods to correctly categorize responders.
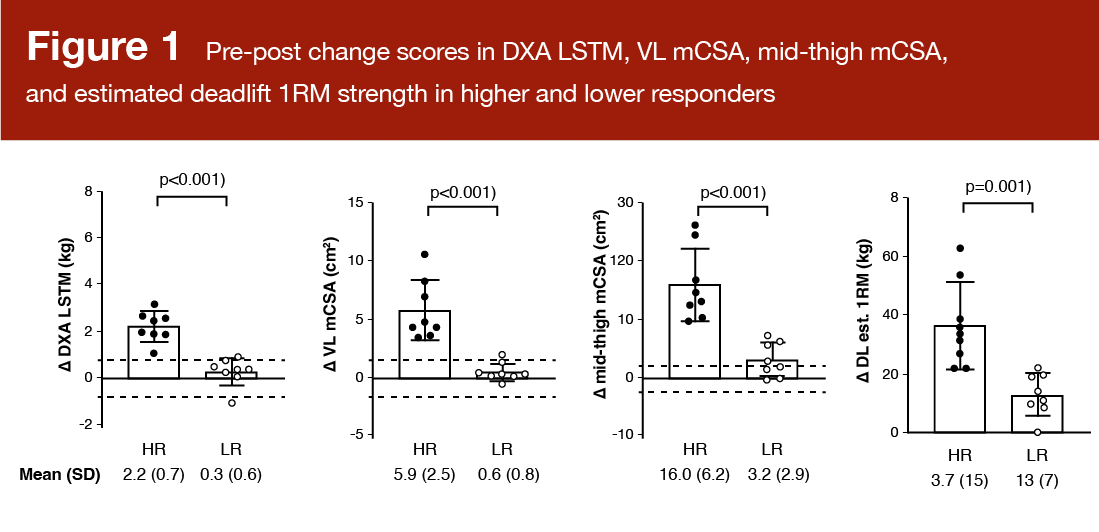
There have been no variations between increased and decrease responders within the 24-hour myofibrillar protein artificial response to the train bout at baseline. The typical fee was 2.25 ± 1.05% per day (HR: 1.88 ± 0.98% per day; LR: 2.43 ± 1.25% per day). There was no important affiliation between myofibrillar protein synthesis and the change in vastus lateralis cross-sectional space (r = 0.095; p = 0.602). The researchers weren’t stunned by these findings, notably as a result of they solely assessed a 24-hour interval, and the train bout was a novel, probably damaging stimulus.
There was no distinction in RNA content material per mg of moist muscle from baseline to post-training in any of the contributors, and there was no important correlation between modifications in muscle ribosome content material and the change in vastus lateralis cross-sectional space (r = 0.014; p = 0.937). This discovering will not be according to earlier knowledge in untrained males (2), which factors to modifications in ribosome content material as a distinguishing issue between increased and decrease responders. Whereas RNA focus, or ribosome density, is reflective of ribosome biogenesis, this measurement is only a snapshot at one time level, and doesn’t give us an entire image of a really dynamic course of. In any case, it could be, for my part, extremely untimely to focus on this as a recognized sex-based distinction with out much more analysis.
Satellite tv for pc cell quantity elevated considerably from baseline to post-training in increased responders (p = 0.026), however not decrease responders (p = 0.118). There was a major optimistic correlation (r = 0.471; p = 0.007) between the % change in satellite tv for pc cells per fiber and the imply change in fiber cross-sectional space. These outcomes are proven in Figures 2 and three.
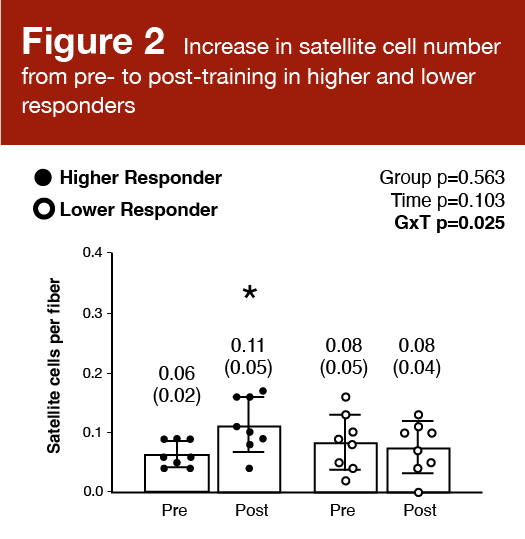

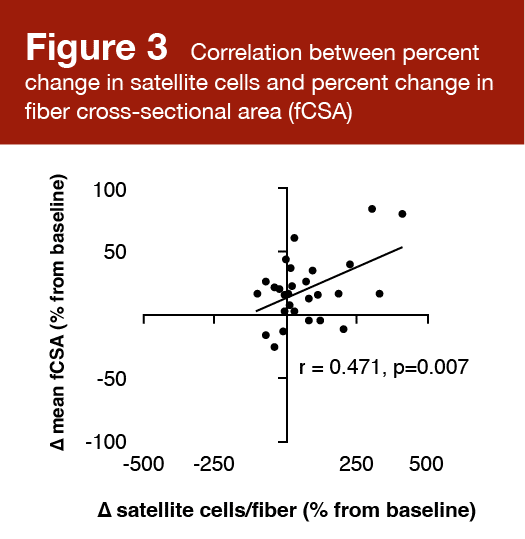

These findings align with different knowledge suggesting that myonuclear addition drives superior progress (5), and that the variety of satellite tv for pc cells in an untrained particular person is a determinant of his/her hypertrophic potential (6). That stated, the extent to which satellite tv for pc cells are required for hypertrophy is closely debated. Satellite tv for pc cells can restore or exchange broken muscle fibers or divide and self-renew to take care of the stem cell pool. A rise in muscle fiber dimension is commonly related to a rise within the variety of myonuclei. Satellite tv for pc cell differentiation ends in fusing and donating nuclei to an current fiber. There’s some proof to counsel that the proliferation, differentiation, and fusion of satellite tv for pc cells are required for hypertrophic variations in each younger and older people (7) that happen with a concomitant enhance in fiber cross-sectional space (8). An “excessive” progress response to resistance train seems to incorporate a big enhance within the satellite tv for pc cell pool. The best proof to help the contribution of satellite tv for pc cells to muscle fiber progress is an analysis of long-term anabolic steroid customers. Eriksson and colleagues reported vastly bigger muscle fibers and a higher variety of myonuclei per fiber in these people (9). There was a optimistic correlation between the variety of myonuclei per fiber and the fiber cross-sectional space, which supplies compelling proof that myonuclear quantity contributes to hypertrophic variations.
That stated, satellite tv for pc cells definitely serve different capabilities, together with transforming of the satellite tv for pc cell area of interest and upkeep/renewal of the satellite tv for pc cell pool. Thus, a rise in satellite tv for pc cell quantity will not be essentially indicative of a progress response (10). That is additional demonstrated by proof that satellite tv for pc cells contribute to non-hypertrophic transforming in response to cardio interval coaching (11). It’s conceivable that satellite tv for pc cells are nonessential for muscle hypertrophy within the quick time period, assuming an upregulation of transcriptional capability by current myonuclei. Nonetheless, they’re probably required for longer-term progress and the upkeep of muscle mass, tissue well being, and performance.
Utility and Takeaways
This physique of literature doesn’t present very sensible take-home messages for the coach or the lifter. Nonetheless, it offers us some perception into the advanced strategy of muscle hypertrophy, which is fairly fascinating for my part! It’s also a reminder of the variability within the response to resistance coaching between people. Maybe sooner or later sooner or later, we can tease out the mechanisms for increased and decrease responses to specific resistance coaching packages. For instance, why do some people reply higher to increased quantity or increased depth coaching than different people? There’s much more work to do on this space, and our capacity to discover these nuanced, advanced processes will enhance with the event of extra delicate analytical methods.
References
- Smith MA, Sexton CL, Smith KA, Osburn SC, Godwin JS, Beausejour JP, Ruple BA, Goodlett MD, Edison JL, Fruge AD, Robinson AT, Gladden LB, Younger KC, Roberts MD. Molecular predictors of resistance training outcomes in young untrained female adults. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023 Mar;134(3):491-507.
- Roberts MD, Haun CT, Mobley CB, Mumford PW, Romero MA, Roberson PA, Vann CG, McCarthy JJ. Physiological Differences Between Low Versus High Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophic Responders to Resistance Exercise Training: Current Perspectives and Future Research Directions. Entrance Physiol. 2018 Jul 4;9:834.
- Brook MS, Wilkinson DJ, Smith Okay, Atherton PJ. It’s not just about protein turnover: the role of ribosomal biogenesis and satellite cells in the regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019 Aug;19(7):952-963.
- Sexton CL, Smith MA, Smith KS, Osburn SC, Godwin JS, Ruple BA, Hendricks AM, Mobley CB, Goodlett MD, Frugé AD, Younger KC, Roberts MD. Effects of Peanut Protein Supplementation on Resistance Training Adaptations in Younger Adults. Vitamins. 2021 Nov 9;13(11):3981.
- Petrella JK, Kim JS, Cross JM, Kosek DJ, Bamman MM. Efficacy of myonuclear addition may explain differential myofiber growth among resistance-trained young and older men and women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Nov;291(5):E937-46.
- Petrella JK, Kim JS, Mayhew DL, Cross JM, Bamman MM. Potent myofiber hypertrophy during resistance training in humans is associated with satellite cell-mediated myonuclear addition: a cluster analysis. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008 Jun;104(6):1736-42.
- Roth SM, Martel GF, Ivey FM, Lemmer JT, Tracy BL, Metter EJ, Hurley BF, Rogers MA. Skeletal muscle satellite cell characteristics in young and older men and women after heavy resistance strength training. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001 Jun;56(6):B240-7.
- Blocquiaux S, Gorski T, Van Roie E, Ramaekers M, Van Thienen R, Nielens H, Delecluse C, De Bock Okay, Thomis M. The effect of resistance training, detraining and retraining on muscle strength and power, myofibre size, satellite cells and myonuclei in older men. Exp Gerontol. 2020 Could;133:110860.
- Eriksson A, Kadi F, Malm C, Thornell LE. Skeletal muscle morphology in power-lifters with and without anabolic steroids. Histochem Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;124(2):167-75
- Mackey AL, Holm L, Reitelseder S, Pedersen TG, Doessing S, Kadi F, Kjaer M. Myogenic response of human skeletal muscle to 12 weeks of resistance training at light loading intensity. Scand J Med Sci Sports activities. 2011 Dec;21(6):773-82.
- Joanisse S, Gillen JB, Bellamy LM, McKay BR, Tarnopolsky MA, Gibala MJ, Parise G. Evidence for the contribution of muscle stem cells to nonhypertrophic skeletal muscle remodeling in humans. FASEB J. 2013 Nov;27(11):4596-605
[ad_2]
Source link








