[ad_1]
Because the outdated adage goes, you’re solely as sturdy as your weakest hyperlink, and grip power will be the limiting consider efficiency for a lot of completely different power athletes. Whether or not you’re a powerlifter, strongman, weightlifter, Crossfitter, or a leisure lifter who needs to be throughout sturdy, life is healthier with a robust grip. On this article we’re going to discover the science and apply of grip power coaching and forearm muscle growth. Whereas I shall be referencing power athletes all through this text, the identical data will be utilized to enhancing grip power for athletes in quite a lot of different sports activities akin to mountain climbing, impediment course racing, wrestling, Brazilian jiu-jitsu, and archery. For readers who’re extra involved with aesthetics over grip power, this text may also delve into how you can enhance the dimensions of the forearm musculature and which muscular tissues are most impactful to whole forearm measurement.
Varieties of Grip
Broadly talking, I’ll classify gripping workouts into three completely different major classes with the popularity that there are different official methods to categorise them and that my definitions should not universally used. The commonest sort is help grip, which is used for all kinds of power coaching workouts akin to deadlifts, rows, pullups, and farmer’s walks. Since most people who try to enhance grip power prioritize help grip, I shall be discussing any such grip most frequently all through this text.
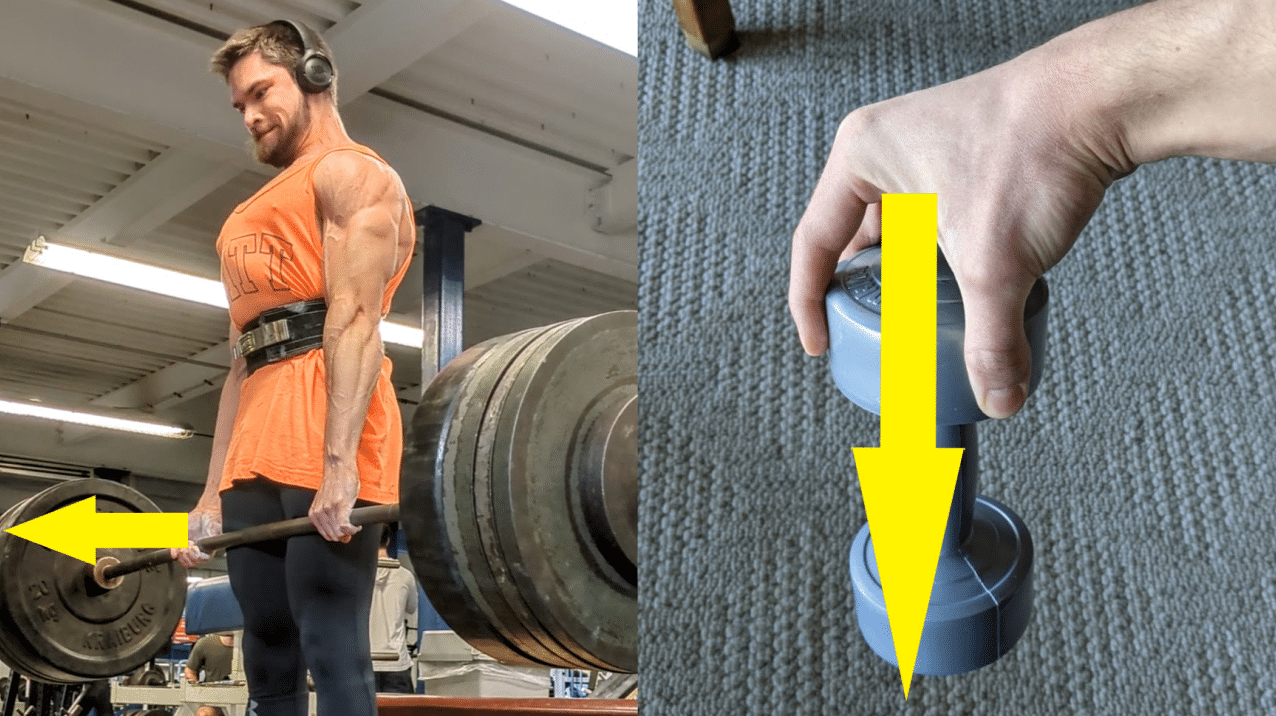
Much less steadily utilized is the pinch grip, which because the identify suggests, will be skilled with plate pinches or pinch blocks. Help grip and pinch grip workouts are each carried out with a static intent, however I think about the first distinction between them to be the route of resistance relative to the hand. If we consider our palm as a laser pointer, this imaginary laser shall be directed nearer to parallel with the road of resistance throughout a pinch grip train, whereas it will likely be directed nearer to perpendicular with the road of resistance throughout a help grip train. For example, throughout a blended grip deadlift, resistance is offered by gravitational power performing on the burden in a downward route, whereas your palms are going through ahead and backward. If we think about a laser declaring of the palms, near a proper angle is shaped between these lasers and the vector of gravitational power. When holding a weight plate with a pinch grip, the palm is pointed largely downward near parallel with the vector from gravity performing on the burden plate. Given this distinction in orientation, considerably much less load can be utilized for pinch grip workouts that require you to generate a excessive quantity of friction power as a way to preserve finger contact with the implement.




The third sort of grip is the crush grip, which is usually skilled dynamically with hand gripper units however can be skilled statically by trying to crush an object like a baseball. In distinction to help grip or pinch grip workouts that usually are loaded through gravitational forces, the resistance for a crush grip train is generated internally by the implement. For example, a torsion spring normally gives the resistance when crushing a hand gripper. In accordance with Newton’s third legislation of movement, a power that’s equal and reverse to your crushing power can function the resistance when statically trying to crush one thing like a baseball.


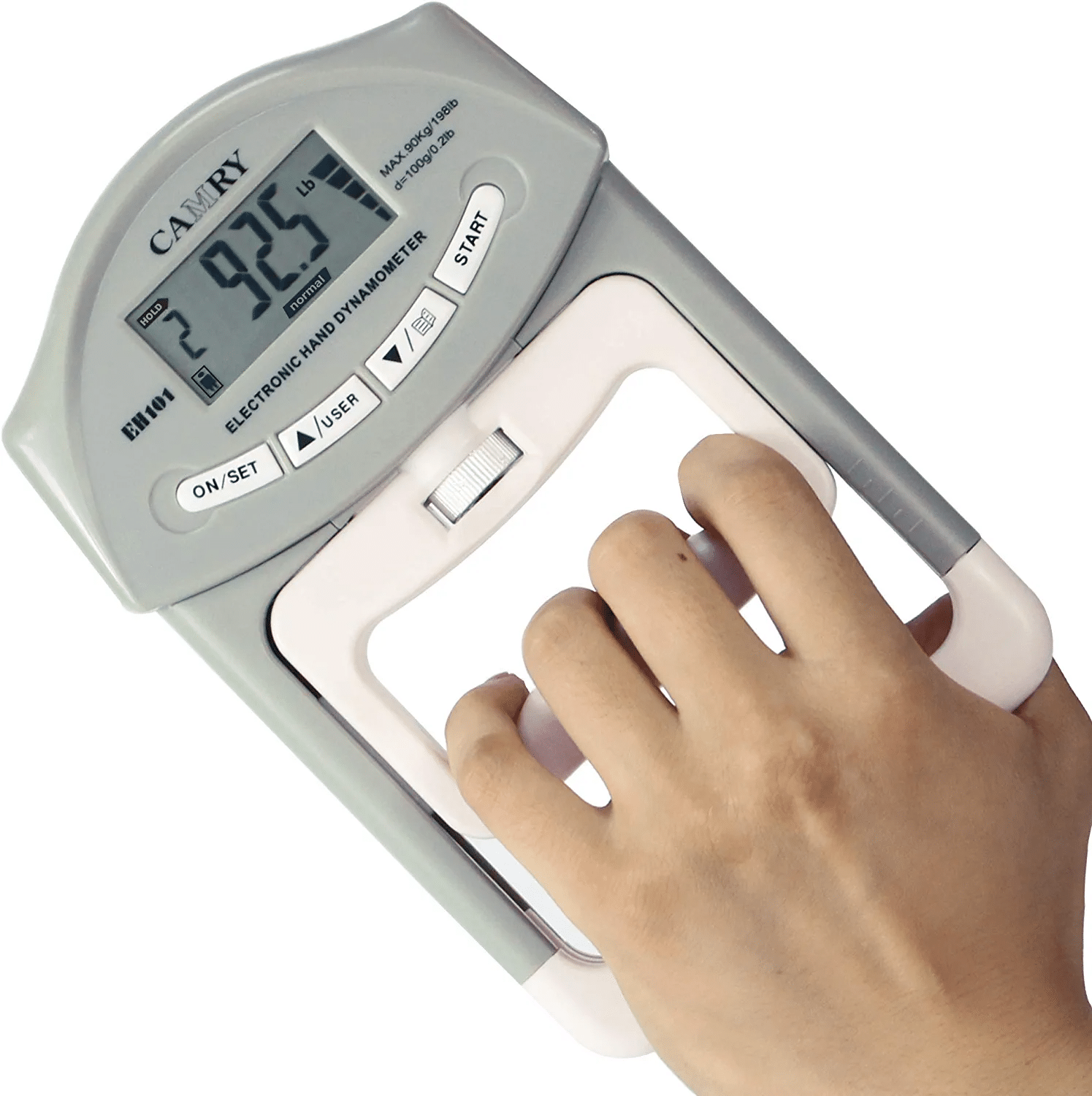
Whereas not concerned in most gripping actions, crushing grip is by far probably the most generally examined sort of grip power in analysis because of the accuracy, reliability, and ease of use of grip dynamometers (72,165). Along with being an final result worth that can be utilized to trace rehab progress in a quantitative method after quite a lot of higher extremity or neurological accidents, crush grip power measured with a grip dynamometer can also be a marker of general well being (24,26). Even when controlling for muscle mass, researchers have reported that grip power is inversely associated to all-cause mortality, and it may be an excellent stronger predictor of cardiovascular mortality than systolic blood stress (i.e., the highest worth in a blood stress measurement) (67,109,110,127,144,146,164,171). Moderately than purely being a causal relationship, I believe that the magnitude of this relationship is influenced by grip power being positively related to different variables conducive to well being akin to full physique power and bone mineral density (115,159,177,209). Different power metrics akin to bench press and leg press 1RMs are additionally considerably related to mortality threat, so grip power doesn’t essentially have a novel relationship to longevity relative to some other sort of power (71,204). Particularly for aged girls, declining hip flexor power can also be extra strongly related to elevated mortality threat than declining grip power (213). Nevertheless, maximal grip power will be examined on a mass scale extra readily than different kinds of train that will require a sure diploma of technical proficiency to carry out safely (e.g., again squat 1RM) or want costly specialised tools (e.g, isokinetic dynamometer). The hydraulic grip dynamometers which might be generally utilized in medical settings could value lots of of {dollars}, however quite a lot of completely different digital dynamometers will be bought for about $30 and yield measurements which might be moderately just like the gold normal (i.e., lower than 10% of a distinction) (134). Along with utilizing dynamometers to trace whether or not a block of grip power coaching has been productive, some lifters will use these units as a part of a neuromuscular readiness evaluation in an analogous approach to coronary heart fee variability or vertical leap peak (76,206). To my information, the potential for an acute grip power measurement to operate as an indicator of systemic fatigue has but to be studied in lifters.



A foundational precept of train science is that the diversifications that happen after a choose sort of coaching are particular to the actual calls for imposed by that sort of coaching. Consequently, if you wish to enhance your power with a specific sort of grip, you ought to be coaching that particular sort of grip. Nevertheless, this doesn’t imply that maximizing specificity is the important thing to maximizing outcomes. There’s a purpose why coaching for profitable powerlifters will not be solely composed of maxing out of their competitors model squat, bench press, and deadlift.
For some people, grip power won’t be a limiting consider efficiency of competitors actions in the event that they persistently carry out their sport particular coaching, however this isn’t all the time the case. The quantity of coaching that’s required to deal with a relative grip power weak spot could exceed somebody’s restoration capability if the competitors motion is solely used for grip coaching. For example, if a powerlifter’s deadlift is proscribed by his grip power and he already usually trains deadlifts with out straps, merely performing extra deadlifts with out straps might not be sustainable. Some folks can use this strategy with success, however others will discover that their low backs and hand pores and skin can not get better from additional deadlift quantity. To enhance deadlift particular grip power, using a double overhand grip on heat up units and performing a static maintain over the last rep of a piece set are two generally used approaches. Alongside performing rows, vertical pulls, farmer’s walks, suitcase carries, and rack pull holds with out straps, these are easy, time-tested strategies for enhancing deadlift grip power. Nevertheless, you should use quite a lot of different coaching strategies to extend long-term grip power and forearm muscle mass in a fashion that’s much less fatiguing than merely performing extra deadlift particular coaching. To reap the best efficiency switch to a specific sort of grip, needless to say these decrease specificity types of coaching must be used to complement your sport particular grip coaching relatively than exchange it.


Grip Anatomy and Physiology
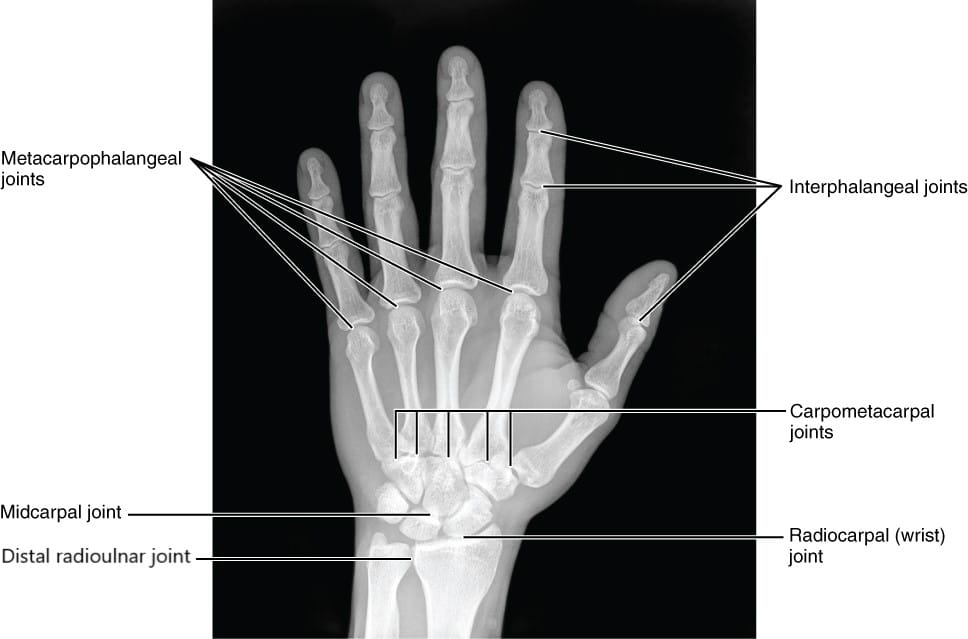
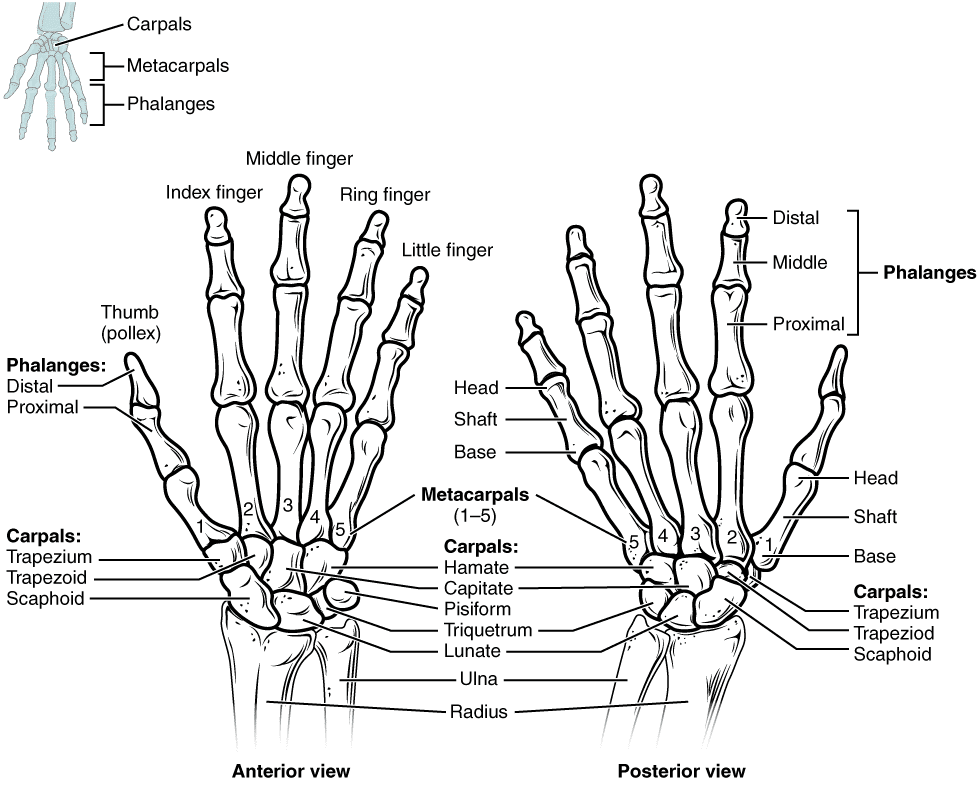
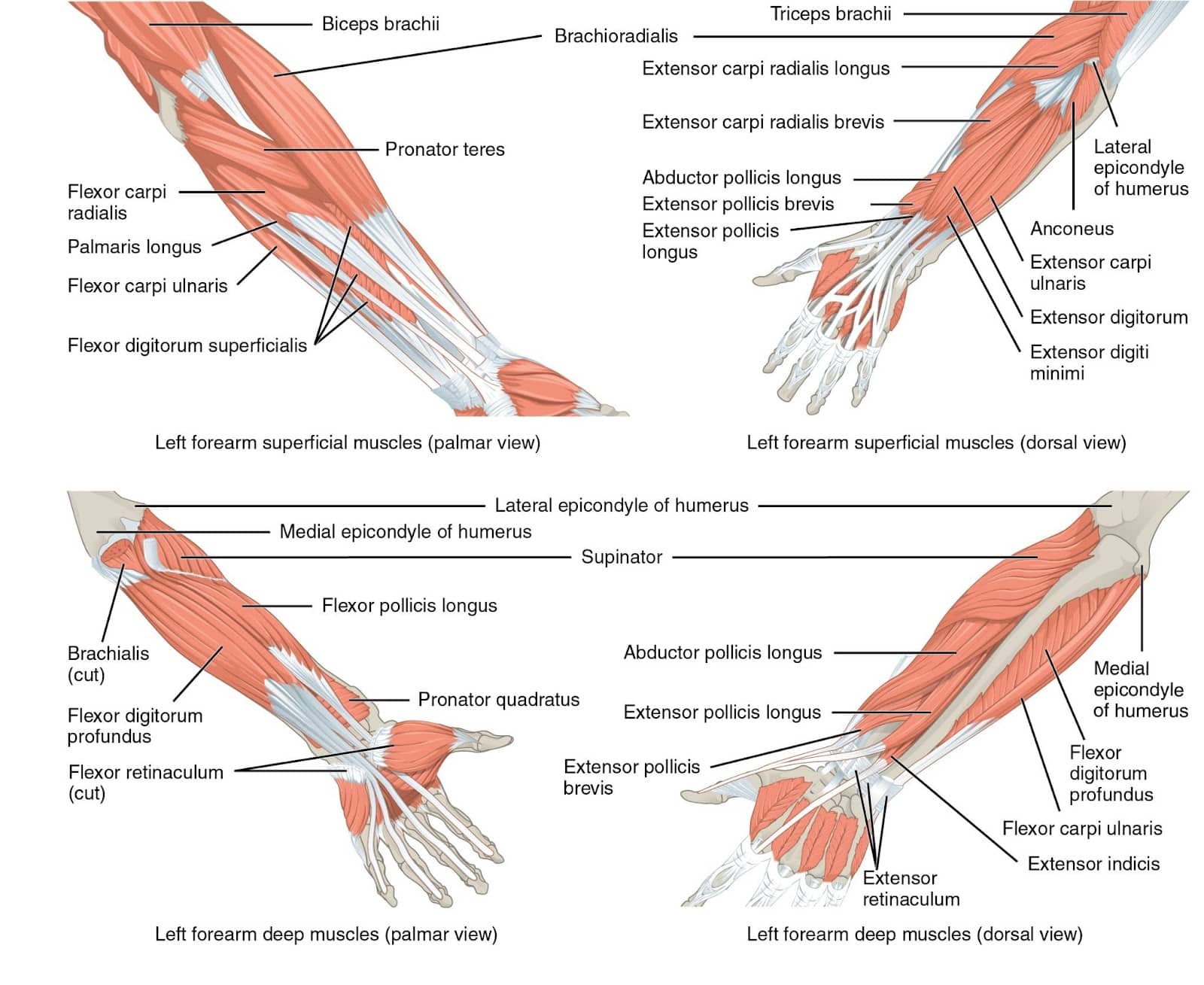
The human hand has 27 bones which might be categorised into three teams. Most distally (i.e., furthest away from the arm) lie the 14 phalanges that represent the skeletal construction of the fingers. Collectively, adjoining phalanges kind interphalangeal joints that enable flexion (i.e., bending) and extension (i.e., straightening). Aside from the thumb, which incorporates two phalanges and a single interphalangeal joint, every finger has three distinct phalanges and two interphalangeal joints. The one closest to the fingertip is named the distal interphalangeal joint, whereas the one nearer to the knuckle is named the proximal interphalangeal joint. The central portion of the skeletal hand consists of 5 bones generally known as the metacarpals, which every work together with a phalange to kind a metacarpophalangeal joint that permits flexion, extension, abduction (i.e., spreading aside), and adduction (i.e., coming collectively).
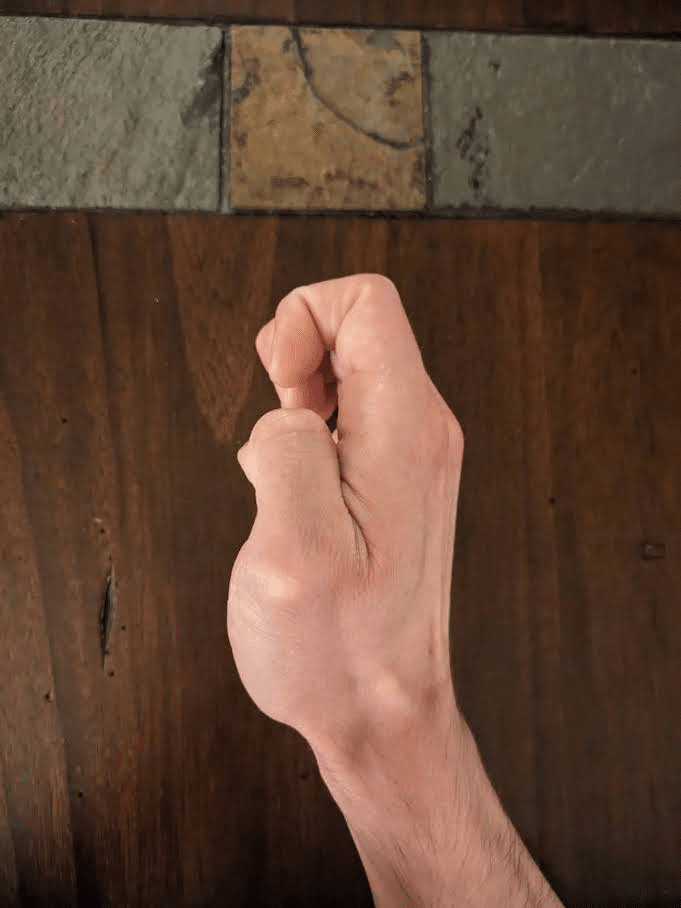
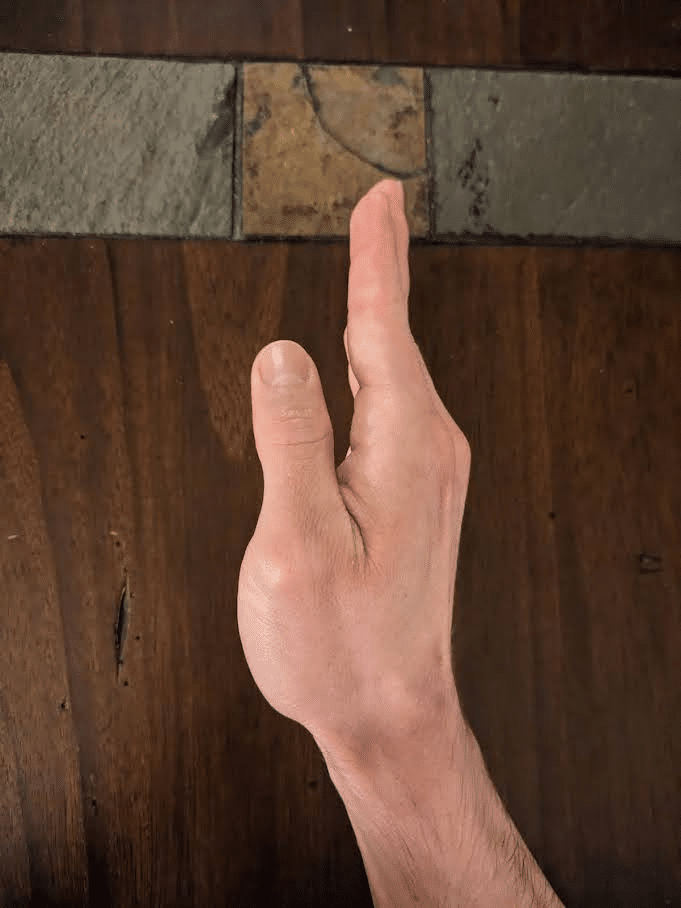
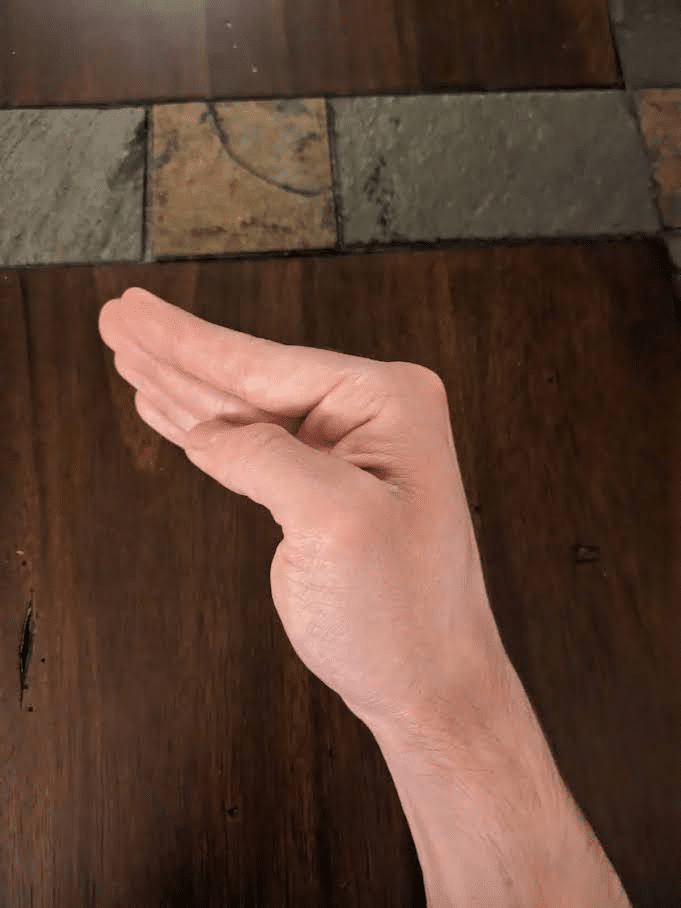
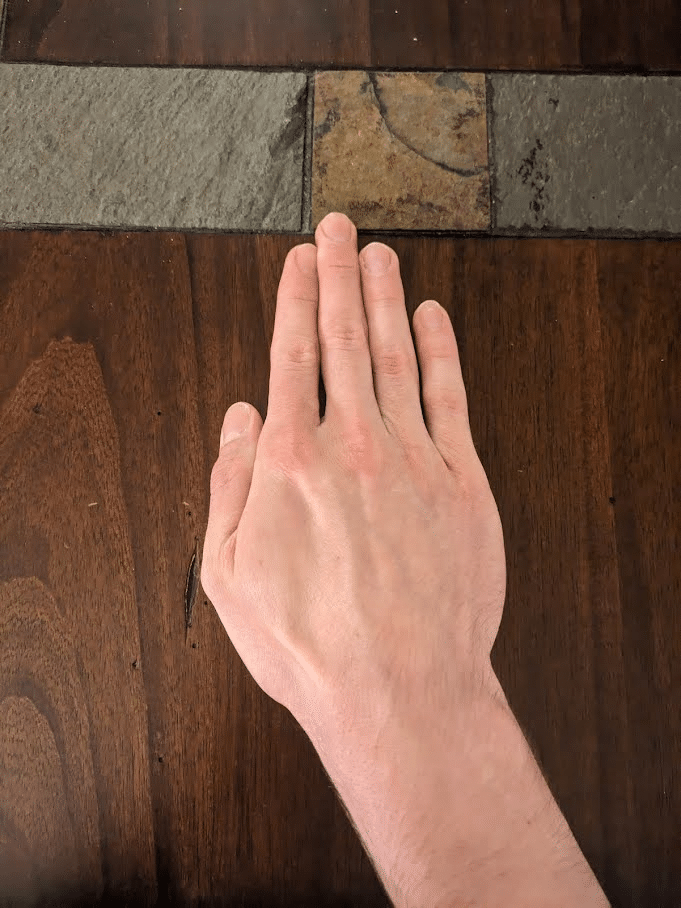
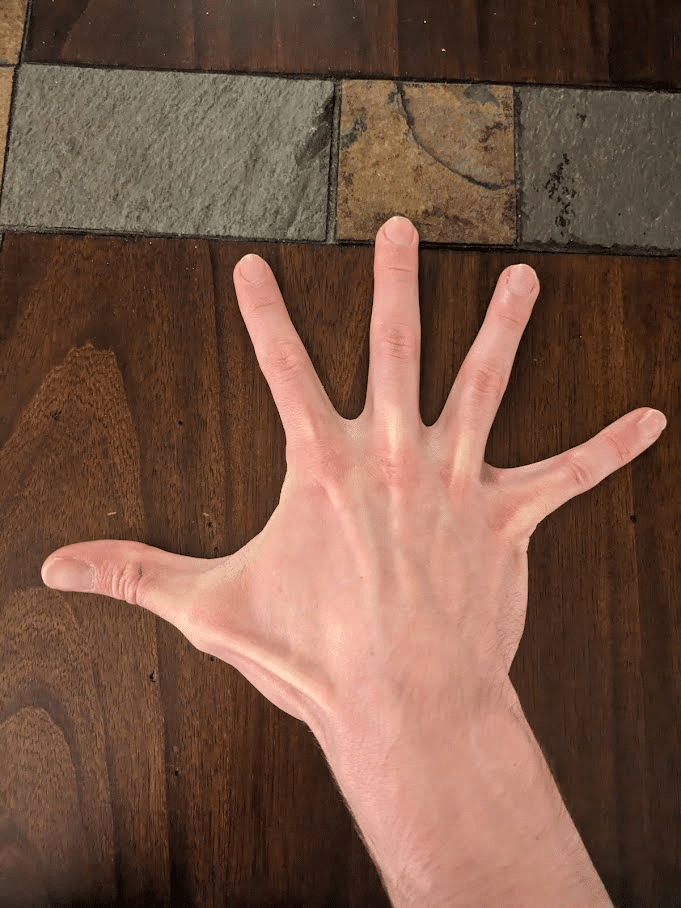













Relying on the place they originate, muscular tissues that act on the hand’s joints are categorised as intrinsic or extrinsic hand muscular tissues. The muscle bellies of the smaller intrinsic hand muscular tissues are located throughout the hand, whereas these of the extrinsic muscular tissues are located throughout the forearm and have tendons that cross the wrist as they course towards the phalanges. Our fingers normally include 19 intrinsic muscular tissues (some folks have fewer) that enable us to carry out outstanding feats of dexterity solely achievable by Homo sapiens (130). Fairly related to grip power, the vast majority of these intrinsic muscular tissues contribute to flexing the metacarpophalangeal joints (11,62,98,211).
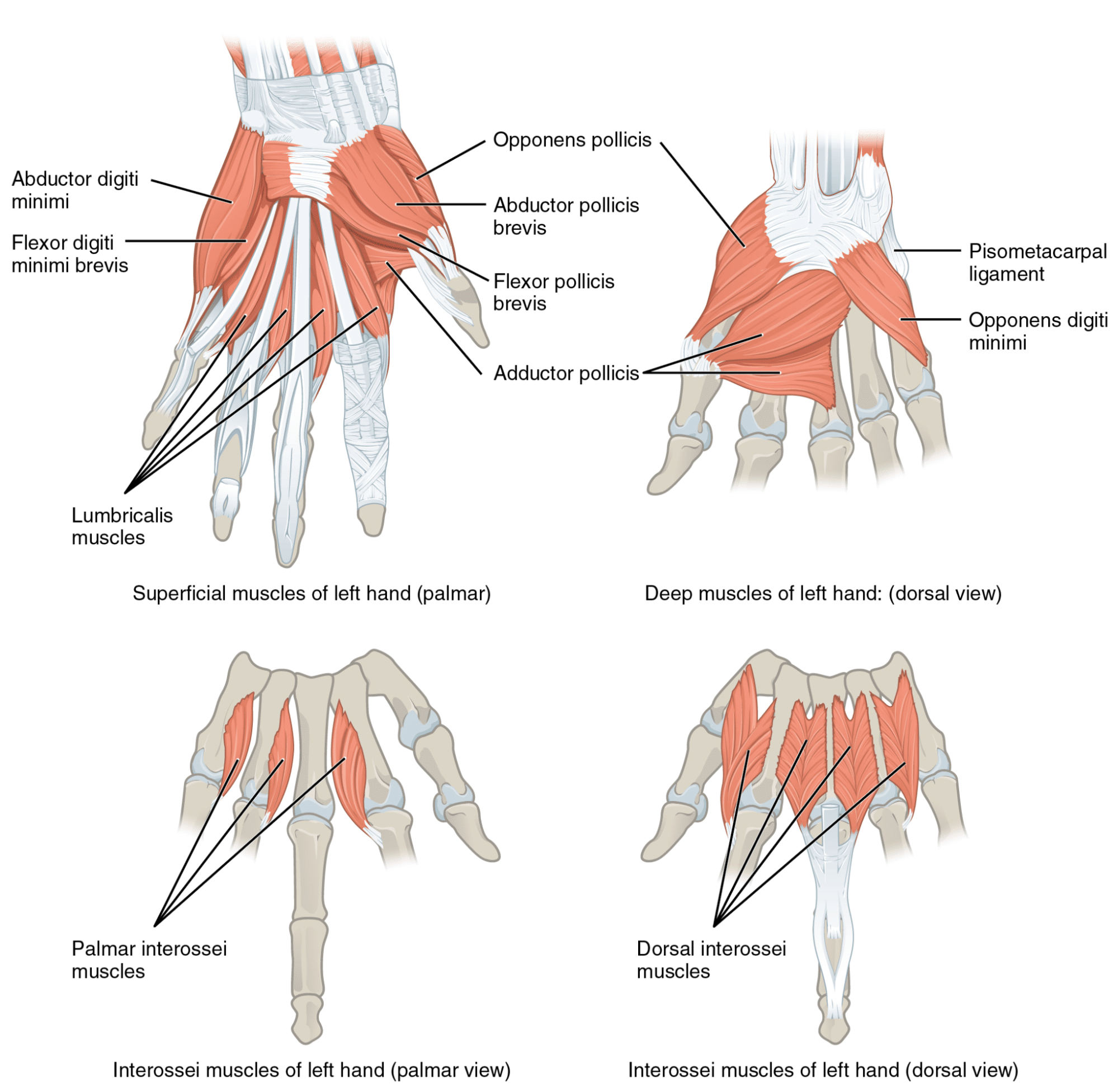

Nevertheless, a lot bigger extrinsic muscular tissues additionally cross these joints and are in a position to generate meaningfully extra flexion torque on the metacarpophalangeal joints because of the shut relationship between muscle measurement and power manufacturing (31). Whereas I’ve but to see the identical evaluation utilized to the thumb, the proportion of whole metacarpophalangeal flexion torque that may be produced by the intrinsic muscular tissues varies among the many fingers, starting from 8-28% for the index by little fingers (33,98). For these 4 fingers, the rest of metacarpophalangeal flexion torque shall be produced by two extrinsic muscular tissues which might be indispensable to grip power efficiency, particularly the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor digitorum superficialis (33,98). Together with the flexor pollicis longus, which flexes the thumb’s joints, these are the one muscular tissues within the physique which have the flexibility to flex the interphalangeal joints. These three extrinsic muscular tissues, situated throughout the anterior (i.e., entrance) compartment of the forearm, operate as wrist flexors together with three different muscular tissues throughout the identical forearm compartment. As a result of extrinsic muscular tissues crossing the wrist and finger joints, wrist place and wrist workouts can meaningfully have an effect on grip power.

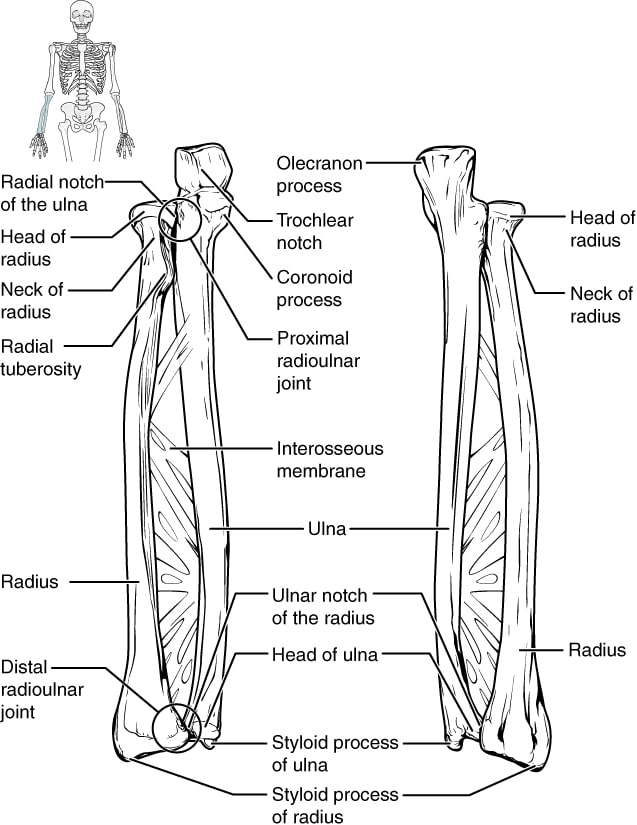
Proximally (nearer to the forearm) to the metacarpals lie eight carpal bones that work together with metacarpals to kind carpometacarpal joints and one another to kind intercarpal joints. In live performance with different finger and wrist actions, these hand joints allow variable vary of movement, however their particulars should not notably related to our coaching (55,131). The three carpal bones that lie closest to the forearm work together with the radius to kind the wrist joint (radiocarpal joint), which permits flexion, extension, radial deviation (abduction), and ulnar deviation (adduction). Forearm pronation and supination, which individuals could generally attribute to the wrist joint, happens because the radius interacts with the ulna on the two radioulnar joints, one in every of which is correct subsequent to the wrist joint whereas the opposite lies close to the elbow joint.
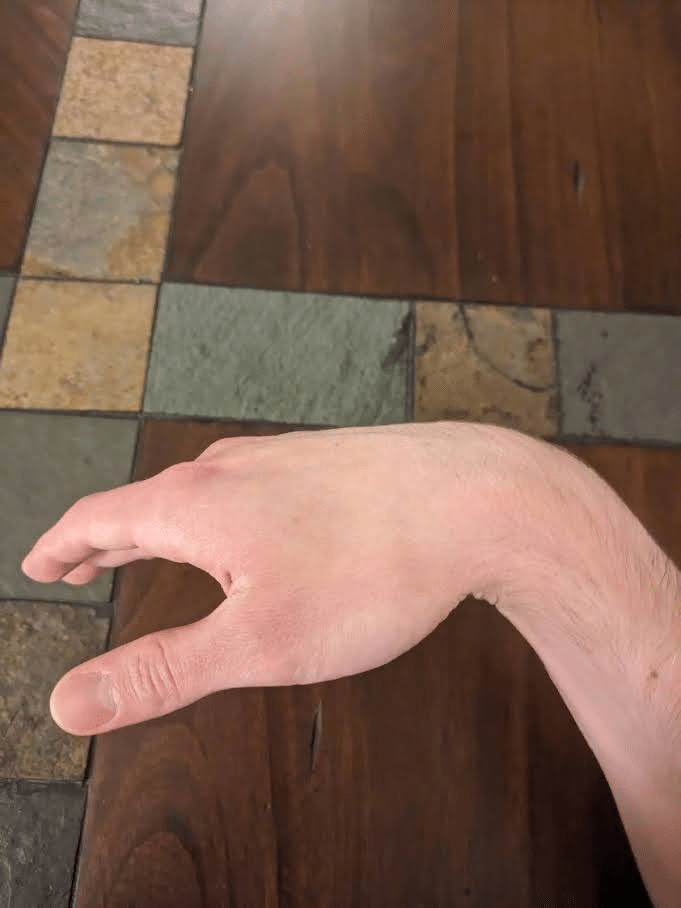












Determinants of Grip Power
When examined with a dynamometer, grip power reveals an “inverted U curve” relationship with the dimensions of the implement being gripped. An optimum span is current to maximise grip power, and growing or reducing the span from that optimum measurement reduces how a lot power may very well be generated (23,54,108,156,168). The common optimum span for producing grip power will increase as hand measurement will increase, however most research discover spans near 55mm (2.2”) to allow the best grip power for the everyday individual (54,64,108,168).
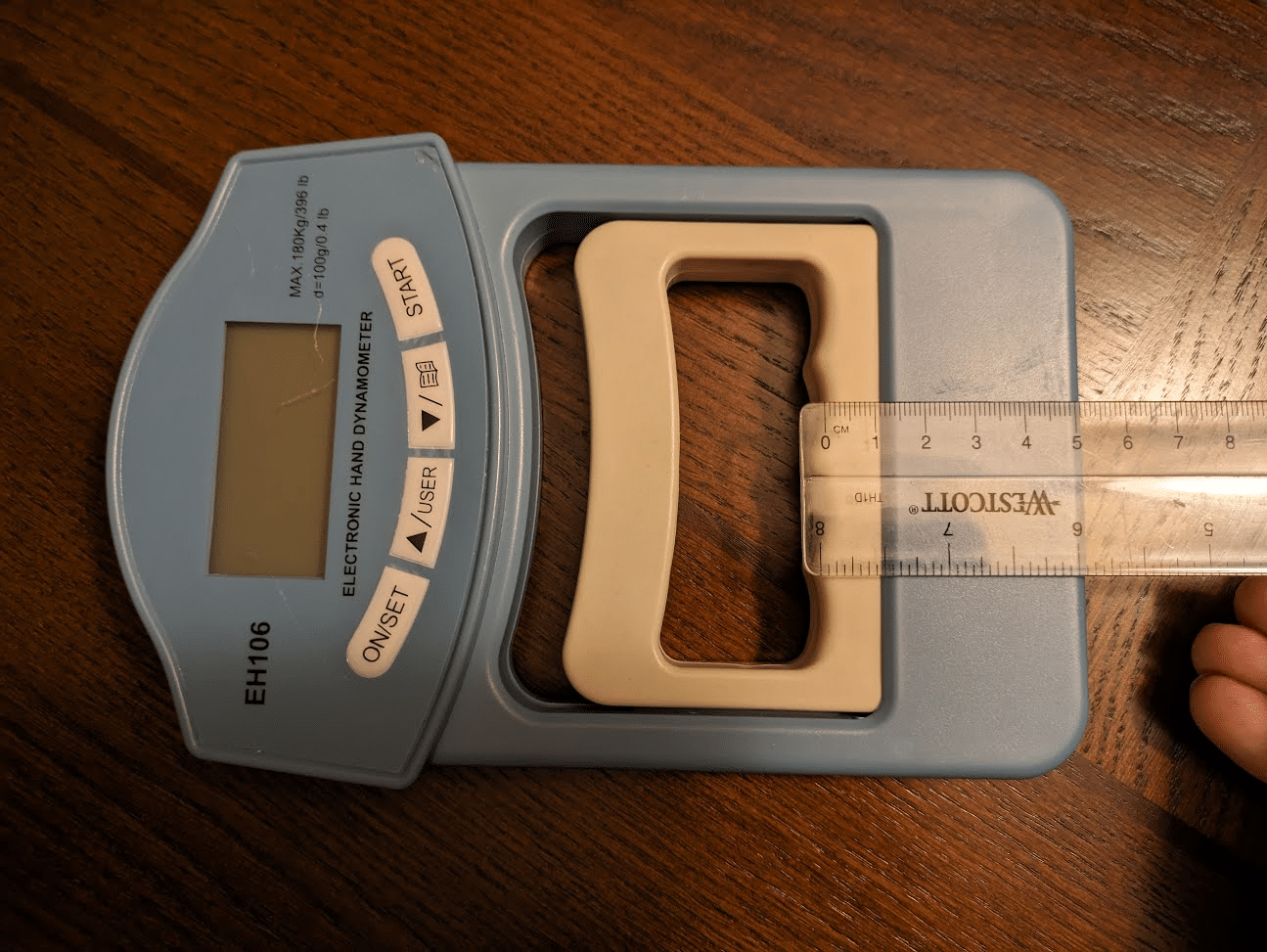
When measuring the person contributions from the index by little fingers throughout maximal crush gripping, the center finger is normally the strongest, adopted by the index finger, ring finger, after which the little finger, which is meaningfully weaker than the remaining (8,53,107,112,133,161,196). In distinction to the a number of research I discovered that assessed the contributions of the index by little fingers, I used to be solely in a position to establish a single examine that additionally assessed the contribution of the thumb when maximally gripping with all 5 fingers (38). Cha et al (2014) attributed 17% of whole grip power to contributions from the thumb, which was lower than the contributions from the center (31%) and index (22%) fingers. Cha et al reported the contributions of the ring and index fingers collectively (29%), however they acknowledged their findings to nonetheless point out that the little finger contributed the least, which is congruent with the opposite research on this subject.
Whereas some pinch grip lifts are an exception that contain prolonged interphalangeal joints, most kinds of grip workouts are carried out with the interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints concurrently flexed across the implement. Grip failure normally happens as a lifter is unable to keep up a enough diploma of flexion on the interphalangeal joints because the resistive power causes them to progressively lengthen. When gripping an object related in diameter to a barbell, a lifter could possibly full a rep if the metacarpophalangeal joints lengthen and the thing drifts towards the fingertips as long as the interphalangeal joints proceed to stay flexed.
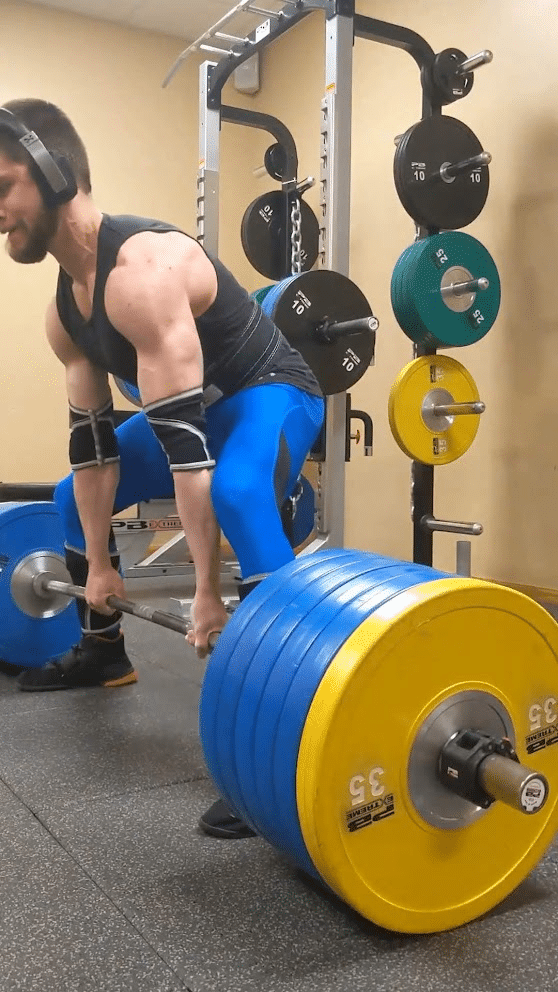
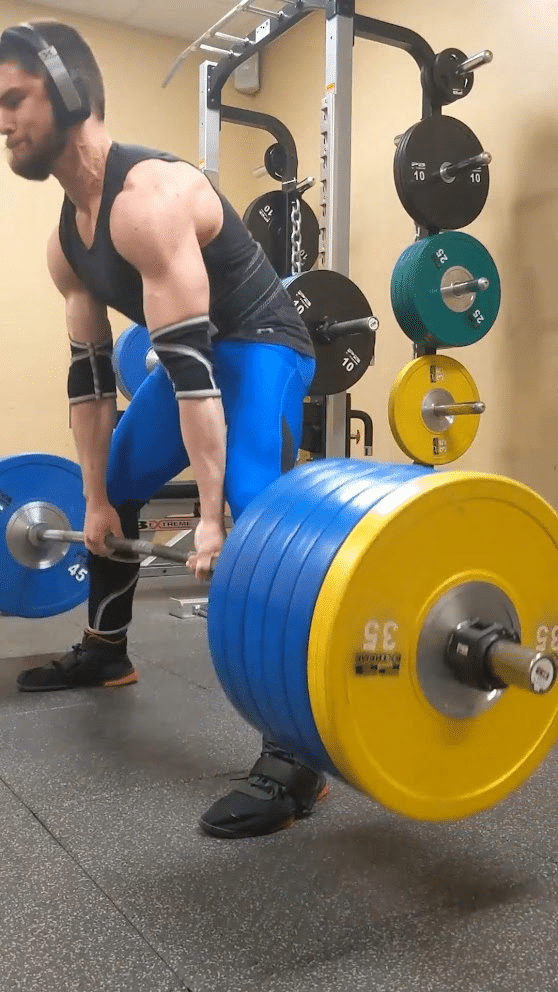
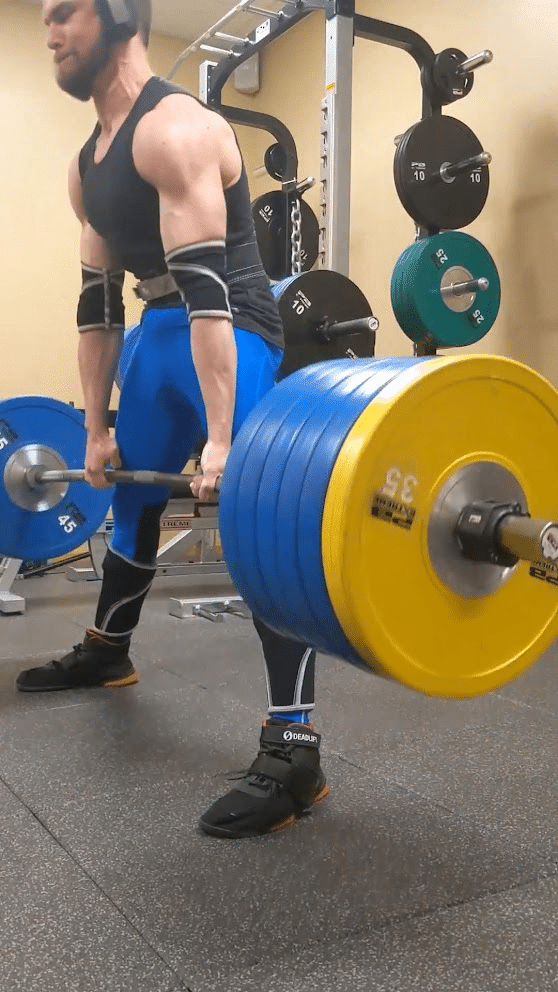
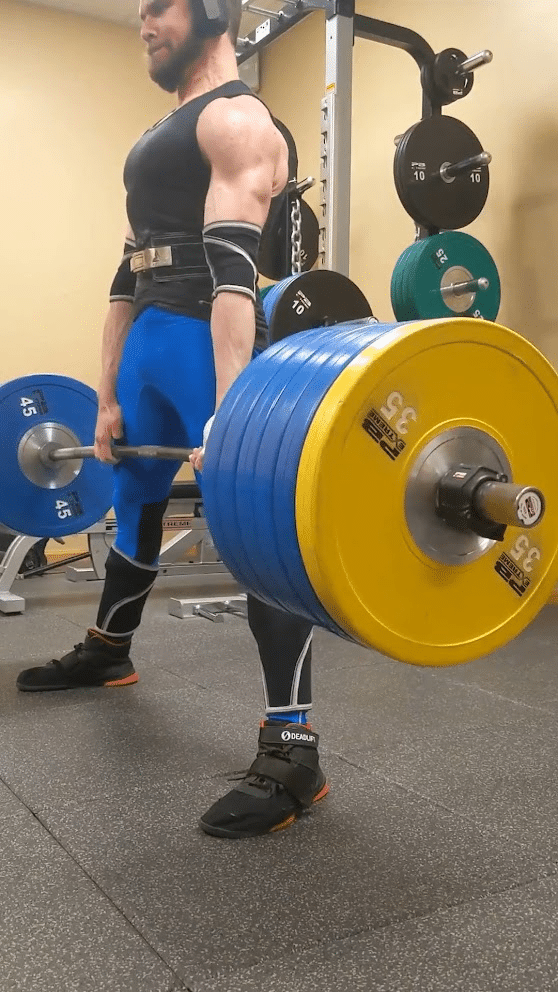








Whereas deadlifting, some lifters will deliberately provoke the pull with this extra prolonged metacarpophalangeal joint place, which some folks check with as a “fingertip grip” place. In distinction, lifters will usually grip a barbell with these joints extra tightly flexed because the bar rests nearer towards the palm. In comparison with utilizing a deeper grip, when starting a deadlift rep with a “fingertip grip,” the lifter can use a barely extra upright beginning place that could be advantageous for somebody who has lengthy fingers particularly if using a sumo stance. Past serving to a lifter preserve sufficient contact with the bar to make use of a “fingertip grip” efficiently, having lengthy fingers (notably lengthy proximal phalanges) will enable a lifter to begin from a extra upright place relative to having shorter fingers. Virtually this extra upright place could make the beginning of a “fingertip grip” deadlift akin to a really low block pull. Variations amongst people definitely exist, however breaking the ground tends to be probably the most difficult level in a sumo deadlift extra usually than a standard deadlift. Consequently, the “fingertip grip” is extra more likely to benefit a sumo puller in the identical method {that a} barbell with higher whip (i.e., deadlift bar) will.




No matter which grip is used, almost each sort of gripping exercise will depend on somebody’s capability to supply flexion torque on the interphalangeal joints and/or metacarpophalangeal joints. Correspondingly, the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus are the three key grip muscular tissues since they’re the one muscular tissues that may flex the interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints concurrently.
Understanding Forearm Muscle Names
Just like the hand and foot muscular tissues, the names of the forearm muscular tissues are a mouthful to say, however understanding why they’re named this fashion could make it rather a lot simpler to recollect and perceive them whereas not complicated them with different muscular tissues. The “flexor” half in the beginning of every identify communicates that they operate to flex the joints they cross. Any muscle with “pollicis” in its identify implies that it acts on the thumb, whereas muscular tissues with “digitorum” act on the opposite 4 digits. If a muscle has “longus” in its identify, it’s longer than a muscle performing an analogous operate that can have “brevis” in its identify. For example, the hand has a flexor pollicis brevis that additionally flexes the thumb’s carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joint, however it doesn’t act on the wrist or interphalangeal joint as a result of it’s shorter than the flexor pollicis longus. “Profundus” is a Latin time period for “deep,” so the flexor digitorum profundus lies deeper within the forearm relative to the flexor digitorum superficialis, which lies nearer to the floor (i.e., superficially).
Word on Muscle Measurement Comparisons
All through this text, I evaluate the dimensions of various muscular tissues, and it’s value noting that almost all of those measurements are derived from analysis on cadavers. Naturally, older people usually tend to donate their our bodies to the development of science than youthful people because the present common international life expectancy is barely greater than 70 years outdated (which is remarkably higher than the 46 12 months outdated international life expectancy in 1950) (74). Within the common inhabitants, common whole muscle mass declines with growing old past the fifth decade in life (82,111). Nevertheless, simply as quick twitch muscle fibers are extra aware of hypertrophy following resistance coaching, so too are quick twitch fibers extra inclined to atrophy with growing old (111,141,187,203). Consequently, the dimensions of a gradual twitch dominant muscle (e.g., soleus) relative to the dimensions of a muscle with a higher proportion of quick twitch fibers (e.g., gastrocnemius) could also be higher in cadavers than non-elderly grownup lifters (52,215). The final lifting neighborhood additionally trains sure muscle teams rather more robustly than others, so common muscle proportions can meaningfully differ between lifters and non-lifters of comparable ages. For example, leisure lifters have exhibited shoulder inside rotation to exterior rotation power ratios which might be considerably higher than the overall inhabitants (1,99). Whereas neurological diversifications can contribute to this power ratio discrepancy, the lifters additionally most certainly have proportionally higher mass of the shoulder inside rotator muscular tissues relative to the exterior rotators, given the shut relationship between muscle measurement and power (4). The infraspinatus and teres minor (that are the 2 major shoulder exterior rotators) have been measured to have a mixed quantity that’s about half that of the pec main (a major shoulder inside rotator) within the common inhabitants (77,103). Nevertheless, lifters usually prioritize coaching their chests to a higher diploma than their rotator cuffs, so their pec majors are seemingly proportionally bigger on common. The general takeaway from this digression is that the forearm muscle measurement proportions we cowl all through this text could considerably differ from these within the lifting neighborhood. Within the absence of information on muscle proportions of skilled people, we nonetheless are nonetheless utilizing probably the most pertinent obtainable proof. Whereas the exact measurement comparisons will fluctuate amongst completely different populations, this variance won’t detract from the utility of the sensible purposes based mostly on this physique of proof.
The Forearm’s Finger Flexor Muscle mass
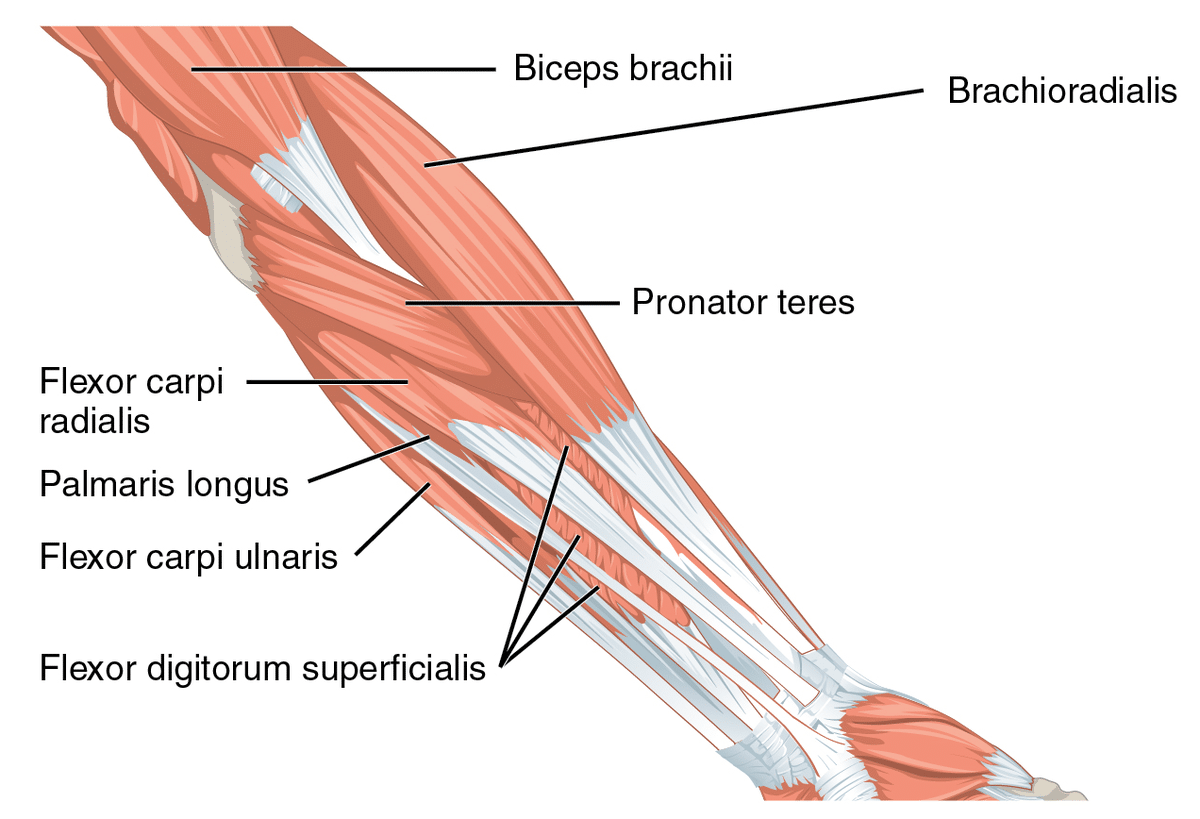
Lifters generally carry out wrist curl variations in an effort to enhance grip power, and carryover can certainly be achieved, however not from growing wrist flexion power immediately. The flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus all have significant wrist flexion second arms, which implies they’ve favorable leverage for producing wrist flexion torque (69,162). Consequently, they are often skilled with wrist curls alongside three different muscular tissues within the forearm’s anterior compartment (i.e., flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and palmaris longus) (69,162). Whereas all of those forearm muscular tissues have pretty related wrist flexion second arms, the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus are in a position to produce the vast majority of whole wrist flexion torque because of their measurement (69,77,162).
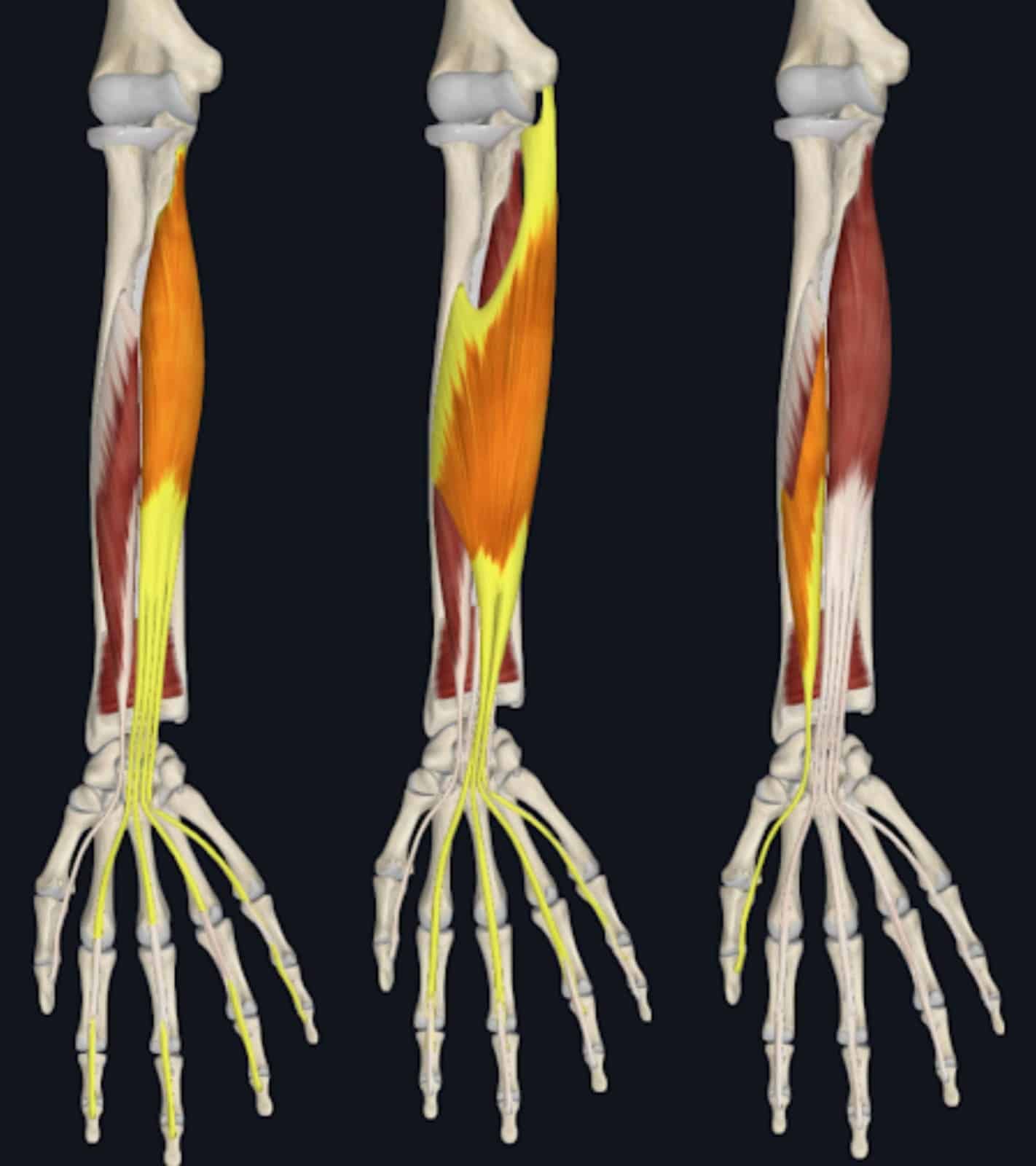

Relative to the flexor pollicis longus, these two muscular tissues generate significantly extra power on the wrist and finger joints as a result of their mixed cross sectional is about 4 to seven occasions higher (relying on the supply) (9,69,77). Consequently, a given proportion enhance within the power of those two muscular tissues may have a a lot higher absolute impact on grip power in comparison with if the flexor pollicis longus was strengthened by the identical proportion. Primarily because of this discrepancy in power manufacturing capability, I think about strengthening the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus to be much more necessary to enhancing grip efficiency than strengthening the flexor pollicis longus. Moreover, you should still proceed holding onto a bar throughout a help grip train even when your thumb slips off as long as your index by little fingers stay in touch with the implement. With this mentioned, the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus can all be strengthened concurrently throughout quite a lot of workouts, however I don’t deem all three of them to be equally impactful. Coaching these three muscular tissues by a wrist flexion train could switch to improved grip power in the identical means that coaching the hamstrings with a knee flexion train can switch to improved hip extension power (28). Hip hinges and leg curls should not related motion patterns, however coaching one in every of them can enhance your power within the different largely because of hamstring hypertrophy.
As I beforehand mentioned on Stronger By Science, I don’t anticipate that solely coaching a muscle with isometric workouts that by no means load the muscle at lengthy lengths is an optimum technique of inducing muscle hypertrophy. I’ve little doubt that performing varied pulling workouts and weighted carries can present a stimulus to the finger flexor muscular tissues to develop as much as a sure level provided that isometric coaching definitely can induce hypertrophy (114). Nevertheless, I’m extremely skeptical that this model of coaching by itself might maximize hypertrophy for these muscular tissues in the identical means that I doubt that hip flexion workouts (e.g., hanging leg raises) carried out with out dynamic trunk flexion are an optimum technique of rising the rectus abdominis. Muscle measurement doesn’t essentially equate to power, and a lifter can expertise vital power positive factors because of neural diversifications (154). Nonetheless, within the long-term, the power potential of a muscle group can’t be absolutely reached with out accruing extra contractile tissue. It ought to come as no shock that maximal grip power is strongly positively correlated with forearm muscle measurement (2,3,83,197). With this in thoughts, I strongly suggest performing workouts which might be properly suited to extend the dimensions of the finger flexor muscular tissues for those who prioritize growing grip power.


To my information, no examine has but to research whether or not coaching the finger flexor muscular tissues at lengthy peak muscle lengths can induce higher development than coaching them at reasonable to brief muscle lengths. This absence of analysis applies to most muscle teams within the human physique. Nevertheless, the obtainable physique of proof largely helps that coaching a muscle in a lengthened place generally is a notably efficient technique of inducing hypertrophy for quite a lot of muscle teams (93,94,117,125,210). Until new proof emerges indicating that the finger flexor muscular tissues are an exception to this development, I’d program workouts that practice them at lengthy lengths when striving to extend their measurement. Like three of the 4 hamstring heads, the finger flexor muscular tissues cross a couple of joint, so we have to account for the positions of a number of joints when figuring out the lengths at which they’re loaded throughout an train. The finger flexor muscular tissues work at relatively brief lengths when the wrist and finger joints are concurrently flexed in the identical means that the biarticular (i.e., crossing two joints) hamstrings are absolutely shortened ready of knee flexion and hip extension. On this shortened place, the muscular tissues can function in a state of energetic insufficiency the place power manufacturing is submaximal. When the wrist and finger joints are in prolonged positions, the finger flexor muscular tissues are elongated past their resting lengths in the identical means that the biarticular hamstrings will be absolutely stretched when the hip is flexed whereas the knees are prolonged.
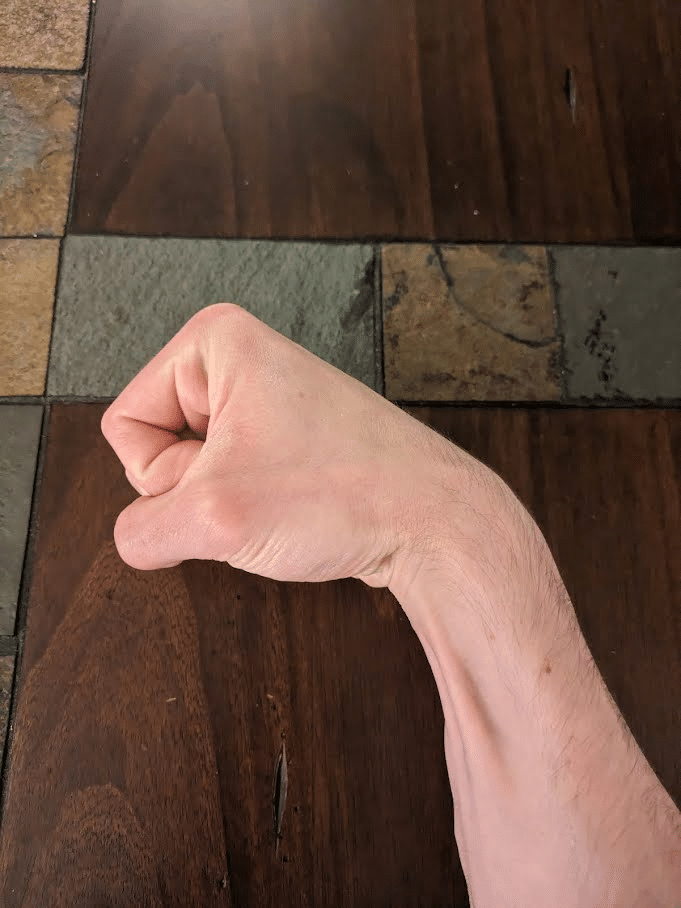



Wrist Curls and Hand Grippers
Throughout many help grip workouts akin to deadlifts and farmer’s walks, the finger flexor muscular tissues shall be frequently skilled at reasonably brief lengths given the flexed finger joints and impartial wrist place. With a regular wrist curl variation utilizing a instrument akin to a barbell or dumbbell, these muscular tissues will nonetheless be shortened on the finger joints, however they are often lengthened on the wrist because it extends throughout the eccentric part of the motion. When accounting for the wrist and finger positions, the finger flexor muscular tissues will be skilled at longer peak lengths than most help grip workouts, however they nonetheless won’t be loaded past reasonable lengths because of the flexed finger place.
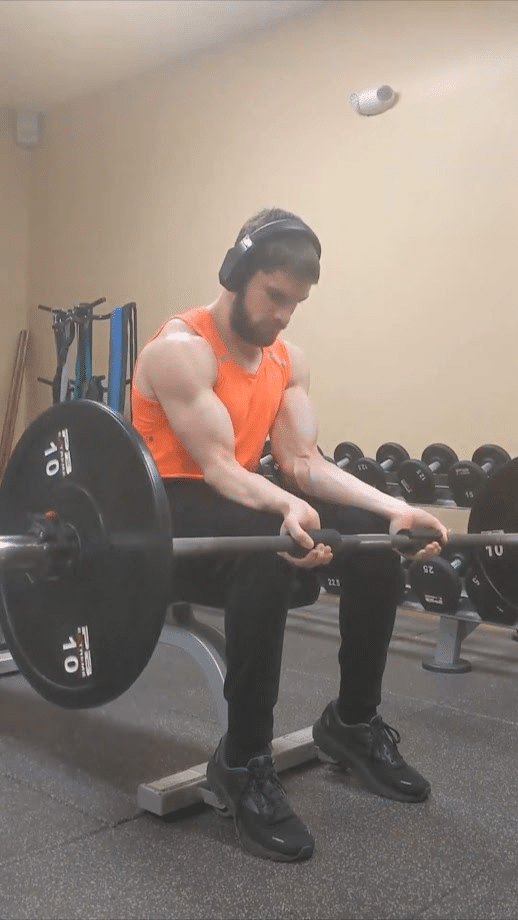


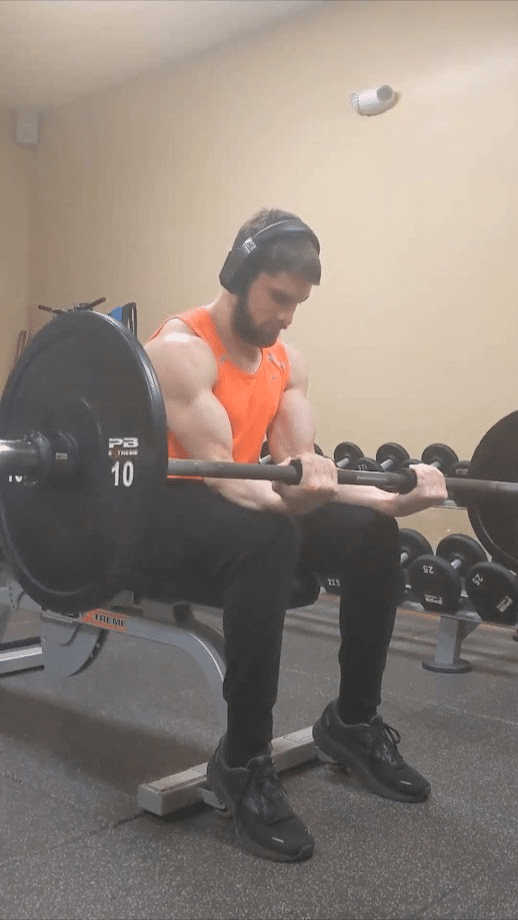
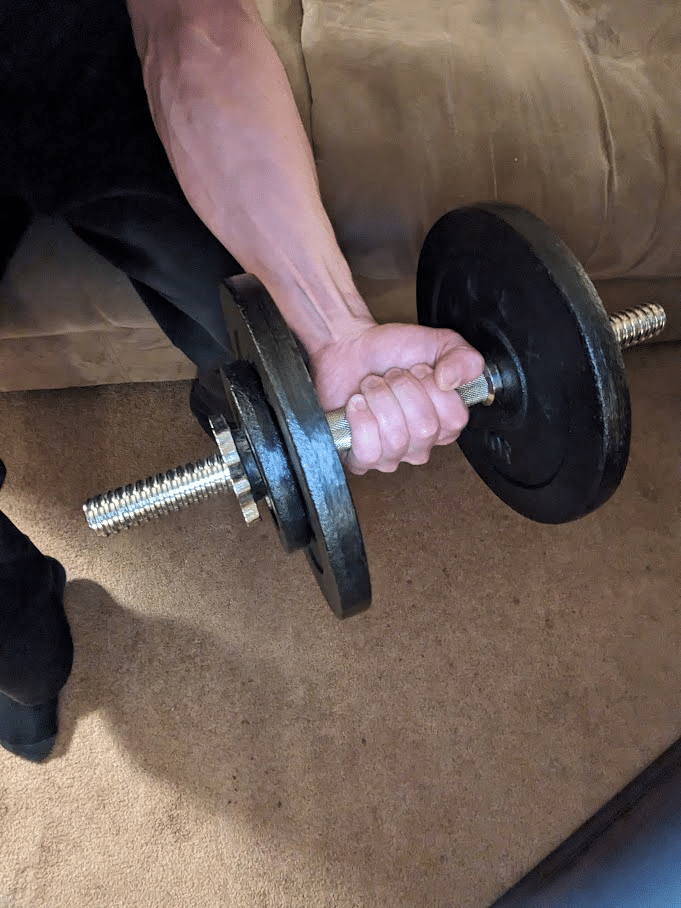
Alternatively, you may carry out a wrist curl variation the place your fingers dynamically lengthen (on the metacarpophalangeal joints) throughout the eccentric part because the implement rolls towards your fingertips and also you lengthen your wrist, permitting you to coach the finger flexor muscular tissues at longer lengths. To take care of management of the burden, you’d then flex your fingers across the implement throughout the concentric part as you flex your wrist. Doing so will mean you can practice the wrist flexion and metacarpophalangeal joint flexion capabilities of the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus concurrently in a dynamic method. The addition of metacarpophalangeal joint flexion may also mean you can practice the intrinsic hand muscular tissues that help the bigger forearm muscular tissues in performing this operate throughout gripping actions. With this modified wrist curl method, it is advisable be sure that the barbell/dumbbell doesn’t roll too far towards your fingertips to the extent that the burden slides out of your fingers. In comparison with the usual wrist curl method, you’ll require much less load with this variation to attain the identical issue as a result of the lever arm of the resistance performing on the wrist joint will increase because the implement rolls towards your fingertips.
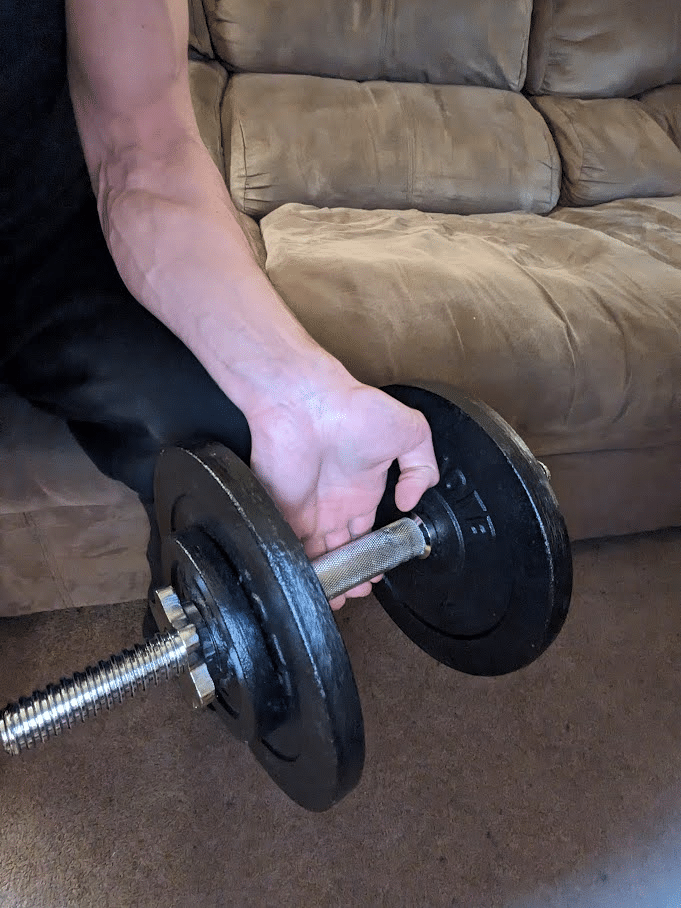



To amplify the stimulus per set offered to the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and intrinsic hand muscular tissues, I like to recommend that you simply carry out pure finger curl reps as soon as you may not carry out wrist curl reps because of fatigue. As a result of the lever arm of the burden performing on the metacarpophalangeal joints is shorter than the lever arm performing on the wrist, ending a set with these finger flexion reps basically acts as a mechanical drop set. This system is just like what I like to recommend for rowing variations to maximise the stimulus offered to the rhomboids and traps, the place you may carry out pure scapular retraction reps immediately after you may not carry out any extra rowing reps.
Past the potential to induce higher hypertrophy, performing wrist curl variations that stretch the flexor digitorum muscular tissues could present further mobility advantages for lifters who want to enhance their entrance rack positioning. When cleansing and entrance squatting, lifters require a significant quantity of wrist extension vary of movement with prolonged metacarpophalangeal joints to attain a secure clear grip entrance rack. To take action requires a enough diploma of flexibility within the flexor digitorum muscular tissues that could be missing for some lifters. Whereas static stretching definitely can be utilized to extend flexibility, loading muscular tissues in absolutely lengthened positions through resistance coaching can yield comparable flexibility enhancements (132,183).


Through the use of a hand gripper, you even have the flexibility to coach the finger flexion operate of the flexor digitorum muscular tissues in a dynamic method at longer lengths than might in any other case be achieved with most help grip workouts. With a hand gripper, you may preserve an prolonged wrist place that means that you can load these muscular tissues at reasonable lengths whereas concurrently coaching the smaller intrinsic hand muscular tissues that flex the carpometacarpal joints.


If I might solely carry out just a few units per week of a single accent train to enhance my help grip power for the deadlift over a mesocycle, hand grippers or wrist curls wouldn’t be my prime selections. Within the short-term, I’d anticipate a low quantity of extra particular workouts (e.g., heavy barbell holds) to be best in inducing the specified neural diversifications that may manifest extra quickly than hypertrophy (14,60). Nonetheless, decrease specificity train will be helpful because of the ease into which they are often added right into a program and dynamically practice finger flexor muscular tissues at favorable lengths whereas imparting minimal systemic fatigue. You’ll be able to practice with hand grippers in a number of various environments the place some other sort of grip coaching will not be possible, enabling you to accrue higher coaching volumes with out additional time commitments within the gymnasium. Whereas not as handy as grippers, wrist curls can readily be carried out throughout the remaining intervals of different workouts you already practice that don’t tax your grip. Alternatively, you may carry out wrist curls at house whereas watching TV you probably have a pair of sunshine dumbbells as a result of they don’t require a lot weight to be difficult to the working muscular tissues. Over time, the hypertrophy that may consequence from this technique of coaching could make a distinction in your long-term grip power potential. With this mentioned, I nonetheless suggest together with some heavy coaching with the exact sort of grip you prioritize enhancing to induce neural diversifications particular to that grip.
Fats Grip and Thick Bar Coaching
Together with hand grippers and wrist rollers, fats grip attachments that may be added to barbells, dumbbells, or pull-up bars are a number of the hottest grip coaching instruments. To my information, fats grip attachments initially turned extra extensively utilized when the aptly named Fats Gripz turned commercially obtainable in 2009 with a diameter of two.25” (57.15mm), doubling the everyday barbell diameter of 1.1” (28mm). At present, fats grip attachments are available in quite a lot of sizes, with diameters normally starting from 1.75” (44.45mm) to 2.75” (69.85mm). When fats grip attachments are added to barbell workouts, their utility is sort of just like an axle bar, which regularly has a 2.0” (50.8mm) diameter and is utilized in strongman occasions such because the axle bar clear and press. Whereas usually cheap in comparison with different specialty bars, most industrial gyms and residential gyms lack axle bars, and they’re nonetheless extra expensive than fats grip attachments with out the identical portability.




One of many major benefits of fats grip attachments is that they are often added to workouts you already carry out that use a help group however should not notably difficult to your grip power by the point you end the set because of fatigue in different muscle teams. For example, after I carry out dumbbell rows with a strict method, my grip will not be meaningfully fatigued by the point I end the set because of again muscle fatigue. Nevertheless, after I add fats grip attachments, my grip power is noticeably challenged by the point I end the set because of again muscle fatigue. If I want to additional amplify the grip coaching stimulus per set, I can merely carry out a static maintain till my grip power fails after finishing the rows. Doing so requires little further time as a result of my grip muscular tissues are already meaningfully fatigued from the fats grip rows. To make sure that I’m not compromising the stimulus offered to the again muscular tissues, I choose an train variation and kind of fats grip that permits me to carry out an analogous variety of reps with the fats grips as I’d be capable to do with out the fats grips. Doing so permits me to coach grip power extra successfully with out coaching different muscle teams much less successfully, due to this fact growing coaching effectivity. Assuming you’ve gotten different coaching objectives along with enhancing grip power, I’d suggest that you simply be considered through which workouts you determine so as to add fats grips as a way to not neglect different muscular tissues.
No less than two research (neither of which utilized chalk) have investigated how 1RMs for widespread workouts that use a help grip could also be affected by utilizing fats grip attachments or axle bars in comparison with a regular barbell. Krings et al (2021) assessed recreationally energetic males as they carried out 1RMs with a double overhand grip for the deadlift, bent over row, upright row, and biceps curl utilizing a regular barbell with or with out 2.2” (5.6cm) diameter fats grip attachments (102). Additionally they examined what number of body weight pull-ups may very well be accomplished in a single set as a grip endurance metric and reported that their individuals accomplished a median of 11 reps with out the fats grips however solely 3 reps with the fats grips. When utilizing the fats grips, the imply 1RMs of the deadlift, bent-over row, upright row, and biceps curl have been respectively 41%, 30%, 24%, and 5% decrease relative to utilizing the barbell by itself.
Krings et al moreover offered some information on how fats grips could affect muscle activation by measuring EMG activation for eight muscular tissues throughout the aforementioned workouts. A number of forearm muscular tissues (i.e., flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi ulnaris, and the extensor carpi radialis muscular tissues) have been assessed alongside the triceps, biceps, trapezius, and lateral head of the deltoid. For the biceps curl and upright row, EMG exercise didn’t considerably differ for any muscle when fats grips have been current or absent. Nevertheless, vital variations in sure muscular tissues have been current in numerous EMG outcomes for the opposite three workouts relying on whether or not fats grips have been used. For example, peak EMG exercise of the biceps was decrease when fats grips have been utilized to rows and pullups, whereas imply EMG exercise of the extensor carpi ulnaris was higher below these situations. With out delving too deeply into the nuances of the varied EMG findings, the principle takeaway is that fats grips can pose a commerce off through which elevated exercise of 1 muscle could also be accompanied by diminished exercise of one other muscular tissues throughout sure workouts.
Ratamess et al (2007) additionally examined the 1RMs of resistance skilled males as they carried out these 4 workouts along with the bench press and overhead press with barbells having a 1” (2.5cm), 2” (5.8cm), or 3” (7.6cm) diameter (163). For the 2 presses, the 1RMs with the three completely different bars have been related, and the 1RMs for the biceps curl and upright row have been additionally related with the 1” and a pair of” bars. Unsurprisingly, the best distinction occurred throughout the deadlift the place 1RMs have been 28% and 55% decrease when respectively utilizing 2” and three” bars in comparison with the 1” bar. As was the case for Krings et al, the bent-over row was the second most affected elevate, having 1RMs that have been 9% and 33% decrease when respectively utilizing 2” and three” bars in comparison with the 1” bar. When utilizing the three” bar, the 1RMs for the biceps curl and upright row have been additionally 18% and 26% decrease respectively in comparison with with the 1” bar.
The affect that thicker implements can have on the load that may be utilized for any specific train will definitely fluctuate amongst people and be influenced by somebody’s relative strengths, anthropometry, and method. Basically, lifters who’ve massive fingers and robust finger flexor muscular tissues relative to different muscle teams will have a tendency to have the ability to carry out a higher number of workouts with thick bars with out compromising how a lot load they will use (163). Utilizing a strict method that minimizes momentum and contributions from muscular tissues that you don’t prioritize strengthening with a given train may also enhance the breadth of train variations for which you should use fats grips with out worsening the stimulus offered to an train’s prime movers. For example, if I carry out a bent-over barbell row the place I management the eccentric part, have a short pause on the prime and backside of every rep, and preserve my knees and hips in a static place for the entire set, I can add fats grips with out sacrificing weight or reps. Nevertheless, if I carry out a “cheat row” the place I dynamically use leg and hip drive to maneuver the burden up every rep in an explosive method, utilizing fats grips or an axle bar will significantly restrict how a lot load I can use and make it a mediocre again train.
If you’re an skilled lifter, you could possibly subjectively assess how properly an train focused sure muscular tissues with or with out fats grips. Sensations will be troublesome to speak by phrases and might not be notably exact, however it may be very obvious to a skilled lifter when a muscle group is acutely focused by an train. Experiencing a burning sensation and a “pump” because of metabolite and fluid accumulation from reasonably high-rep units or a pronounced feeling of rigidity within the working muscular tissues throughout lower-rep units can point out which muscle teams a specific train could also be coaching successfully. Like localized muscular soreness that will manifest after coaching, these sensations will be helpful proxies to higher gauge how seemingly an train could also be offering a stimulus of a enough magnitude to induce adaptation in numerous muscular tissues. These proxies definitely have their limitations and must be utilized in live performance with different assessments when guiding programming choices, however I like to recommend being conscious of them when figuring out which workouts so as to add fats grips. In the event you expertise a notable burning sensation in your forearm muscular tissues when performing a 20-rep set of rows with fats grips however don’t really feel a lot in your again muscular tissues in distinction to while you row with out fats grips, the fats grips could seemingly be detracting out of your again coaching. Nevertheless, for those who really feel related sensations in your again muscular tissues whereas rowing with or with out the fats grips, this tradeoff between again and grip coaching is much less more likely to be current. When making these qualitative observations together with quantifying the variety of reps you may carry out with a given weight with or with out fats grips, it is best to be capable to decide if fats grips deleteriously have an effect on how properly completely different muscular tissues are focused throughout a specific train.
Apart from being added to workouts you already carry out (e.g., strict rows, curls, and shoulder raises) that focus on muscular tissues aside from these concerned with gripping, making use of fats grips to particular grip workouts gives distinct advantages. One such benefit is that fats grip workouts mean you can practice your finger flexor muscular tissues at longer lengths extra conducive to stimulating hypertrophy than when utilizing smaller diameter implements. With impartial wrist place help grip workouts akin to barbell holds and farmer’s walks, fats grips will nonetheless not allow you to coach the finger flexor muscular tissues on the identical lengths that may be reached throughout completely different workouts that load these muscular tissues in an prolonged wrist place. Nevertheless, the extra prolonged finger joint angles ensuing from the addition of fats grips means that you can practice these muscular tissues in additional lengthened positions that would in any other case be achieved when performing the identical workouts with smaller diameter implements.




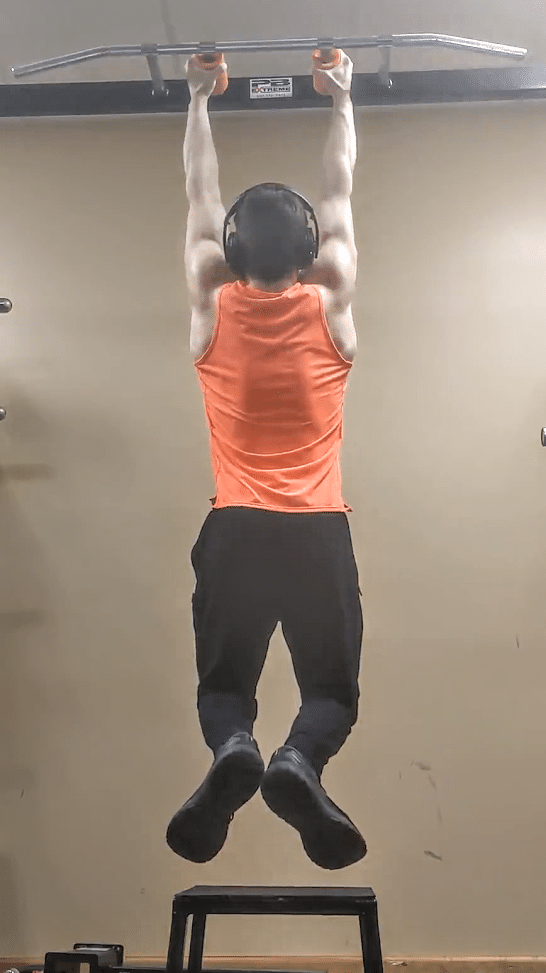

One other profit is that lighter weights shall be required to supply a grip strengthening stimulus when utilizing fats grips. After already performing deadlift and squat variations, a lifter whose deadlift is proscribed by grip power could decide to carry out barbell holds from an above-the-knee rack pull or block pull with the purpose of accelerating grip power particularly for the deadlift. Whereas not inherently injurious by any means, loading the lumbar backbone with compressive forces is a stressor that imposes a restoration value. Lifters who’re already experiencing excessive volumes of excessive magnitude compressing loading from their major lifts could favor to reduce additional spinal loading from their accent workouts. When utilizing a regular diameter barbell, a significant quantity of weight shall be required to carry out a maintain with at the least a reasonably excessive depth. If fats grips are used with these holds, noticeably lighter absolute hundreds shall be wanted and the train will nonetheless be pretty particular to gripping a barbell.
Whereas looking by the literature, I’ve recognized three research that in contrast the longitudinal results of coaching with or with out the two.25” diameter Fats Gripz. The power outcomes (e.g., pull-ups, deadlifts) of every of those research have been examined with normal diameter bars. Cummings at al (2018) assessed 10 Division 1 collegiate male golfers as they carried out three weekly full-body resistance coaching periods for eight weeks (45). In distinction to the management group coaching with out Fats Gripz, which didn’t expertise any enchancment, the Fats Gripz group considerably elevated drive distance and carry distance over the eight weeks. Related to lifters, entice bar deadlift 1RM, max pull-up reps, proper hand grip power, and left hand grip power have been additionally examined earlier than and after the interventions. With respect to the magnitude of results, the adjustments that occurred for these variables didn’t meaningfully differ between teams to any sensible diploma. Medina et al (2017) assessed 14 male collegiate lacrosse gamers who carried out three weekly coaching periods for 5 weeks, the place every session concerned three units to failure of pull-ups (126). Comparable will increase in grip power, max pull-up reps till fatigue, lat pulldown 1RM, and lacrosse shot velocity occurred in each the group utilizing Fats Gripz and the group not utilizing Fats Gripz for pull-up coaching. Moreover, Rogers (2016) assessed 13 feminine college college students who carried out two weekly typical double overhand deadlift periods for 4 weeks (166). Every session consisted of 25 reps distributed over 5-6 units, and individuals have been permitted to make use of chalk whereas coaching with or with out Fats Gripz. After the intervention, the Fats Gripz and management teams elevated imply deadlift 5RMs respectively by 29.8% and 39.0%. Peak crush grip power elevated by 11.0% within the management group however solely 3.6% within the Fats Gripz group.
When evaluating these three research collectively, fats grip coaching didn’t yield notably spectacular results on grip power in comparison with typical coaching. With out over-generalizing these findings, it’s cheap to say that the addition of fats grips to any train won’t essentially lead to superior grip power coaching. Nevertheless, it could be faulty to conclude that fats grip coaching can’t be a helpful part of a bigger program that goals to extend grip power. Every of the three aforementioned research utilized completely different populations (none of which have been power sport athletes) and had small pattern sizes, which is a limitation extraordinarily widespread in longitudinal resistance coaching analysis. As with numerous train variations, the potential utility of fats grip coaching is most certainly context dependent, and the three research in contrast coaching with solely fats grip workouts to coaching with none fats grip workouts. This “all or none” determination is cheap when designing a managed examine, however it doesn’t mirror actual world coaching packages. Additional analysis on this subject is required to attract firmer conclusions, however I’d be cautious about relying solely on fats grips for grip coaching simply as I’d be optimistic about their potential utility when sensibly included in a broader program.
Briefly digressing from fats grip coaching, the absence of axial compressive loading is a major purpose why useless hangs carried out on a pull-up bar are a helpful grip coaching train. Lifeless hangs mean you can improve your help grip power whereas concurrently decompressing the backbone and coaching overhead shoulder mobility with a extensively obtainable piece of apparatus. For people with pretty excessive grip power to body weight ratios who may have to hold bilaterally for some time to problem their grip power, unilateral hangs are a easy development that don’t require any further tools like a dip/pullup belt so as to add weights. When performing a unilateral cling, I like to recommend utilizing your ft or free hand to stability in opposition to one thing akin to a rack or doorway to maintain your physique from unintentionally rotating. With this system, the intent is to not press down into the thing in order to make the train simpler in your working facet (except you do want to regress the depth). Moderately, you should use your ft or free hand to merely preserve the beginning place you want to practice.




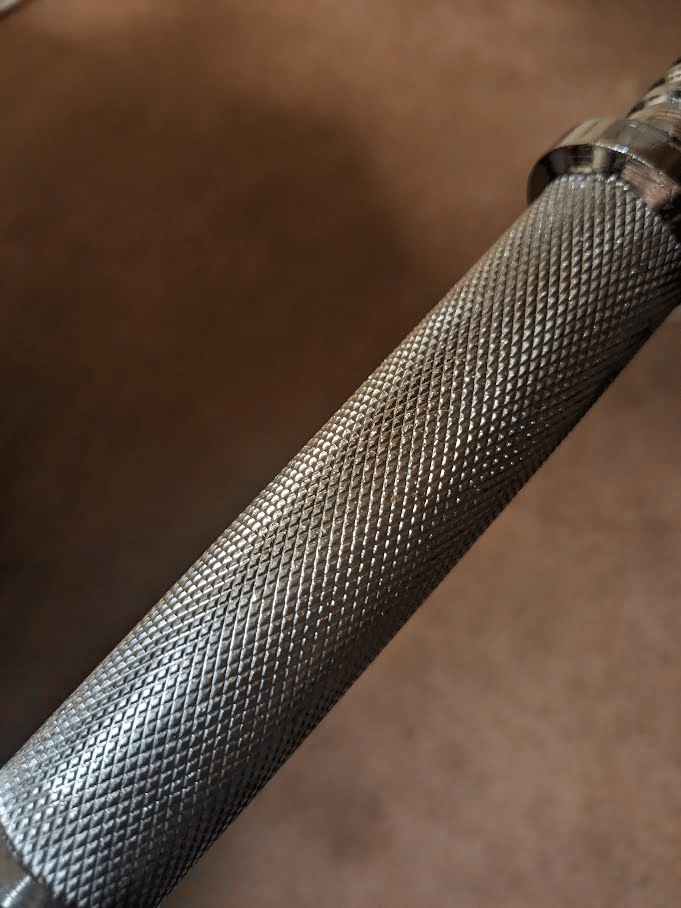
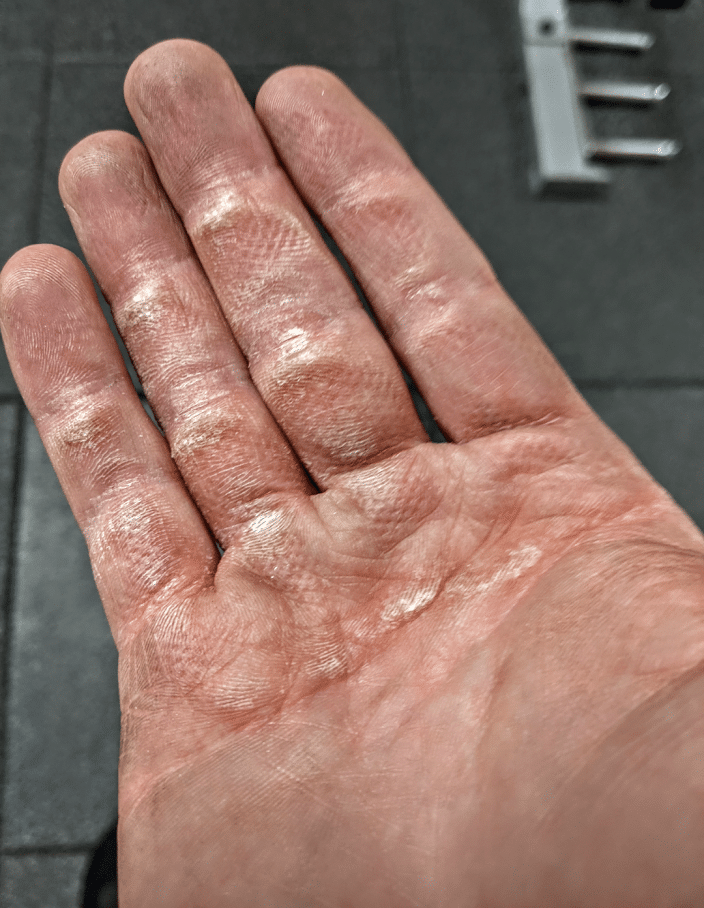
A part of what permits fats grip workouts to problem your grip power with lighter hundreds than normal barbells and dumbbells is the truth that fats grips lack knurling. The knurling discovered on barbells, dumbbells, and metallic pull-up bars makes gripping the implement significantly simpler relative to a clean floor. Even when utilizing a dynamometer, knurling facilitates considerably higher grip power in comparison with utilizing a clean floor (81). With a sure dosage of coaching with tools that has pronounced knurling, it is possible for you to to situation your pores and skin and develop calluses that shield your fingers. Nevertheless, your hand pores and skin can solely get better from a lot grip coaching with implements which have aggressive knurling earlier than you threat tearing a callus that may intrude together with your coaching and different every day actions all through the following week. After your hand pores and skin has been sufficiently harassed by coaching with tools that has knurling, you may proceed to coach your help grip power with a minimal threat of tearing a callus by utilizing fats grips which might be normally composed of rubber or silicone based mostly compounds.




Like fats grip implements, kettlebells generally lack knurling, and heavier kettlebells could have handles which might be thicker than typical barbells and dumbbells. These qualities will be advantageous for coaching your grip with workouts such because the suitcase carry, which is a very helpful loaded carry variation because of its capability to coach a lot of the core musculature and hip abductor muscles concurrently. Nevertheless, heavy kettlebells should not extensively obtainable, partly because of their excessive value, so extra skilled lifters could also be confined to performing longer length units with kettlebells that focus extra on grip endurance.
Pinch Grip Coaching
Whereas the effectivity of having the ability to modify many lifts you’re already performing into efficient grip coaching workouts is distinct to fats grip attachments, pinch grip workouts share a lot of their advantages with the added benefit that you don’t want to purchase specialised tools. If you want, you definitely can buy specialty units akin to pinch blocks, however you may practice the identical sort of train with extensively obtainable weight plates.
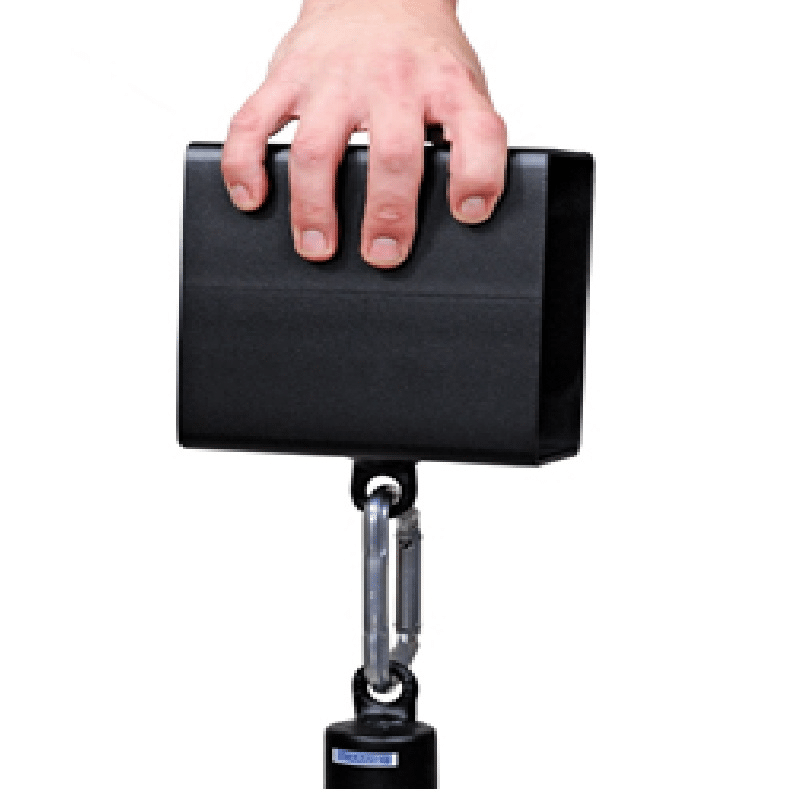


A wide range of completely different weight plates exist with various thicknesses and textures that can have an effect on how difficult greedy a specific load with a pinch grip shall be. With a thick rubber bumper plate, a single plate could also be sufficiently troublesome for a lot of lifters to carry with a pinch grip, whereas a number of plates could also be required if utilizing thinner iron plates or if an skilled lifter not finds a single 45lb (20.4kg) bumper plate to be difficult.
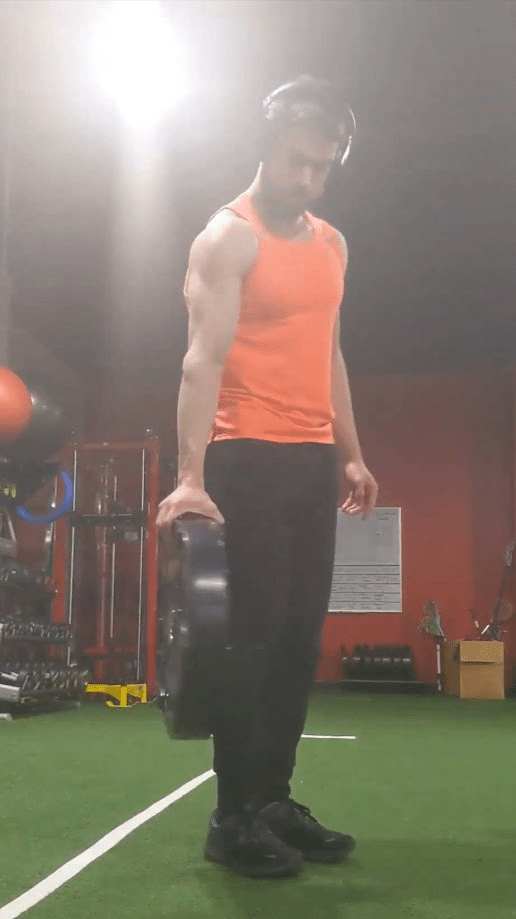
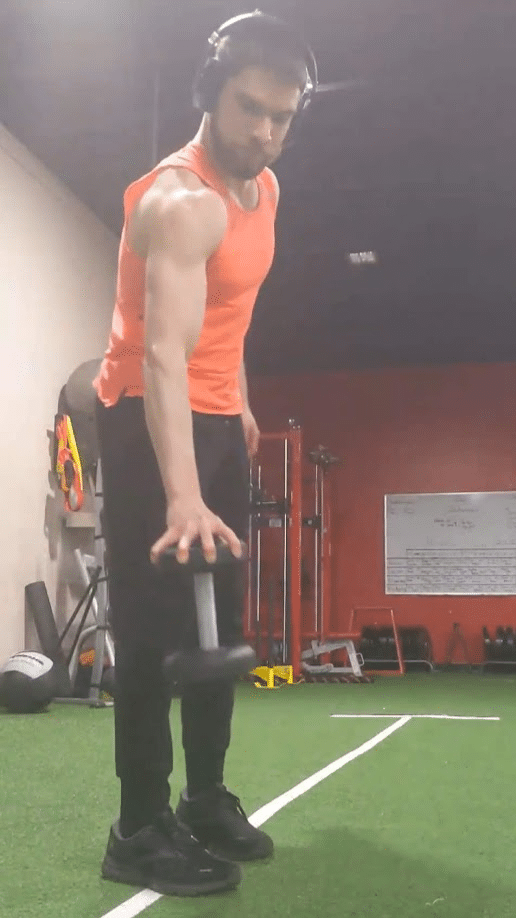




Pinch grip workouts can be carried out with a dumbbell by holding it together with your fingers unfold aside (i.e. kidnapped) round one finish of the burden as the opposite finish of the burden is directed towards the bottom. This open-hand pinch grip train is sort of humbling, and you may be restricted to utilizing gentle dumbbells that usually present no problem to your grip power when greedy their handles. As the burden of a dumbbell will increase, the issue of this train will assuredly enhance from the higher load, however the higher diameters that heavier dumbbells usually have relative to lighter dumbbells could make an much more profound distinction within the problem. Whereas hand measurement and finger size have an effect on efficiency in quite a lot of grip workouts, these morphological traits are notably impactful in dictating which dumbbells a person can use for this pinch grip train (59,64). You could have world-class grip power however be merely incapable of holding a 25lb (11.3kg) dumbbell on this method in case your fingers are bodily not lengthy sufficient to contact the edges of the burden. Along with fastened load dumbbells that enhance in diameter as they enhance in weight, adjustable plate loaded dumbbells might also be used for this pinch grip train with the best setup.
When an adjustable plate-loaded dumbbell is often loaded with a lightweight weight, the sleeve could prohibit you from greedy the plate. Nevertheless, for those who apply a collar to 1 finish whereas leaving sufficient area between the shaft and the collar earlier than including a weight plate and one other collar, the sleeve could not stop you from greedy it with an open-hand pinch grip. When performing a pinch grip train with both a dumbbell or a plate with a raised lip, a delicate shift in finger place can meaningfully affect how troublesome holding a given weight shall be. Greedy the dumbbell together with your distal phalanges immediately on the edges of the burden with out the center phalanges contacting the burden shall be most difficult. Holding the dumbbell inside your distal interphalangeal joints such that your distal phalanges are nearer towards the underside floor whereas your center phalanges wrap across the prime side of the facet floor shall be comparatively easier. Equally, a plate pinch train shall be simpler if you’ll be able to wrap your distal phalanges below a plate’s raised lip relative to in case you are holding onto the flat floor.
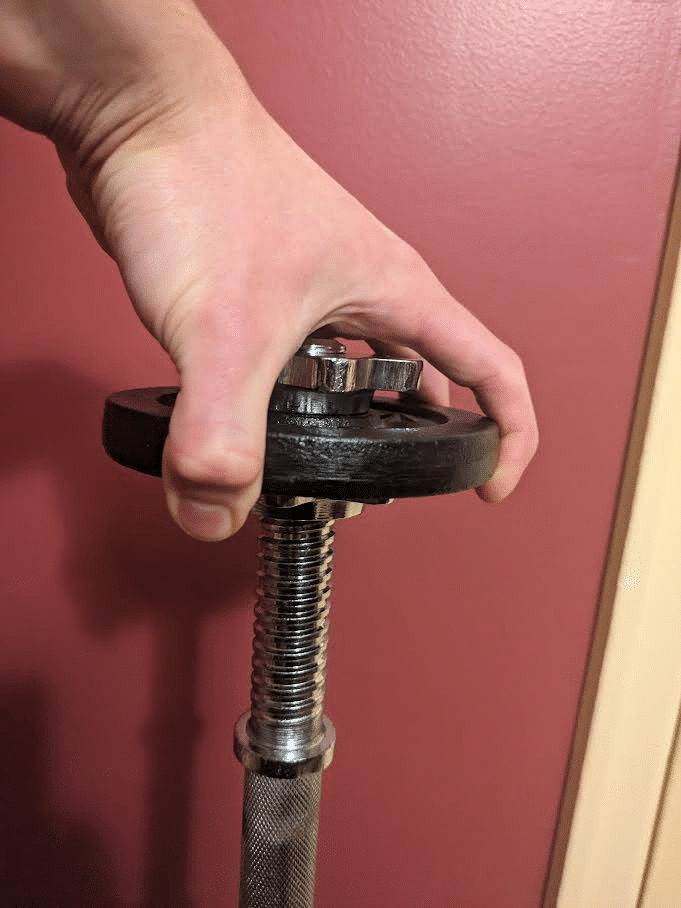
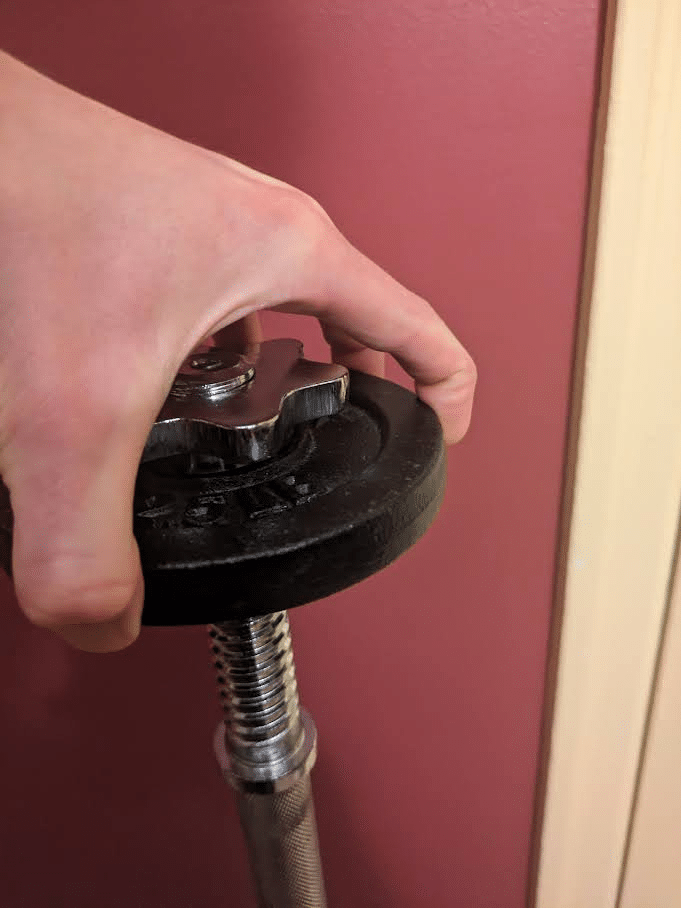




Relative to most help grip workouts with normal diameter shafts, pinch grip workouts will impart decrease axial loading, stress the hand pores and skin to a lesser diploma, and practice the finger flexor muscular tissues at longer lengths. These three qualities are exhibited by many fats grip workouts, however they are often much more exaggerated with pinch grip workouts, particularly with the aforementioned dumbbell variation. Nevertheless, relative to fats grip workouts, pinch grip workouts should not as particular to enhancing help grip power, and their capability to boost different attributes in addition to grip power are rather more restricted given the train variation constraints.
When incorporating pinch grip train right into a program with both a plate or a dumbbell, integrating it right into a unilateral carry is a high quality choice if enough area is out there. Given its load constraints, any such carry won’t present the identical stimulus to the core or higher again muscular tissues {that a} heavy dumbbell suitcase carry can. Nonetheless, brisk strolling is helpful in its personal respect for growing vitality expenditure and offering common well being advantages, notably in case your gymnasium exercise is your important type of bodily exercise in an in any other case pretty inactive day (96,201). When performing units of pinch carries till grip fatigue, the unilateral variation could assist scale back the chance of dropping a weight in your foot. With the pinch grip, a slight downward motion of the burden as fatigue and/or sweat accumulates could cause the burden to begin quickly slipping out of your hand. If this occurs, having a free hand means that you can information that weight to the bottom in order that it doesn’t unintentionally drop. Having any perspiration in your fingers can negatively have an effect on efficiency for any sort of grip train, however its impact is disproportionately higher for pinch grip workouts which might be completely reliant upon how a lot friction power you generate. Consequently having a towel to dry your fingers and/or chalk could make a substantial distinction you probably have been working up a sweat throughout your session.
Wrist Extension Train




Relative to the beforehand lined grip workouts, the advantage of wrist extension train for somebody who needs to enhance grip power will not be notably intuitive. Not one of the wrist extensor muscular tissues operate as finger flexors like three of the wrist flexor muscular tissues do. Nevertheless, growing wrist extension power can nonetheless switch to improved grip power as demonstrated by a resistance coaching intervention that Shiomose et al (2011) carried out. After assessing baseline grip power, the researchers assigned 13 untrained topics to carry out one set of wrist extension workouts 5 occasions per week for eight weeks with their proper fingers whereas their left fingers served as controls (180). Every set concerned 30 two-second isometric wrist extension reps with an depth equal to 70% of the topic’s maximal voluntary contraction output, two-second inter-rep relaxation intervals, and a impartial wrist place (which was the identical place the place wrist extension power was additionally examined). After the intervention, imply maximal gripping power elevated within the skilled limb by 19.2% and maximal wrist extension power elevated by a formidable 90.9%. For power athletes, it’s value noting that grip power was examined throughout this examine with a circumference of 6.1” (155mm), which is bigger than the three.6” (91mm) circumference of the everyday barbell.
The wrist extensor muscular tissues will help the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus function at favorable muscle lengths the place they will generate maximal finger flexion power (184). Power is actively produced by a muscle by the cyclic formation of actin-myosin cross bridges inside its sarcomeres, that are the purposeful models of its muscle fibers. Relative to reasonable lengths, fewer cross bridges can kind at brief lengths, so energetic power manufacturing is submaximal in a shortened sarcomere place.
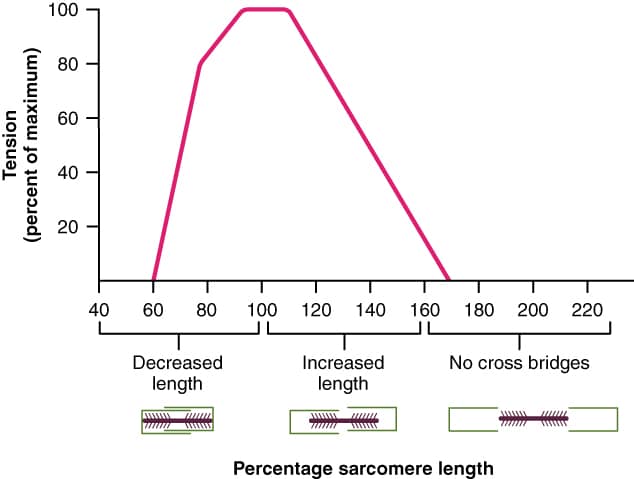

If the wrist maintains a impartial place when the fingers are in a flexed place, the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus are shortened and consequently won’t be able to generate maximal power. Given this relationship, maximal grip power is often produced in an prolonged wrist place, which analysis has usually discovered to be about 20-45° past impartial (112,143,180). Because the diameter of the implement that somebody grips will increase, the optimum wrist angle for producing grip power tends to be much less prolonged (143). This seemingly happens as a result of thicker implements will enable the extrinsic finger flexor muscular tissues to function at longer lengths in comparison with thinner implements. When making a fist as forcibly as you may, you’ll seemingly discover that your wrist naturally strikes into this mildly to reasonably prolonged place. In the event you initially flex your wrist earlier than making a fist, it’s evident that grip power is submaximal on this place.
Sustaining the optimally prolonged wrist place throughout an intense crush gripping effort will not be essentially a straightforward feat as a result of the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus generate wrist flexion torque as they flex the fingers. General these three muscular tissues have related leverage on the wrist joint because the wrist extensor muscular tissues do (69). Nevertheless, their cross sectional space is bigger than the entire wrist extensor muscular tissues mixed primarily because of the measurement of the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus (69). Compounding this measurement distinction, solely a number of the wrist extensor muscular tissues are properly suited to help with gripping since over half of the wrist extensor muscular tissues additionally operate to increase the fingers (62). Maximally activating the finger extensor muscular tissues whereas gripping could be biomechanically inefficient as a result of their power would partially be counteracting finger flexion power.




A number of muscular tissues contribute to wrist extension, however solely the extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, and extensor carpi ulnaris can meaningfully accomplish that with out inadvertently producing finger extension torque (17,62,69). Collectively, the cross-sectional space of those three muscular tissues is lower than half that of the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus mixed (9,69). Consequently, these three wrist extensor muscular tissues will be fairly challenged in sustaining probably the most advantageous wrist place throughout a maximal crush grip bout. If these three muscular tissues are weak, somebody could depend on higher contributions from the opposite wrist extensor muscular tissues (which additionally lengthen the fingers) to maintain the wrist prolonged whereas crush gripping, which might lead to decrease grip efficiency because of their actions on the fingers. Earlier than and after the intervention, Shimose et al measured EMG exercise of the extensor carpi ulnaris and extensor carpi radialis muscular tissues throughout maximal gripping and located their exercise to extend considerably. In distinction, EMG exercise of the extensor digitorum (which capabilities as an extensor for each the wrist and fingers) whereas gripping didn’t enhance following the intervention.
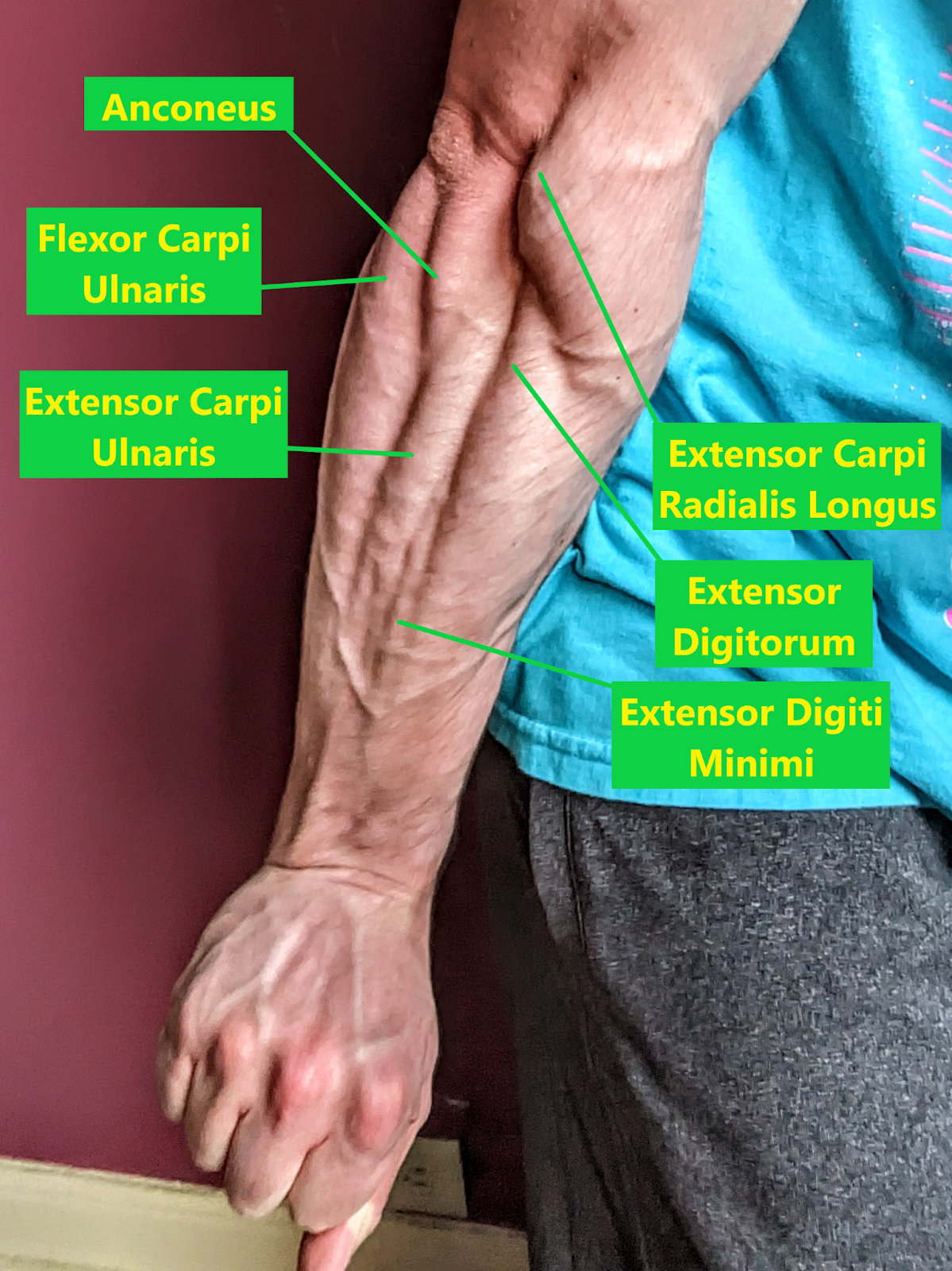

In gentle of the findings from Shiomose et al (2011), it’s fairly believable that wrist extension train can switch to improved grip efficiency, however the diploma of carryover seemingly varies relying on the kind of gripping. Past measuring grip power, the researchers additionally measured “grip power” as a definite variable, which I initially discovered complicated. Grip power was measured with a tool referred to as a piezosensor at 16 completely different fastened wrist positions in 10° increments starting from 70° of flexion to 80° of extension. Of those 16 power measurements, the best was thought-about to be maximal grip power. Typically, grip power and “grip power” are used as interchangeable phrases, however the researchers moreover examined “grip power” with a dynamometer the place individuals used whichever wrist place they freely chosen. Whereas the distinction reached statistical significance, “grip power” solely elevated by 1.4% after 8 weeks of coaching in distinction to the 19.2% enhance in “grip power.” From my interpretation of the textual content, the authors didn’t focus on any potential reasoning underlying this discrepancy.
Probably, individuals could have self-selected wrist positions the place their grip power was submaximal throughout “grip power” testing with the dynamometer. Based mostly on the graphical depiction of how individuals’ grip power assorted with wrist angle, it’s obvious that the wrist extension coaching yielded the smallest results in wrist positions that have been very prolonged or flexed. If individuals self-selected wrist positions that have been suboptimal for producing grip power, they could have did not see a lot of a change in “grip power” with the dynamometer. If this occurred, the values for “grip power” wouldn’t have mirrored the individuals’ maximal potential grip power that would have in any other case been measured with the wrist nearer to a impartial place.
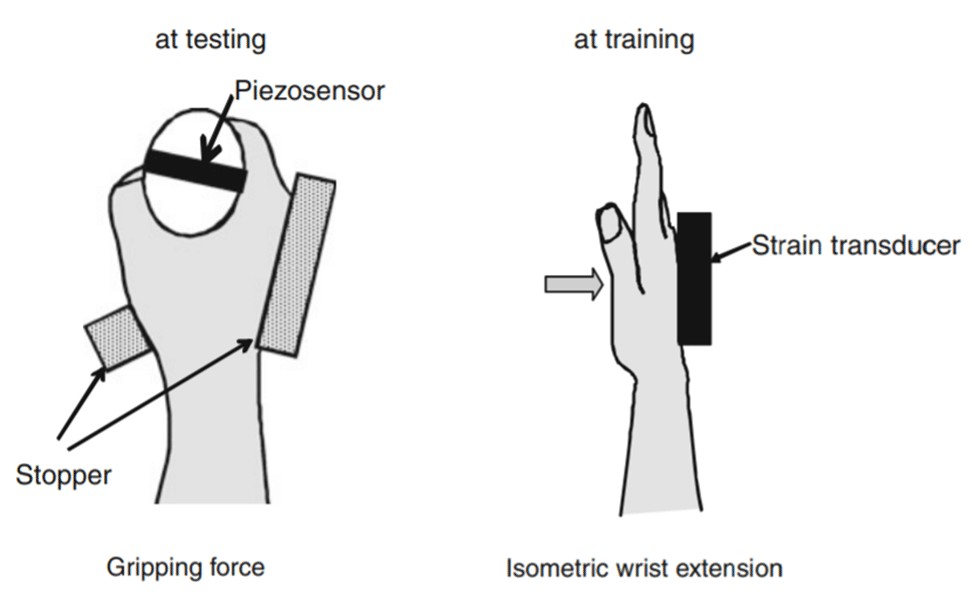


When interested by potential carryover to a heavy help grip train just like the deadlift, it’s worthwhile to contemplate the constraints it imposes on wrist place. Given the gravitational forces performing on the load being lifted, it merely will not be possible to keep up an prolonged wrist place to any notable diploma throughout any such gripping train. In distinction, the wrist is free to maneuver into an prolonged place the place the finger flexor forearm muscular tissues could generate most grip power throughout a crush grip train, which isn’t resisted by gravity. Consequently, I deem the grip power adjustments examined by Shiomose et al (2011) with wrist place constraints to be extra related to help grip carryover than the “grip power” that was examined with out wrist constraints. From the determine revealed of their article, it’s clear that the wrist extension coaching intervention elevated grip power in a impartial wrist place. Whereas the distinction didn’t attain statistical significance because of significant inter-subject variability, the imply wrist place the place maximal gripping power was produced additionally shifted from 34° to 25° of extension. For people who want to categorical maximal grip power in heavy help grip workouts, this development towards a impartial wrist place for producing max grip power is advantageous. As depicted by the determine above from Shiomose et al (2011), imply grip power was fairly related when examined from 0-50° levels of wrist extension after the intervention. Whereas we beforehand lined the mechanism by which wrist extension coaching can switch to grip power with out wrist place constraints, it’s presently unclear to me particularly how carryover happens to gripping when the wrist positions are fastened. With constrained wrists, the manufacturing of wrist extension torque can not affect the size rigidity relationship of the finger flexor forearm muscular tissues. Extra stays to be investigated about how wrist extension coaching could switch to grip efficiency, however its potential worth is promising nonetheless.
If strengthening the wrist extensor muscular tissues can contribute to enhanced grip power, fatiguing them ought to acutely impair grip power, which is what Souza et al (2017) reported to happen (186). Of their examine, individuals examined their maximal crush grip power with a dynamometer earlier than and after performing a set of wrist extension workouts loaded with 75% 1RM till fatigue. In distinction to if dumbbells or barbells have been used, the individuals carried out wrist extension train with a strap that circumvented the necessity to grip the burden, which might have in any other case immediately induced some finger flexor muscle fatigue. Following the wrist extension train, crush grip power was 16% decrease than beforehand, offering additional proof in help of how the wrist extensor muscular tissues contribute to grip power.

Forearm Muscularity
The main focus of this text has been on enhancing grip power for efficiency, however the strategies mentioned can be immediately related to lifters who merely want to simply visibly look extra muscular. Aside from the face and neck muscles, the forearm muscular tissues are seen extra usually than almost some other muscular tissues within the physique since they are often immediately seen when sporting a short-sleeve shirt. Relative to some other wrist or hand motion, wrist flexion train will practice the best quantity of muscle mass, so I think about wrist curls to be probably the most environment friendly sort of train for enhancing forearm muscularity. Wrist extension train can also be helpful for this goal, however its capability to stimulate will increase in whole forearm mass shall be decrease because of the measurement discrepancy between the muscular tissues within the anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm. Growing the dimensions of the wrist flexor muscular tissues by 50% would add roughly as a lot muscle mass as doubling the dimensions of the wrist extensor muscular tissues (9,69). Nonetheless, wrist extension train is sort of simple so as to add right into a program as a minimally fatiguing antagonist superset with wrist curls, whether or not carried out at a gymnasium or at house with reasonably gentle dumbbells. With an antagonist superset, you’d carry out a set of wrist extension train instantly after finishing a set of wrist curls or vice versa. These workouts can be readily included into non-competing big units (performing three or extra units of distinct workouts in succession that practice completely different muscle teams) with different accent workouts to extend your time effectivity. Each time we think about including new workouts into an current program, time constraints have to be thought-about so use of non-competing big units is a method I strongly suggest using for quite a lot of different muscle groups.
As with hand grippers, I like to recommend initially utilizing hundreds for wrist workouts that mean you can practice in a reasonable to reasonably excessive rep vary, akin to someplace throughout the span of 10-25 reps per set. Throughout every rep, you’re solely shifting the burden a small distance in comparison with most different workouts, and a few people could expertise wrist discomfort in the event that they load their wrists in deep ranges of wrist flexion and extension with greater hundreds if they don’t seem to be accustomed to doing so (36,97). Nevertheless, a relatively big selection of reps can induce related hypertrophic responses on a per set foundation if units are taken sufficiently near failure, so be at liberty to check out completely different rep ranges (173). Whereas deciding on weights for wrist flexion and extension workouts, it’s value noting that wrist extension power has been measured to be 57-60% of wrist flexion power on common (46,121,216). When performing wrist flexion and wrist extension train supersets, you should use the identical dumbbells for every for those who practice flexion within the greater finish of the 10-25 rep vary and extension within the decrease finish. Alternatively, you may simply use completely different dumbbell hundreds for supersets, however that will not all the time be sensible in a busy gymnasium the place it’s a must to share tools or time-efficient if utilizing a pair of plate-loaded dumbbells at house.
With respect to coaching quantity, your proximity to failure per set, relaxation intervals, train choice, sleep, weight loss plan, genetics, intercourse, stress ranges, and up to date coaching historical past could all affect what number of units per week are optimum for inducing muscle hypertrophy. For some populations, low quantity coaching can induce vital hypertrophy, however coaching quantity reveals a dose-dependent optimistic relationship with muscle hypertrophy as much as a sure level (174). The place that time lies for you as a person will not be essentially simple to find out, particularly since optimum volumes could differ amongst muscle teams and alter over time even throughout the identical individual. As coaching volumes rise, in addition they impart diminishing returns on hypertrophy, so loads of lifters could not favor to take a position disproportionate time coaching to chase that more and more small profit that separates fairly efficient from optimum. With all of this mentioned, performing at the least 10-12 high quality units per muscle group divided over 2-3 periods is a smart strategy for muscle teams that you simply prioritize growing based mostly on the obtainable information (18,174).
Nevertheless, relative to what number of muscular tissues within the human physique lifters could want to develop, the analysis investigating the connection between quantity and hypertrophy is pretty restricted. Along with measurements of adjustments in full physique lean mass, research have investigated the quads, triceps, biceps, hamstrings, and trapezius (with the latter two muscle teams having very restricted analysis) (18,174). To my information, no analysis has assessed how hypertrophy of any forearm muscular tissues is affected by coaching quantity as is the case for many muscular tissues. Past any potential variations in how these muscular tissues could reply to quantity in comparison with these which have been studied, quantifying coaching quantity generally is a problem for the forearm muscular tissues that operate as finger flexors. These muscular tissues could also be fairly energetic throughout many workouts, and we merely lack any proof that would inform us about how effectively isometric gripping workouts can develop these muscular tissues. Whereas the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus represent a significant proportion of whole forearm muscle mass, the finger flexor muscular tissues nonetheless don’t comprise the vast majority of forearm muscle mass (31).
In the event you prioritize growing forearm muscle measurement for the aim of getting extra visibly muscular forearms and would not have grip power objectives, I’m unaware of any benefit that gripping workouts have over dynamic wrist workouts. When wrist curls are carried out with the beforehand mentioned finger flexion method, they are going to practice the entire finger flexor muscular tissues concerned with gripping workouts along with different forearm muscular tissues solely successfully skilled with wrist workouts. Gripping workouts could yield greater activation of the wrist extensor muscular tissues than wrist curls, however I’ve little doubt that any sort of train can develop these muscular tissues extra successfully than direct wrist extension train (129). With this mentioned, gripping workouts can definitely serve a task in a program for somebody who strives to induce forearm muscle hypertrophy with out caring about grip power. Particularly within the long-term, train selection will be psychologically refreshing and show you how to get pleasure from coaching. Using wrist flexion and extension workouts is simply probably the most direct approach to enhance forearm muscle measurement. Progressing to 10-12 weekly units of wrist flexion and extension train could also be an easy means to make sure that a lot of the forearm musculature receives a strong hypertrophic stimulus no matter what else is in your coaching program. Will increase in forearm muscle measurement will be achieved with decrease volumes, however the aforementioned set vary (divided over 2-3 weekly periods) is an affordable goal for those who actually prioritize growing forearm muscularity.
The Remainder of the Forearm
Given {that a} clear majority of the muscular tissues within the forearm both operate as a flexor or extensor of the wrist, performing a mix of wrist flexion and extension train will practice a lot of the forearm musculature. Nevertheless, 5 muscular tissues throughout the forearm, which collectively have a complete mass shut to 1 quarter of the entire forearm muscle mass, don’t cross the wrist joint and consequently won’t be skilled by wrist workouts (10,31). One in all these muscular tissues is the anconeus, which lies slightly below the place the distal triceps tendon inserts on the bony prominence behind your elbow generally known as the olecranon. The small anconeus constitutes about 2.5% of the forearm’s muscle mass and assists the triceps in extending the elbow along with serving a task in stabilizing the elbow joint (10,31). Resulting from its operate, any elbow extension train you employ to coach your triceps may also practice your anconeus.
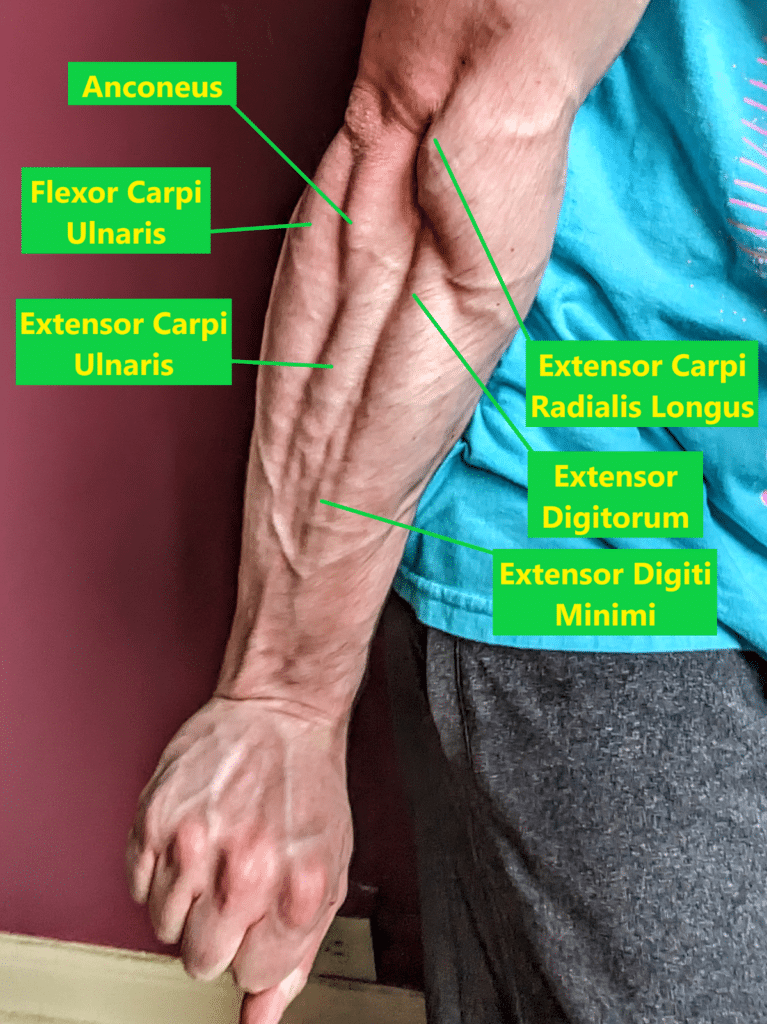

The biggest of the muscular tissues that don’t cross the wrist is the brachioradialis, which has the best peak second arm for producing elbow flexion torque of any muscle within the physique (10,57,136,137,138). Consequently, it capabilities as a major elbow flexor together with the biceps and the brachialis, which each have higher muscle volumes and cross sectional areas than the brachioradialis (10,137). All three of those muscular tissues shall be skilled with any train that meaningfully resists elbow flexion akin to variations of curls, vertical pulls, and (to a considerably lesser diploma) rows (68,119). In comparison with utilizing a supinated grip, I’ve beforehand heard lifters and researchers advocate that the brachioradialis will be skilled to a higher diploma with a impartial grip (e.g., hammer curl) when performing elbow flexion workouts (49,75). Some biomechanical analysis does point out that the biceps has a mildly higher elbow flexor second arm with a supinated forearm in comparison with a impartial forearm at sure elbow joint angles, however the identical applies to the brachioradialis, which might nonetheless have higher elbow flexion leverage than the biceps with any forearm place (10,139). EMG research, which has its limitations, has additionally indicated that the brachioradialis reveals related and even higher activation when performing curls with a supinated grip in comparison with a impartial or pronated grip (27,37,40,66,105,106,190). Whereas new proof could emerge sooner or later suggesting in any other case, I’m not presently below the impression that impartial grip workouts are superior to supinated grip workouts for growing the brachioradialis.
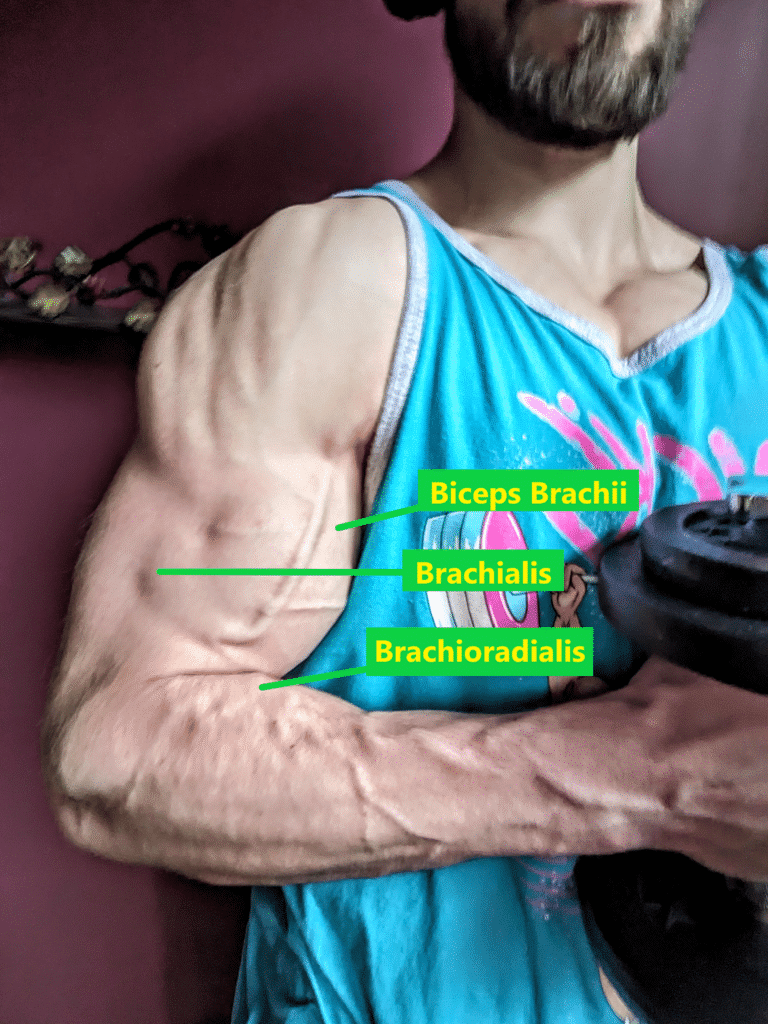



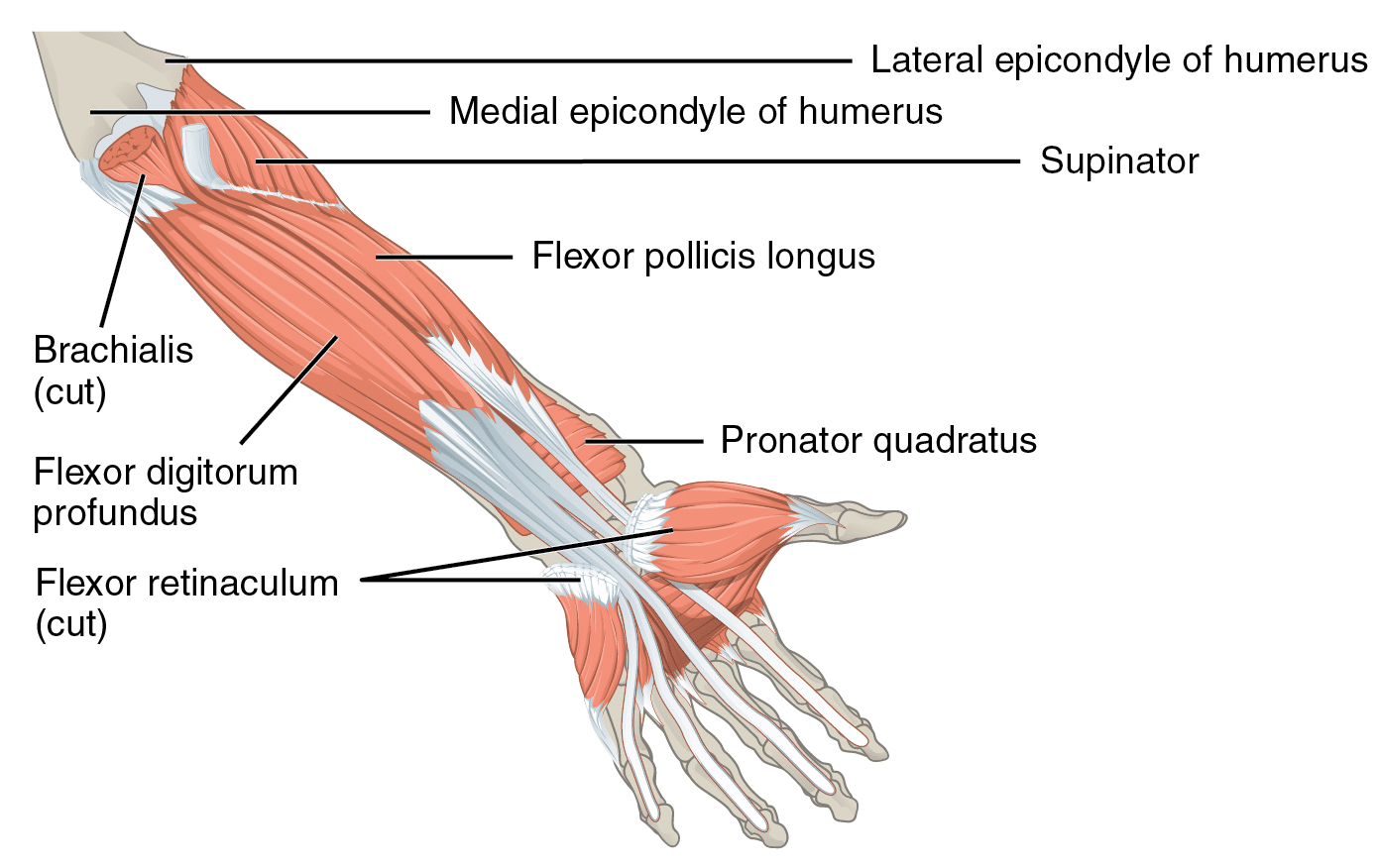

The forearm moreover incorporates the supinator, which capabilities as a major forearm supinator together with the biceps, in addition to the pronator teres and pronator quadratus, which each operate as major forearm pronators (32,57,70,73,139). To variable levels, different beforehand mentioned forearm muscular tissues secondarily help with supination and pronation, however they’ve higher leverage to carry out completely different actions akin to wrist flexion or extension (32,57,69,73,139,162). Elbow flexion workouts will practice the biceps (and to a lesser diploma the pronator teres), however folks hardly ever carry out workouts that immediately resist pronation and supination (162,190). Consequently, the first forearm pronators and supinators might not be notably properly developed for a lot of lifters apart from the biceps. By way of aesthetics, their lack of growth wouldn’t be simply detected since collectively they contribute to a little bit over 10% of the entire muscle mass contained throughout the forearm and hand (31). Apart from arm wrestling, pronation or supination power can also be unlikely to have a direct affect on efficiency in most power sports activities. Given the shortage of analysis on the subject, I can’t declare that performing pronation or supination workouts will scale back the chance of sustaining any harm, however it’s biologically believable that these workouts can improve energetic joint stabilization and the load tolerance of tendons. For example, the pronator teres could help the wrist flexor muscular tissues and ulnar collateral ligament in stabilizing the elbow joint (which is especially related to baseball pitchers), and its tendon is usually concerned with golfer’s elbow (84,147,151,176,200,208).
In the event you want to carry out pronation or supination train, an asymmetrical weight is a great tool for doing so. An adjustable dumbbell with plates loaded solely on one facet, a sledgehammer, or a bat can be utilized to coach dynamic pronation and supination in an alternating vogue the place you cyclically transfer from full pronation to full supination. On common, supination power exceeds pronation power, so that you’ll most certainly fail the pronation half of this train earlier than the supination half (12). To coach the supinators as successfully because the pronators, you may merely end the set with pure supination reps by alternating between pronated and impartial positions. Since there are significantly extra impactful workouts that advantage a higher proportion of coaching time, I’d usually suggest treating pronation and supination workouts like different commonly neglected movements for those who decide to coach them. Performing 1-2 units twice per week must be enough to reap the potential advantages of those workouts in a time-efficient method except you’ve gotten a extra particular want (e.g., are a aggressive arm wrestler or are rehabbing an harm).




As talked about within the wrist anatomy passage, the wrist joint allows radial deviation (AKA abduction) and ulnar deviation (AKA adduction) along with flexion and extension, which we already mentioned intimately. Like forearm pronation and supination, radial deviation and ulnar deviation workouts will be skilled with an asymmetrical weight, akin to a hammer or an adjustable dumbbell loaded solely on one facet. Alternatively a band could also be used for wrist deviation train. Unsurprisingly, a mix of radial deviation, ulnar deviation, wrist flexion, and wrist extension workouts can successfully practice extra forearm muscular tissues than solely utilizing wrist flexion and extension workouts. Nevertheless, the addition of wrist deviation workouts gives notably diminishing returns because of the overlapping wrist capabilities exhibited by forearm muscular tissues.
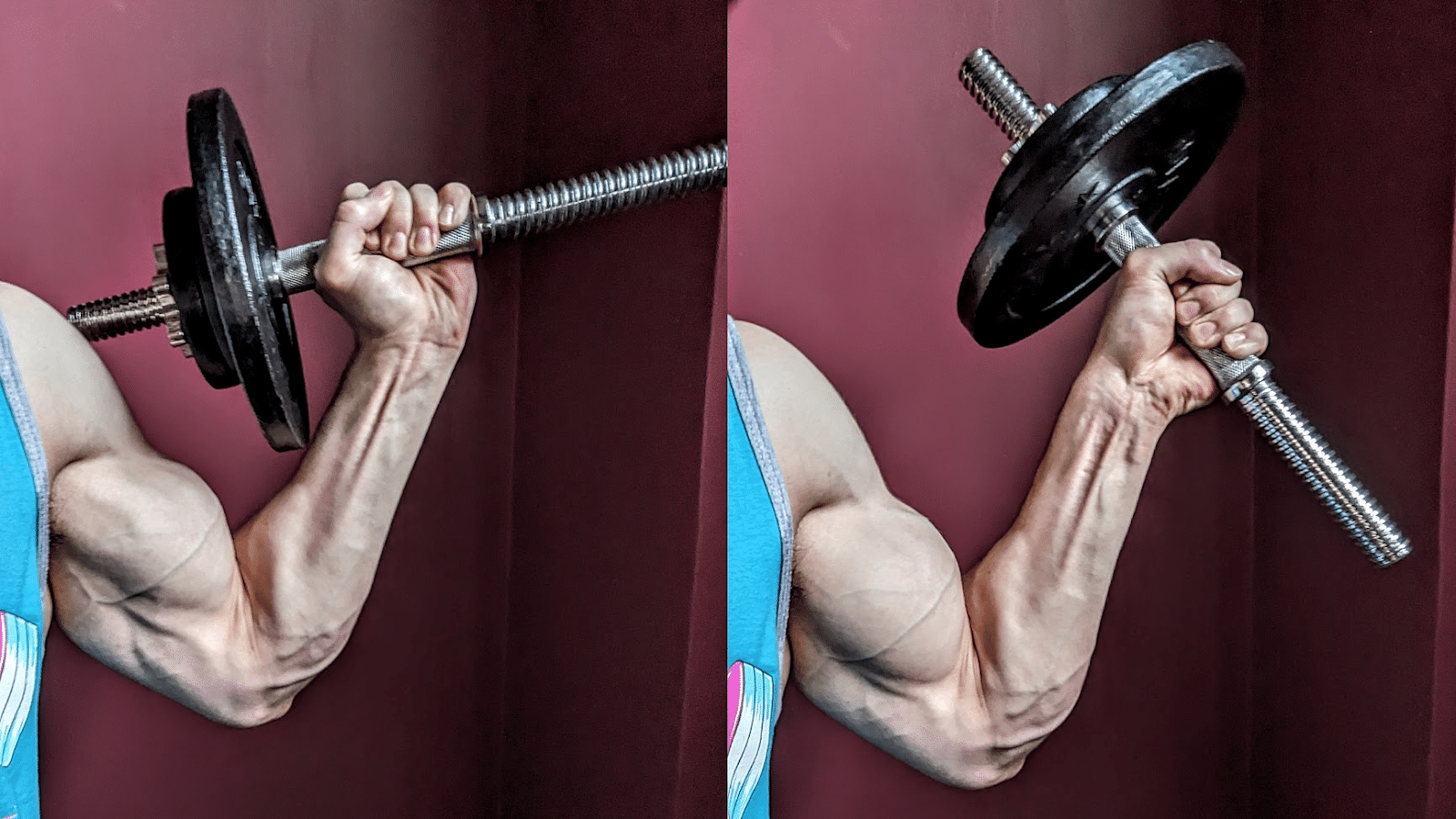









The vast majority of muscular tissues that may meaningfully contribute to radial or ulnar deviation additionally operate as wrist flexors or extensors (69,162). Two muscular tissues that insert onto the thumb, the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, are exceptions. These two small muscular tissues that represent about 3.5% of the entire muscle mass within the forearm and hand, operate as major radial deviators however can not meaningfully contribute to producing wrist flexion or extension torque (31,69,162). In distinction, a mix of wrist flexion and extension workouts can practice the opposite forearm muscular tissues that operate as radial deviators or ulnar deviators. For example, the extensor carpi radialis longus and extensor carpi radialis brevis operate each as major wrist extensors and radial deviators. Equally, the flexor carpi ulnaris and extensor carpi ulnaris operate as ulnar deviators but in addition respectively contribute to wrist flexion and wrist extension. Consequently, radial deviation and ulnar deviation workouts should not required to coach a lot of the muscular tissues that contribute to those actions. If you’re striving to attain each gram of forearm muscle mass you may probably attain or have a extra specialised purpose, wrist deviation workouts can serve a task. Nevertheless, they might be a really low precedence for a lot of lifters provided that coaching time is finite.
Resistance Coaching Intervention Results on Grip Power
In gentle of what we’ve got lined so far, it’s fairly cheap to hypothesize that resistance coaching interventions consisting of workouts for all 4 wrist actions together with forearm pronation and supination would enhance grip power. Hughes et al (2004) and Szymanski et al (2004, 2006) carried out three related research the place they respectively assigned collegiate baseball gamers to 6-week interventions or highschool baseball gamers to 12-week interventions (78,194,195). Their management teams carried out widespread resistance workouts (together with squat, bench press, and deadlift), whereas their experimental teams carried out the identical lifts along with workouts coaching the 4 wrist motions together with forearm pronation and supination. After the 2 12-week interventions, crush grip power elevated by related levels for every group, whereas neither group considerably elevated crush grip power after the 6-week intervention. In every examine, Szymanski et al additionally examined 10-rep maxes for the 4 wrist actions together with forearm pronation and supination earlier than and after the interventions. Predictably, the experimental teams that carried out two units of 8-12 reps for every of the six actions thrice per week skilled considerably higher 10RM will increase for every motion relative to the management teams. Given the foremost roles the flexor digitorum muscular tissues serve in producing wrist flexion torque, the shortage of superior grip power enchancment from the teams performing barbell wrist flexion train could also be considerably shocking. Whereas these outcomes point out that performing wrist workouts won’t mechanically enhance any sort of grip power, they don’t imply that wrist workouts are pointless for people who want to enhance grip power.
Supplemental workouts which might be programmed with the intent to induce hypertrophy of muscle teams that operate as prime movers in different lifts don’t essentially present rapid carryover to these completely different lifts. For example, a powerlifter could full an 8-week mesocycle of offseason coaching that prioritizes development on 8-12 rep units of high-bar pause squats, Romanian deadlifts, and bent-over rows however lacks competition-style deadlifts. The lifter could considerably enhance the load used for these workouts over time however fail to expertise any 1RM enhance within the deadlift whether it is examined immediately following that block. Certainly not would this consequence point out that these three workouts are nugatory to a powerlifter striving to boost his/her deadlift max. In isolation, the supplemental workouts could not essentially yield rapid efficiency switch. Nevertheless, they could nonetheless be helpful elements of a long-term coaching program if they assist enhance the dimensions of the deadlift’s prime movers. A interval of coaching the deadlift can subsequently enable a powerlifter to have the rise in power potential from the supplementary workouts manifest as an precise efficiency enchancment.
Equally, a block of wrist workouts has the potential to potentiate higher grip power enhancements if particular grip workouts are skilled afterwards. Alternatively, performing wrist workouts throughout a coaching block that features some high-intensity grip workouts has the potential to yield higher grip power will increase in comparison with if solely the grip workouts are utilized. Moreover, using the beforehand mentioned dynamic finger flexion method with wrist curls might also positively affect carryover to grip power in comparison with the usual wrist curl method used within the three intervention research.
No examine has assessed an intervention with finger flexion wrist curls, however one examine has assessed a resistance coaching intervention solely involving dynamic finger flexion train for the index by little fingers. Shim et al (2008) assigned 33 untrained younger adults to a management group that didn’t practice or experimental teams that adopted six-week packages consisting of dynamic finger flexion train carried out for six units of 10 reps with 70% 1RM thrice per week (179). Three completely different coaching teams have been assessed, one in every of which carried out the train with the 4 fingers concurrently, whereas the opposite two teams skilled every finger independently. Of the 2 unbiased finger coaching teams, one group was directed to attempt to limit motion of the non-training fingers throughout the train, whereas the opposite group didn’t obtain this route. Shim et al didn’t take a look at the individuals’ “grip power,” however they did take a look at the maximal isometric flexion power that they may generate with the 4 fingers concurrently whereas the hand, wrist, and forearm have been stabilized with braces. In distinction to the management group, every coaching group equally elevated maximal finger flexion power after six weeks by a mixed common of 39%. With the absence of any thumb contribution, this final result will not be the identical because the extensively examined crush grip power with a dynamometer. Nevertheless, the magnitude of isometric finger flexion power produced by the index by little fingers determines a lot of the grip power displayed with all 5 fingers engaged (38).
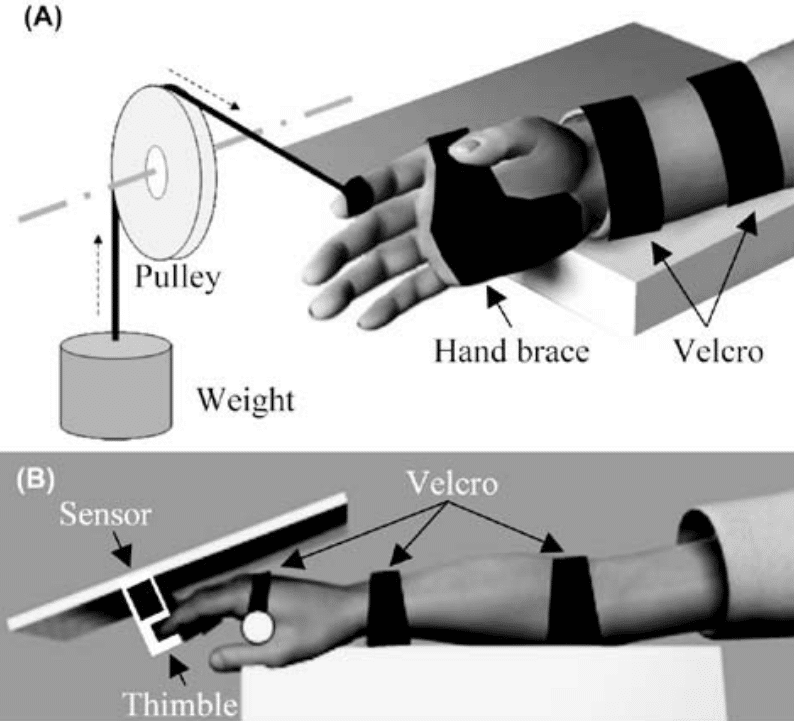

Simply as crush grip power will not be the identical as help grip power, so too is the finger flexion power examined by Shim et al not equivalent to the varied kinds of process particular grip power somebody could want to enhance. Nonetheless, there may be little purpose to suppose that coaching strategies that considerably enhance isometric finger flexion power can not switch to enhanced potential power efficiency when utilizing grips reliant on this power. When assessing the knowledge lined all through this text so far, finger flexion wrist curls can consequently be helpful elements of a grip coaching program even when superior grip power positive factors didn’t happen immediately after interventions with wrist flexion train.
Whereas looking for analysis on how completely different grip coaching protocols could have an effect on adjustments in grip power, I additionally discovered two research that assigned untrained younger grownup individuals handy gripper train interventions. Berg et al (2018) designed a customized hand gripper machine that allowed dynamic crush grip train to be incrementally loaded with a pulley (20). Throughout a progressively overloaded six-week program, their individuals carried out 4 units of 4 reps for the hand gripper train 4 occasions per week loaded with 90% 1RM. After the intervention, they elevated their common dynamic hand gripper 1RM by 26.5%. Berg et al additionally carried out forearm measurements and calculations to estimate forearm muscle mass of their individuals. Their estimated forearm muscle mass was 2.8% higher following the intervention, however this distinction was not statistically vital. In a decrease depth examine, Sharma et al (2020) assessed adjustments in isometric crush grip power examined with a dynamometer after two completely different six-week train interventions (178). The management and experimental teams each carried out crush grip train with a squeeze ball for 10 reps of 10-second squeezes with 2-second inter-rep relaxation intervals thrice per week. The experimental group’s individuals additionally skilled with a hand gripper (with 20kg of resistance) as they carried out 10 reps with 2-second isometric actions within the contracted place thrice per week. After the intervention, the experimental and management teams respectively elevated their imply dynamometer grip power by 26% (a statistically vital change) and 10.6% (not a statistically vital change).
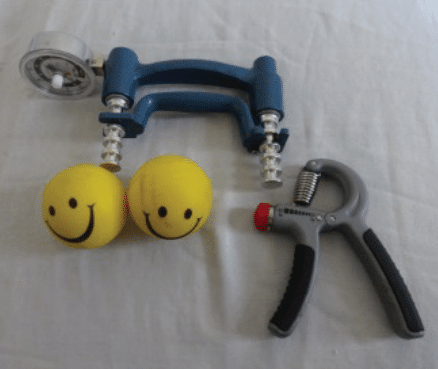

General the findings from Berg et al and Sharma et al that hand gripper train interventions can improve dynamic or isometric crush grip power are unsurprising. Whereas Berg et al and Sharma et al chosen completely different grip power outcomes measures, it’s attention-grabbing to see that every of their experimental teams skilled basically the identical magnitude of grip power enchancment. Through the use of a progressively overloaded intervention with greater intensities and set volumes than Sharma et al, I’d have predicted that the experimental group from Berg et al would expertise a higher diploma of grip power enchancment. Nevertheless, comparisons between research utilizing completely different final result measures that mirror an analogous assemble must be taken with a grain of salt. Untrained individuals might also reply in a different way than skilled people, who could require extra sturdy coaching stressors to expertise enhancements in power.
Tennis Elbow and Golfer’s Elbow
Whereas exploring many aspects of grip coaching, it’s worthwhile to cowl the 2 most typical kinds of grip-related accidents that have an effect on lifters and the overall inhabitants. The human physique has a mess of various tendons, however sure tendons are more likely to develop tendinopathy, an overuse harm that essentially outcomes from a tendon being repeatedly loaded past its load tolerance with out enough time to get better (128). Beforehand, the time period “tendinitis” was used to explain this situation, however the suffix “-itis” denotes irritation, which isn’t essentially current in a pathological tendon (6,175). Alternatively, “tendinosis” could also be used to explain structural degradation within the absence of irritation, whereas “tendinopathy” can describe a tendon dysfunction extra broadly and embody pathological adjustments that precede degeneration (16). Along with the pronator teres, 4 of the wrist flexor muscular tissues (together with the flexor digitorum superficialis) originate from the widespread flexor tendon on the humerus’ medial epicondyle (7). Equally, 4 of the wrist extensor muscular tissues originate from the widespread extensor tendon on the humerus’ lateral epicondyle, which additionally serves as an origin for the supinator (65). In case you have your arms at your facet together with your palms going through ahead (i.e., supinated), the medial epicondyle is the bony bump on the within of your elbow, and the lateral epicondyle is the bony bump on the surface of your elbow.


Golfer’s elbow and tennis elbow respectively check with tendinopathy that develops on the medial epicondyle or lateral epicondyle, which clinicians generally name medial epicondylitis or lateral epicondylitis (65). The tendons from different muscular tissues (e.g., extensor digitorum) could also be concerned, however the widespread extensor tendon’s portion equivalent to the extensor carpi radialis brevis is mostly affected with tennis elbow (142,172). Alternatively, the widespread flexor tendon’s parts equivalent to the flexor carpi radialis and pronator teres are sometimes affected with golfer’s elbow, which can additionally contain diffuse harm all through the widespread flexor tendon (145). These two accidents can lead to notable elbow ache throughout and after actions which load these tendons, to allow them to turn into significant impediments to lifting and quite a lot of different athletic actions such because the sports activities for which they obtained their names. Whereas grip coaching workouts will be fairly painful in consequence, different workouts that use the forearm muscular tissues as stabilizers such because the bench press and again squat can be relatively provocative after the tendinopathy is aggravated. If a tendinopathy has reached a very irritable part, even every day actions which impart low tendon loading akin to holding a mug of espresso or opening a door can provoke ache (116). As soon as it has developed, tendinopathy can take some time to resolve, and persevering with to load an injured tendon excessively past its tolerance can worsen the scenario to the extent that it could turn into a persistent dysfunction (39).


Occupational information from the overall inhabitants signifies that the chance of experiencing golfer’s elbow and tennis elbow is considerably elevated for individuals who repetitively carry out forceful actions involving the elbow, forearm, and wrist (47,48,58,182,205). To my information, no examine has but to research how completely different resistance coaching program variables could have an effect on a lifter’s threat of growing golfer’s elbow or tennis elbow. Correspondingly, I gained’t be making any definitive claims as to how programming choices will enhance or lower your threat of experiencing these accidents, nor will I be offering medical recommendation. Nevertheless, I’ve two common suggestions based mostly on the proof obtainable about tendinopathies and accidents extra broadly and what we learn about golfer’s elbow and tennis elbow particularly.
The primary suggestion is to make use of a gradual quantity development for those who want to add a number of the train variations mentioned all through this text into your program with the intent of enhancing grip power and forearm muscle measurement. Together with many lifts that you could be already be performing, all of these grip workouts will present a coaching stressor to the widespread flexor tendon and/or widespread extensor tendon. With repeated publicity to emphasize, tendons can adapt over time to progressive loading, however a sudden spike in loading to which they’re unaccustomed could enhance the chance that the stress exceeds their capability (100). Individuals who prioritize enhancing grip power could notably discover that it’s simple to overuse hand grippers because of their comfort and minimal systemic fatigue. These qualities make them helpful instruments for growing whole coaching quantity, however watch out to not be extreme with what number of units you carry out every week.
Secondly, for those who start to note clear signs of both golfer’s elbow or tennis elbow, I like to recommend not merely to push by it with out making any modifications to your coaching. If you’re keen about lifting and dedicated to reaching your objectives, it could be fairly tempting to take action, notably as a result of a tendinopathy could initially manifest as solely a light ache that doesn’t stop you from having productive coaching periods early on. What could start as a minor nuisance that may be ignored with some NSAIDs and ice can snowball right into a critical obstacle as weeks after which months move by with out the suitable behavioral adjustments.
I anticipate that basically everybody who has been persistently coaching for years on the very least has skilled a light ache or discomfort close to a joint that differs from muscle soreness. Ache is a posh phenomenon, and having a minor ache that develops shortly after a difficult exercise doesn’t essentially imply that an harm occurred and it is best to panic. For example, I’m certain that loads of powerlifters have had a little bit of low again discomfort (that differs from spinal erector muscle soreness) in some unspecified time in the future of their lives a day or two after a tricky deadlift and squat session. These sensations could happen within the absence of precise tissue harm and resolve in a brief time period. Having a transient bout of delicate low again ache every so often doesn’t imply {that a} disc herniated in the identical means that having a little bit of medial epicondyle discomfort for a day doesn’t imply that the widespread flexor tendon is injured. Nevertheless, ache persevering with to persist in a specific space and persistently be aggravated by sure kinds of actions is a warning signal that one thing could also be amiss and value addressing. With respect to golfer’s elbow and tennis elbow, the hallmark function of which to bear in mind is ache and tenderness close to the elbow that’s aggravated by gripping actions (84). For golfer’s elbow, ache and tenderness are localized to the medial epicondyle, whereas they’re localized to the lateral epicondyle for tennis elbow. As a result of loading the concerned tendons can provoke ache from tendinopathy, resisted wrist flexion and/or forearm pronation could also be painful with golfer’s elbow (84). Alternatively, resisted finger extension and/or wrist extension could also be painful with tennis elbow relying on which tendon websites are affected (91). Testing whether or not these resisted actions are provocative is a key part of bodily exams that bodily therapists make the most of when assessing sufferers who’re suspected of getting tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow previous to designing their therapy plans. If both situation turns into persistent, elbow ache might also be accompanied by weak spot in wrist sure actions and grip power deficits (51,157,158,167).
Since I’m not offering any medical recommendation and don’t intend for my suggestion to be misconstrued as such, I’ll briefly clarify a few of what I’d do if I developed signs of golfer’s elbow or tennis elbow. Beforehand I handled a hamstring tendinopathy from operating cross nation in highschool that turned persistent after pushing by it after which patellar tendinopathy from leap coaching that took over a 12 months and a half to resolve due to short-sighted determination making on my half. A pair years in the past, I additionally developed golfer’s elbow from resistance coaching after a block of heavy weighted pullups and chinups. Nevertheless, I used to be in a position to resolve this tendinopathy in a a lot briefer time period after making use of what I discovered from the prior accidents and intensive studying into tendinopathy analysis and medical apply.
If I observed new signs of golfer’s elbow or tennis elbow in my quest to extend grip power, the very first thing I’d do is quickly scale back my quantity of grip coaching and chorus from the notably aggravating actions. For example, if hand grippers, pull ups, and heavy blended grip deadlifts have been probably the most provocative actions, I’ll substitute in lighter cable pulldowns with very strict method for pull ups, carry out heavy deadlifts with straps, and take a break from hand grippers all collectively. The quantity required to keep up power is decrease than what’s required to extend power, so grip power mustn’t meaningfully lower if a pair weeks of coaching are carried out with one third of prior grip coaching quantity (22).
Whereas decreasing the quantity of the notably traumatic actions, I’d usually carry out low velocity (e.g., three-second concentric part and three-second eccentric part) forearm workouts that immediately load the tendons originating on the painful web site. For example, I’d seemingly make the most of wrist flexion, radial deviation, and forearm pronation workouts to handle golfer’s elbow. Alternatively, I’d seemingly use wrist extension, radial deviation, forearm supination, and finger extension workouts to handle tennis elbow. Repeated loading in extra of the tendon’s load tolerance is what contributes to the event of tendinopathy within the first place, however correctly utilized loading can also be a key part of tendinopathy rehab because of its capability to extend a tendon’s load tolerance. As with patellar and Achilles tendinopathies, the obtainable physique of proof signifies that resistance coaching interventions can function viable remedies for tennis elbow (34,42,44,92,113,135,150,160,188,189). The vast majority of resistance coaching interventions assessed for his or her potential to deal with tendinopathies have been eccentric solely in nature, however there is no such thing as a proof indicating that typical concentric-eccentric resistance coaching could be any much less efficient (21,43,100,189). For tendinopathy therapy, eccentric-only train is probably going superior to concentric solely train, however interventions composed of each concentric and eccentric actions have been equally efficient to eccentric solely packages (21,85,100,155,189). Golfer’s elbow is significantly much less widespread than tennis elbow (even amongst golfers paradoxically), and this discrepancy is mirrored within the quantity of analysis that investigates therapy for these two situations (84,124,181). Along with a case collection that lacks any management group, I used to be solely capable of finding a single randomized trial assessing the potential of an train intervention to deal with golfer’s elbow, and it lasted solely 4 weeks with 15 individuals within the train group (5,193). Consequently, there’s a notable hole within the present physique of literature, however it’s fairly believable that golfer’s elbow might reply in a fashion just like different tendinopathies in response to resistance coaching.
Combined Grip Deadlifts & Biceps Tendon Ruptures
A number of research have examined how deadlifting with straps could differ from doing so with out straps, however the analysis has focused on utilization of the double overhand grip when pulling with out straps (41,61,86,87,88,89,198). For non-powerlifters who want to deadlift to extend power and muscularity within the posterior chain, solely utilizing straps for work units is a very viable strategy, particularly if different workouts are used to immediately practice the forearms. When opting to not use straps, some lifters could solely deadlift with a double overhand grip, however it may well severely restrict the burden skilled lifters can pull. To cut back the chance of the bar rolling out of their fingers, the blended grip or hook grip could alternatively be used. Of those two choices, leisure and aggressive lifters alike generally use the blended grip (AKA alternate grip), the place one forearm is pronated whereas the opposite is supinated. The blended grip requires some coaching expertise to adapt to utilizing it, however the time wanted to develop proficiency whereas pulling with it’s significantly lower than the hook grip, which may really feel very uncomfortable on a lifter’s thumbs (202). Nevertheless, some people are involved in regards to the potential to develop muscle imbalances because of persistently pulling with a blended grip. This may increasingly immediate some folks to alternate which facet is supinated from set to set, however I doubt that apply is worth it for many lifters.


To my information, just one examine has in contrast muscle activation between blended grip deadlifts and double overhand deadlifts (19). Beggs (2011) assessed 10 skilled individuals with a median typical deadlift 1RM of 202.5kg (446.4lb) as they carried out 3 units of two reps with 60% 1RM and 80% 1RM. When initially testing their deadlift 1RMs, individuals have been free to make use of straps or whichever grip they most popular. Given the foremost limitations of the double overhand grip for skilled lifters, individuals have been additionally free to make use of straps throughout the double overhand grip trials at 80% 1-RM, which all of them opted to make use of. Nevertheless, straps have been explicitly prohibited when deadlifting 60% 1RM. Because the individuals deadlifted, Beggs measured the EMG exercise of the best and left biceps, brachioradialis, higher entice, and higher lat. Deadlifting with a blended grip yielded considerably higher EMG exercise of the biceps on the supinated facet in comparison with the pronated facet of the blended grip trials or both biceps within the double overhand and straps situations. Common brachioradialis activation additionally exhibited a development of decrease activation on the supinated facet relative to the pronated facet throughout blended grip deadlifts. Nevertheless, higher entice and higher lat EMG exercise have been related whatever the grip used for deadlifting. Asymmetrical activation of different muscle teams or muscle areas not measured probably could also be current throughout blended grip deadlifts. Nonetheless, the web impact on general facet to facet variations in muscle measurement and power should still be insignificant when blended grip deadlifts are included in a program that trains these muscular tissues symmetrically with different workouts. Extra of a hazard than growing any potential delicate asymmetry is the elevated threat of sustaining a distal biceps tendon rupture imparted from a blended grip.
Whereas uncommon within the common inhabitants, the distal biceps tendon of the supinated arm is extra inclined to rupture in males who deadlift (90,95). Empirical information on the matter is unavailable, however I anticipate that the chance of this rupture could be elevated if a deadlift is initiated with slight elbow flexion on the supinated facet in a “grip and rip” model. Doing so might lead to that elbow quickly extending below a really heavy load, imparting appreciable eccentric loading right into a stretched distal biceps tendon. Along with blended grip deadlifts, distal biceps tendon ruptures have additionally been recorded to happen throughout biceps curl variations and strongman occasions such because the tire flip and atlas stone elevate. Whereas I can’t make any definitive claims, distal biceps tendon ruptures probably could also be extra more likely to happen throughout a free weight preacher curl relative to different curls because of its power curve. When gravitational power is offering resistance throughout a free weight curl, resistive torque peaks when the horizontal distance between the burden and elbow joint is best, which happens when the forearm is perpendicular to the bottom. Throughout a regular curl together with your higher arms held close to your sides (i.e., having near about 0° of shoulder flexion), your forearms shall be horizontal to the bottom when your elbows flex to about 90°. In distinction, your elbows shall be in decrease angles of flexion when your forearms are horizontal to the bottom throughout preacher curls because of the flexed shoulder place. This ends in resistive torque peaking at longer muscle lengths for the biceps throughout free weight preacher curls in comparison with normal free weight curls or curls carried out with cables or machines that present an excellent stage of resistance all through the ROM. The diploma to which the biceps are lengthened when resistive torque peaks throughout a free weight preacher curl will fluctuate relying upon the slope of the preacher curl pad and the seat place a lifter selects. Along with utilizing a pad that’s extra horizontally inclined, using a decrease seat peak or sitting additional again can contribute to a extra flexed shoulder place that shifts peak resistive torque to extra prolonged elbow angles. Based mostly on footage, if a distal biceps tendon ruptures throughout a preacher curl, it seems to be most certainly close to the top of the eccentric part when the elbow is in a low angle of flexion and the tendon is loaded in a reasonably lengthened place.
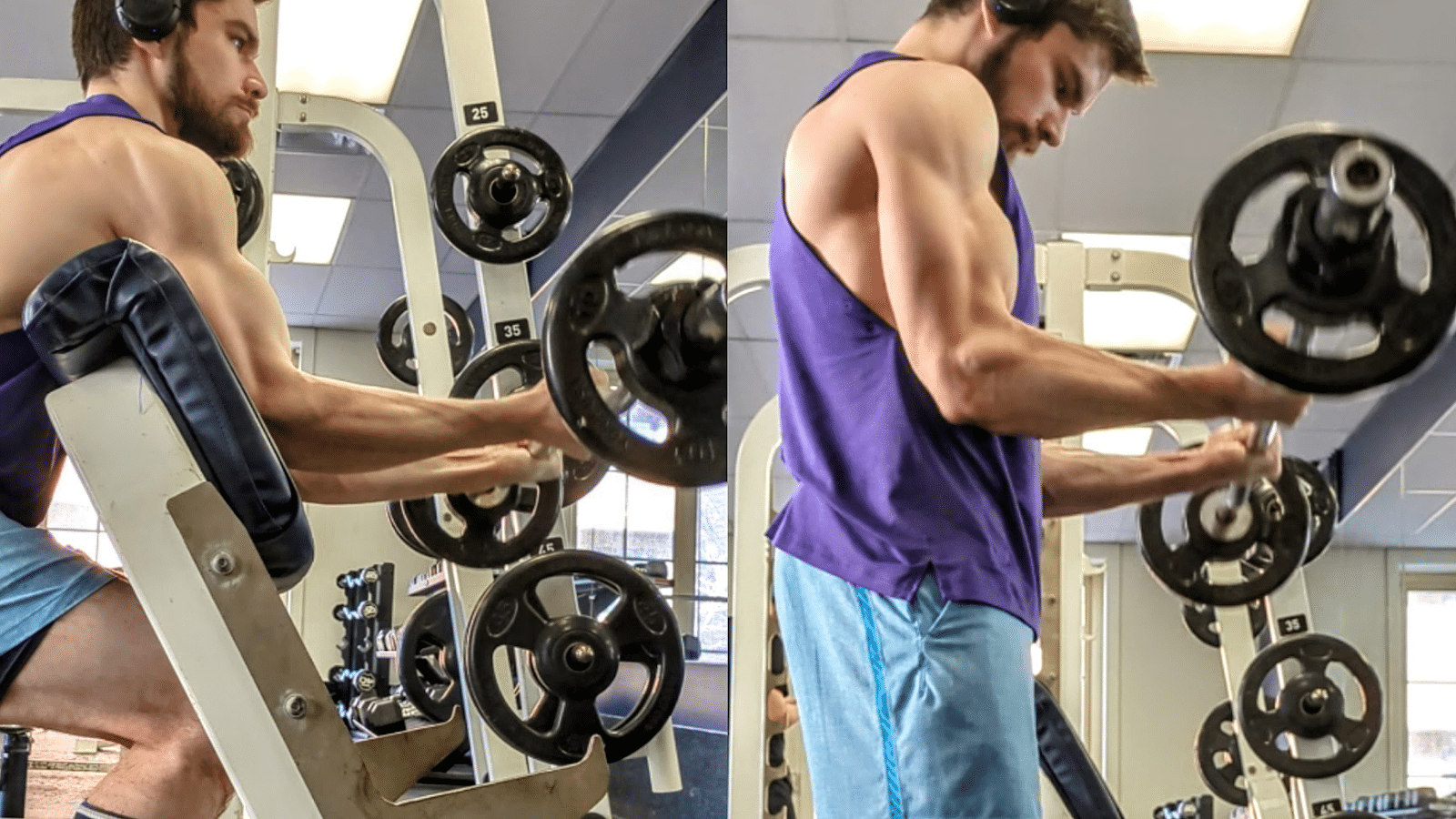


For lifters who intend to carry out free weight preacher curls, I usually suggest that they choose reasonably gentle hundreds (i.e., enabling at the least 12 reps per set) that they will management by a full ROM with a gradual eccentric part. Some lifters deliberately keep away from the extra prolonged elbow angles throughout preacher curls by performing partial ROM reps with weights which might be too heavy to regulate by a full ROM. The priority with that strategy could be if a lifter unintentionally strikes into extra prolonged elbow angles with a weight that exceeds what somebody might transfer concentrically from prolonged joint angles. If this happens, the biceps tendon could be subjected to supramaximal eccentric loading in a stretched place which isn’t skilled by flexed elbow partial ROM curls. As with different accidents, an abrupt spike in coaching quantity additionally has the potential to extend somebody’s chance of a tendon harm (29,30,50,79,118,140). Consequently, a gradual workload development is prudent for workouts that impart excessive loading to the biceps tendon in a stretched place simply as it’s clever when incorporating gripping workouts that we beforehand mentioned.
Conclusion
In the event you prioritize strengthening a specific sort of grip, akin to a blended grip or hook grip for the deadlift, the accent workouts mentioned on this article will be helpful instruments to make the most of alongside greater specificity coaching. After you have tailored to utilizing a selected grip, you don’t want to coach that precise grip with a excessive frequency strategy to progress. Gripping one thing heavy will not be a technically advanced maneuver, however a minimal frequency of publicity to a selected sort of grip remains to be necessary to making sure that extra common coaching is ready to switch successfully. Performing a excessive quantity of common grip coaching for just a few months can enhance your potential deadlift power with a blended grip or hook grip, however these grips can really feel fairly awkward for those who chorus from coaching them for too lengthy. Even for those who decide to not practice with these particular grips intensely on a frequent foundation, I like to recommend using them with a least some extent of regularity for submaximal coaching, akin to gentle velocity pulls. As with all different side of coaching to boost efficiency, some trial and error could also be required to find out what stage of specificity is perfect for you as a person. Whereas a lot information will be gained by exploring the obtainable physique of empirical proof, coaching is each an artwork and a science. A wide range of means can be utilized to achieve sure objectives akin to growing grip power and forearm muscle measurement. Via this text, I hope that you’re now higher outfitted to make the most of these completely different approaches in pursuance of your personal particular person objectives.
Whether or not you try to extend grip power or develop a extra muscular wanting physique, direct coaching of the forearm muscular tissues generally is a helpful part of your program. Whereas different muscular tissues play a task, no two are extra impactful to both pursuit than the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus, which flex the finger joints and the wrist. Coaching these highly effective muscular tissues together with different muscular tissues within the forearm and hand will help enhance long-term grip power and forearm muscle measurement concurrently.
Summaries
As you may readily see, this text is sort of prolonged and actually delves into the main points that may show you how to draw your personal conclusions and apply the obtainable physique of proof to your personal distinctive scenario. Resulting from this size, having some concise summaries about the important thing factors for every coaching technique can be helpful.
Extraordinarily excessive specificity help grip coaching (e.g., coaching heavy blended grip deadlifts to extend blended grip power for the deadlift)
Execs:
- Handiest for inducing neural diversifications which have best rapid switch to the particular grip power
- Could assist will increase in muscle measurement stimulated by different workouts switch to higher efficiency with that particular grip
- Can enhance confidence when executing that particular train
- Facilitates enhancements in method for that particular train
- Could enhance the load tolerance of sure tissues in a fashion troublesome to copy with different workouts
Cons:
- Coaching volumes could also be restricted by different components in addition to restoration of forearm and hand muscular tissues (e.g., lumbar constructions because of excessive axial loading, hand pores and skin because of knurling)
- Seemingly suboptimal for exciting forearm and hand muscle hypertrophy and due to this fact unlikely to maximise long-term grip power potential when used solely
- Could also be extra globally fatiguing than different workouts
- Requires tools that will solely be obtainable to you in a gymnasium
Similarities amongst coaching with hand grippers, fats grips, and dynamic wrist workouts
Shared professionals:
- Seemingly more practical in stimulating forearm and hand muscle hypertrophy than typical help grip workouts, which may enhance long-term power potential for varied grips
- Volumes unlikely to be restricted by restoration of muscular tissues aside from these within the forearm and hand
- Could impart decrease international fatigue than very excessive specificity coaching
- Unlikely to tear a callus
- Can be utilized to coach grip power if an harm precludes excessive specificity coaching
Shared con:
- Suboptimal for inducing neural diversifications particular to a special sort of grip, so switch to a special sort of grip could also be restricted if further workouts should not carried out whereas utilizing that particular grip
Hand gripper coaching distinct professional
- Extraordinarily handy within the sense that it may be carried out almost wherever
Fats grip coaching distinct professional
- Will be very time environment friendly when fats grips are added to workouts you already carry out
Dynamic wrist workouts distinct professional
- Seemingly the best technique of accelerating forearm muscle measurement
Pattern Coaching Packages
Optimum outcomes usually require individualized plans, however pattern coaching packages for various objectives may assist present a stable start line as to how this information will be utilized in a fashion that shall be helpful for many individuals. In the event you decide to make the most of one of many pattern packages as a template, I like to recommend progressively constructing as much as the volumes they embody over the course of a number of weeks. For example, you may start with two units of a specific train within the first week and add one or two units every week till you attain the variety of weekly units you want to persistently carry out. After you have acclimated to performing the set volumes within the pattern packages for a handful of weeks, you may step by step enhance the quantity you probably have extra time obtainable to coach and want to enhance your fee of progress. Within the pattern packages, you’ll discover hand gripper workouts and fats grip workouts should not included. I didn’t particularly program them as a result of I usually suggest performing them when they’re most handy to you as a method of accumulating higher forearm coaching volumes with out investing additional time coaching. Moreover, some folks don’t personal hand grippers or fats grip attachments, and so they usually should not obtainable in a industrial gymnasium.
Aim: Improve forearm muscle measurement in a time-efficient method
Finger flexion wrist curls: 2-3 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use dumbbells or barbell
Wrist extensions: 2-3 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use dumbbells or barbell
Your elbow flexion curl of selection: 2-3 units of 8-15 reps 2x/week
- Can use no matter tools you like
Particulars: Relying in your obtainable tools and choice, you may carry out both train bilaterally or unilaterally. Carry out the 2 wrist workouts as a superset, and execute as many reps as potential till muscular fatigue for every set. Persistently performing 4-6 high quality units of every train per week is probably going enough to stimulate will increase in forearm muscle measurement you probably have not already been using these workouts. Nevertheless, progressing to higher volumes, akin to 4-5 units of every train per session, could yield higher outcomes for extra skilled lifters. Distributing the identical weekly coaching quantity into three periods per week (e.g., performing 2 units 3x/week as an alternative of three units 2x/week) can be equally efficient. With both frequency, I like to recommend spacing your coaching periods evenly all through the week, akin to performing these workouts on Monday and Thursday with a 2x/week strategy or Monday, Wednesday, Friday with a 3x/week strategy.
The place particularly in your pre-existing coaching program that these workouts are most helpful to include shall be influenced by the remainder of your coaching, however the chief purpose is that you simply place them ready that doesn’t noticeably detract out of your efficiency of different workouts. Acutely after performing the wrist workouts, the ensuing fatigue in your forearm and hand muscular tissues will scale back your grip power, so it is best to preserve that in thoughts whereas deciding the place to carry out them inside a specific coaching session and inside a coaching week. As long as you carry out them at a time that doesn’t intrude with different coaching objectives, these workouts will be added right into a decrease physique or higher physique centered coaching session and even an “energetic restoration day” the place you chorus from extra strenuous resistance workouts.
Aim: Improve barbell particular help grip power for the deadlift
Suitcase rack pull maintain: 2 units of 20-40s 2x/week
- Choose a load that causes your grip to strategy failure after about 20-40 seconds
Lifeless cling: 2 units of 20-40s 2x/week
- Relying in your power stage, you may carry out this unilaterally or bilaterally and with or with out resistance added to your body weight. Choose a variation that causes your grip to strategy failure after about 20-40 seconds of hanging.
Finger flexion wrist curls: 2-3 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use dumbbells or barbell
Wrist extensions: 2-3 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use dumbbells or barbell
Particulars: I like to recommend performing these workouts along with utilizing your blended grip or hook grip for the deadlift to expertise the best carryover. The particular programming variables for the deadlift itself should not included on this pattern as a result of the main target of this text is on grip power, and appreciable variation exists with how completely different people program deadlifts. The secret’s that you’re using the particular grip you want to strengthen to your deadlift on a considerably common foundation relatively than solely counting on straps. For example, chances are you’ll use your blended grip for warm-up units and one prime deadlift set in a session whereas utilizing straps for different units in case your grip power would restrict efficiency in these units. To develop your help grip power additional at finger joint angles particular to these used when deadlifting, you may carry out the suitcase rack pull maintain and useless cling after your deadlifts. In the event you solely deadlift as soon as per week and prioritize growing your grip power for the deadlift, you may moreover carry out the suitcase rack pull maintain and useless cling on one other coaching day that’s 3-4 days after your deadlift day. For example, for those who deadlift on Monday and squat on Thursday, you may carry out the suitcase rack pull maintain after your squat units on Thursday. Both on the finish of these periods or throughout the day afterwards, you may carry out the finger flexion wrist curls and wrist extensions as a brilliant set. Given the worth of accelerating muscle measurement for enhancing long-term power potential, the entire programming particulars beforehand mentioned about these workouts can apply to their incorporation right into a plan that focuses on enhancing help grip power.
Aim: Optimize will increase in forearm muscle mass and/or enhance power in every wrist motion for a selected exercise (e.g., arm wrestling)
Finger flexion wrist curls: 4-5 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use dumbbells or barbell
Wrist extensions: 4-5 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use dumbbells or barbell
Forearm pronation and supination: 2 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use asymmetrical weight
Radial deviation: 2 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use asymmetrical weight or band
Ulnar deviation: 2 units of 12-20 reps 2x/week
- Can use asymmetrical weight or band
Your elbow flexion curl of selection: 4-5 units of 8-15 reps 2x/week
- Can use no matter tools you like
Particulars: This strategy is chasing diminishing returns and never required for most individuals to extend forearm muscularity or power in varied wrist actions. Nevertheless, the extra time funding will be worthwhile for sure people, and private objectives are distinctive to every particular person.
Whereas getting ready to put in writing this text, I regarded over lots of of various analysis articles associated to grip power and the forearm muscular tissues. A few of these didn’t present data immediately related to the particular subjects lined all through the article however will be attention-grabbing in their very own proper even when they verify what could also be presumed as widespread information. For many who are curious to be taught extra, this part briefly summarizes the findings from a few of these articles.
On common, untrained people have higher forearm muscle quantity of their dominant facet than their non-dominant facet, and this forearm asymmetry is considerably higher in tennis gamers and fencers (120,123,169,170). The magnitude of distinction meaningfully varies relying upon the supply, however folks usually have higher grip power of their dominant hand (e.g., proper hand for right-handed folks) in comparison with their non-dominant hand (15,25). Based mostly on the obtainable information, a couple of 5% distinction in grip power between fingers seems to be regular within the common inhabitants. Utilizing MRI, Sanchis-Moysi et al (2010) assessed the volumes of various forearm muscle teams in professional tennis gamers and located the superficial flexors, deep flexors, and extensors to be 12.3%, 7.6%, and 5.7% extra voluminous within the forearm of their dominant arms in comparison with non-dominant arms (169). Cross-sectional analysis limits us from concluding {that a} causal relationship exists, however these findings counsel that top quantity submaximal loading of the forearm muscular tissues will be hypertrophic to at the least some extent. On common, grip power is bigger when examined in a standing place in comparison with a seated place, and additionally it is usually higher when examined with an prolonged elbow place in comparison with a flexed elbow place (13,56,104,122,148,152,191,212).
Trossman and Li (1989) assessed untrained individuals as they carried out maximal isometric crush grip assessments 15 seconds, 30s, or 60s after an preliminary grip take a look at to find out how relaxation intervals affect grip power fatigue (199). Relative to the preliminary grip take a look at carried out in an unfatigued state, grip power was on common 12%, 10%, and seven% decrease respectively after 15s, 30s, and 60s relaxation intervals. Finger flexion power and forearm circumference exhibit vital optimistic correlations with mountain climbing efficiency (185). Superior class climbers have considerably higher common finger flexion power and forearm circumference than intermediate class climbers, who themselves have considerably higher common finger flexion power and forearm circumference than novice class climbers. Low load dynamic crush grip train acutely ends in higher will increase in hand and wrist quantity than static crush grip train with the identical load, indicating that dynamic grip train could lead to a higher “pump” to the working muscular tissues (214). In comparison with having a naked hand, sporting gloves can scale back maximal grip power, notably when sporting thicker gloves (101,207). Grip power has been measured to be related acutely after untrained individuals inhale ammonia salts or water (the management) (35). This lack of transient power enhancement following ammonia salt inhalation is congruent with analysis utilizing different power assessments (e.g., deadlift 1RM and squat/bench press reps to failure with 85% 1RM) as lined by Hayden Pritchard on Stronger By Science. For feminine powerlifters, grip power reveals reasonable power optimistic correlations with deadlift 1RM, squat 1RM, and powerlifting whole (192). In younger untrained girls, grip power reveals a statistically vital, albeit small magnitude, optimistic correlation with serum Vitamin D ranges (80). In a landmark examine, Ozerkan (2001) discovered individuals to exhibit higher grip power immediately after a drawing of a “smiling face” in comparison with a drawing of a “crying face” (149).
Forearm Muscle Main Perform Chart
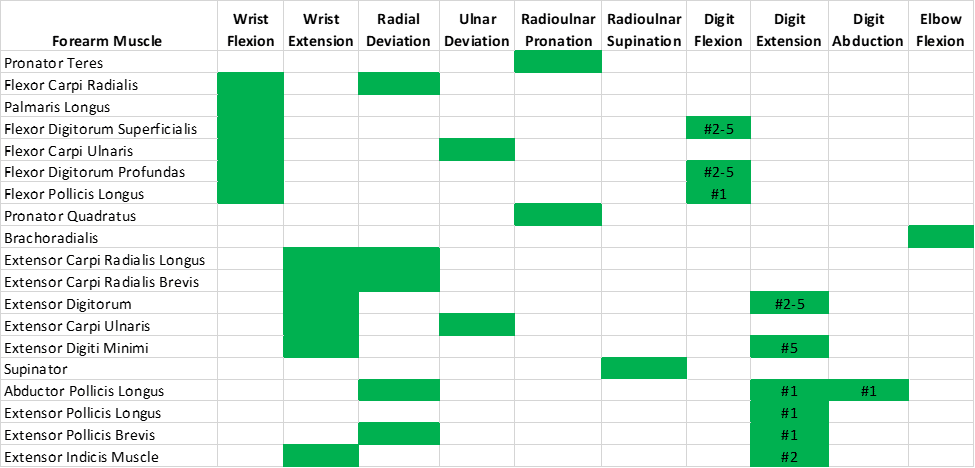

I made this chart as a visible abstract of the first joint capabilities of 19 forearm muscular tissues (excluding the anconeus as a result of it lacks a major dynamic operate) based mostly on the obtainable biomechanical information (62,63,69,153,162). Packing containers shaded in inexperienced point out the first capabilities for the corresponding muscular tissues. For the digit capabilities, #1 corresponds to the thumb, #2 corresponds to the index finger, #3 corresponds to the center finger, #4 corresponds to the ring finger, and #5 corresponds to the little finger. Word that this chart doesn’t show secondary capabilities to which a muscle could contribute akin to elbow flexion for the extensor carpi radialis longus. Whereas the muscular tissues could possibly help in producing torque throughout a number of different actions not shaded in inexperienced, they are going to be skilled meaningfully higher with workouts that resist their major capabilities. For sure muscular tissues, common settlement exists with respect to having a major operate, such because the pronator teres functioning as a major forearm pronator. Nevertheless, discrepancies exist throughout completely different articles and textbooks by way of which major capabilities are assigned to numerous muscular tissues. I consider that these discrepancies come up largely because of an absence of an goal technique to categorise major muscle capabilities. To account for these variations, I developed goal standards to categorise major muscle capabilities for the desk based mostly on quantifiable information. As is usually the case when deciding on numerical thresholds for classifications, the exact cut-off values are considerably arbitrary, and I’m certainly not asserting that the values I selected are the one legitimate ones that can be utilized. Nevertheless, I’m below the impression that the standards I developed lead to purposeful classifications which might be congruent with these the place consensus exists whereas eradicating subjectivity from inconsistent classifications.
Supplied {that a} muscle’s anatomical attachments enable the power generated by its contraction to contribute to producing a second on the joint, a muscle will be categorised as a major contributor to a specific joint operate if:
A) Its peak second arm for that joint operate is bigger than 50% of the muscle with the best peak second arm for that joint operate.
OR
B) Its potential peak second (peak second arm X physiological cross-sectional space) for that joint operate is bigger than 50% of the muscle with the best potential peak second for that joint operate.
Sources
The hand skeletal anatomy, forearm skeletal anatomy, hand joint anatomy, intrinsic hand muscle anatomy, forearm muscle anatomy, size rigidity relationship, superficial forearm muscle anatomy, and deep forearm muscle anatomy photographs have been revealed by “OpenStax,” are licensed as a Artistic Commons work, and will be discovered here.
The fingertip grip deadlift picture of David Woolson was revealed by Brazos Valley Barbell’s YouTube channel and will be discovered here.
The Tom Cruise fingertip grip picture was a screenshot from Mission: Unattainable 2, which was launched by Paramount Footage in 2000 and will be discovered here.
The Jamar® Hydraulic Hand Dynamometer picture was revealed as a product image by World Industrial and will be discovered here.
The CAMRY Digital Hand Dynamometer picture was revealed as a product image by Amazon and will be discovered here.
The flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus muscle anatomy picture was developed with 3D4Medical’s Complete Anatomy for an academic publication as permitted by my scholar license.
The Devon Larratt picture was produced by Jerry Milne and will be discovered here.
The IronMind pinch grip block picture was revealed as a product picture by Grip & Elevate Australia and will be discovered here.
The grip power testing and wrist extension coaching photographs have been developed by Shimose et al (2011) as Determine 2 and Determine 3 from Impact of submaximal isometric wrist extension coaching on grip power, which was revealed within the European Journal of Applied Physiology, and will be discovered here.
The wrist extension train picture from determine 1 from Souza et al (2017) will be discovered here of their article revealed by Fisioterapia e Pesquisa.
The finger flexion coaching and testing photographs from determine 1 from Shim et al (2008) will be discovered here of their article revealed in Motor Control.
The squeeze ball, hand gripper, and dynamometer picture from {photograph} 1 from Sharma et al (2020) will be discovered here of their article revealed by Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development.
The humerus epicondyle anatomy picture was revealed by Physician Jana, is licensed as a Artistic Commons work, and will be discovered here.
The tennis elbow picture was revealed by Bruce Blaus on Wikimedia Commons, is licensed as a Artistic Commons work, and will be discovered here.
The golfer’s elbow picture was revealed by Scientific Animations, is licensed as a Artistic Commons work, and will be discovered here.
[ad_2]
Source link








